Abstract
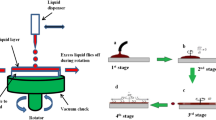
Borosilicate glass is a potential dopant source for producing shallow boron junctions by the use of proximity rapid thermal diffusion. Interest in this technique has increased recently due to its application to the manufacture of solar cells. A borosilicate gel is spun onto a silicon wafer and the layer is rapidly thermally annealed to convert it to a borosilicate glass (BSG). Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, spectroscopic ellipsometry and sheet-resistance measurements have been used to understand and subsequently optimise the conversion of the gel to a BSG nanolayer. Physical properties of the thin, spun-on layer, such as thickness, refractive index and porosity, were monitored. The optimum conversion step involved rapid thermal annealing for 45 s at 900 °C. This avoided any boron loss from the BSG layer during the thermal processing step. The position of the B–O stretching vibration around 1370 cm−1 was found to be sensitive to boron outdiffusion and it is suggested that FTIR spectroscopy provides a simple method for monitoring the outdiffusion of boron from the spin-on dopant nanolayer. Further FTIR studies using p-polarised light at oblique incidence revealed, for the first time, the LO–TO phonon splitting of the B–O stretching vibration band in the glassy layer. Investigation of the stability of BSG layers over long periods showed that unstabilised (or undensified) BSG films demonstrate a dramatic loss of boron over 6 months.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Ilyas, C.A. Hogarth, The optical absorption edge of amorphous thin films of borosilicate glass. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2, 535–537 (1983)
G. Sanchez, J.L. Castano, J. Garrido, J. Martinez, J. Piqueras, Direct writing laser doping from spun-on glasses. J. Electrochem. Soc. 138, 3039–3042 (1991)
C.D. Bagratishvili, R.B. Dzhanelidze, D.A. Jishiashvili, L.V. Piskanovskii, Z.N. Shiolashvili, Boron diffusion from a reactively sputtered glass source in Si and SiO2. Phys. Stat. Sol. (a) 56, 27–35 (1979)
M. Miyake, Diffusion of boron into silicon from borosilicate glass using rapid thermal processing. J. Electrochem. Soc. 138, 3031–3039 (1991)
D.J. Taylor, D.Z. Dent, D.N. Braski, B.D. Fabes, Boron loss in furnace- and laser-fired, sol–gel derived borosilicate glass films. J. Mater. Res. 11, 1870–1873 (1996)
M. Nogami, Y. Moriya, Glass formation of the SiO2–B2O3 system by the gel process from metal alkoxides. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 48, 359–366 (1982)
A.D. Irwin, J.S. Holmgren, T.W. Zerda, J. Jonas, Spectroscopic investigations of borosiloxane bond formation in the sol–gel process. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 89, 191–205 (1987)
B. D. Fabes, B. J. J. Zelinski, D. R. Uhlmann, in Ceramic Films and Coatings, ed. by J. B. Watchman, R. A. Haber (Noyes, 1992)
W. Zagozdzon-Wosik, J.C. Wolfe, C.W. Teng, Doping of trench capacitors by rapid thermal diffusion. IEEE Electron. Dev. Lett. 12, 264–266 (1991)
M. Nolan, T. Perova, R.A. Moore, H.S. Gamble, Boron diffusion from a spin-on source during rapid thermal processing. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 254, 89–93 (1999)
J.Y. Lee, S.H. Lee, Boron back surface field using spin-on dopants by rapid thermal processing. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 44, 1581–1586 (2004)
J. Jourdan, Y. Veschetti, S. Dubois, T. Desrues, R. Monna, Formation of boron-doped region using spin-on dopant investigation on the impact of metallic impurities. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 16, 379–387 (2008)
S. Barth, O. Doll, I. Koehler, K. Neckermann, M. Blech, A. Lawerenz, A. Edler, R. Kopecek, J.J. Schneider, 19.4 Efficient bifacial solar cell with spin-on boron diffusion. Energy Procedia 38, 410–415 (2013)
A. Yadav, G. Singh, R. Nekovei, R. Jeyakumar, c-Si solar cells formed from spin-on phosphoric acid and boric acid. Renew. Energy 80, 80–84 (2015)
M. Nolan, T.S. Perova, A.R. Moore, C. Beitia, J. McGilp, H. Gamble, Spectroscopic investigations of borosilicate glass and its application as a dopant source for shallow junctions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 147, 3100–3105 (2000)
W. Zagozdzon-Wosik, P. Grabiec, G. Lux, Silicon doping from phosphorus spin-on dopant sources in proximity rapid thermal diffusion. J. Appl. Phys. 75, 337–344 (1994)
P. Grabiec, W. Zagozdzon-Wosik, G. Lux, Kinetics of phosphorous proximity rapid thermal diffusion using spin-on Dopant source for shallow junction fabrication. J. Appl. Phys. 78, 204–211 (1995)
R.M. Almeida, C.G. Pantano, Structural Investigation of silica gel films by infrared spectroscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 68, 4225–4232 (1990)
L. Ventura, B. Hartiti, A. Slaoui, J.-C. Muller, P. Siffert, Rapid thermal annealing of spin-on glass films. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 284, 197 (1993)
A. Slaoui, L. Ventura, A. Lachig, R. Monna, J.C. Muller, Rapid isothermal annealing of doped and undoped spin-on glass. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 387, 365 (1995)
D.M. Haaland, C.J. Brinker, In situ FT-IR studies of oxide and oxynitride sol–gel-derived thin films. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 32, 267 (1984)
M. Rastogi, W. Zagozdzon-Wosik, F. Romero-Borja, J.M. Haddleson, R. Beavers, P. Grabliec, L.T. Wood, Boron doping using proximity rapid thermal diffusion from spin-on-dopants. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 342, 369 (1994)
W. Kern, RCA Rev. 32, 429 (1971)
J. Wong, A review of infrared spectroscopic studies of vapour-deposited dielectric glass films on silicon. J. Electron. Mater. 5, 113–160 (1976)
W. A. Pliskin, in Semiconductor Silicon, ed. by H. R. Huff and R. R. Burgess (Electrochemical Society, Pennington, 1973) p. 506
A.S. Tenney, Nondestructive determination of the composition and thickness of thin films of pyrolytically deposited borosilicate glass by infrared absorption. J. Electrochem. Soc. 118, 1658–1661 (1971)
E.A. Taft, Infrared absorption of chemical vapor deposited borosilicate glass films. J. Electrochem. Soc. 118, 1985–1988 (1971)
A.S. Tenney, J. Wong, Vibrational spectra of vapor-deposited binary borosilicate glasses. J. Chem. Phys. 56, 5516 (1972)
W. Kern, G.L. Schnabel, RCA Rev. 43, 423 (1982)
W. Kern, W.A. Kurylo, C.J. Tino, Optimized chemical vapor deposition of borophosphosilicate glass films. RCA Rev. 46, 117–152 (1985)
F.S. Becker, D. Pawlik, H. Shäfer, G. Staudigl, Process and film characterization of low pressure tetraethylorthosilicate–borophosphosilicate glass. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B4, 732–745 (1986)
J.E. Franke, T.M. Niemczyk, D. Haaland, Infrared spectroscopic techniques for quantitative characterization of dielectric thin films on silicon wafers. Spectrochim. Acta 50A, 1687–1723 (1994)
R.A. Carpio, J. Taylor, Advanced optical characterization techniques for borosilicate films. Proc. SPIE 2638, 38–45 (1998)
T.W. Dyer, Moisture instability of borophosphosilicate glass and the effect of thermal treatment. J. Electrochem. Soc. 145, 3950–3956 (1998)
S. Rojas, R. Comarasca, L. Zanotti, A. Borghesi, S. Sassella, G. Ottaviani, L. Moro, P. Lazzeri, Properties of borophosphosilicate glass films deposited by different chemical vapor deposition techniques. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B10, 633–642 (1992)
L.D. Madsen, A.C. de Wilton, J.S. Mercier, Examination of the stability of borophosphosilicate glass films. Chemtronics 5, 35–42 (1991)
D.M. Haaland, Quantitative infrared analysis of borophosphosilicate films using multivariate statistical methods. Anal. Chem. 60, 1208–1217 (1988)
I. Susuki, M. Ejima, K. Watanabe, Y. Xiong, T. Saitoh, Thin Solid Films 313–314, 214 (1998)
B. Drevillon, Spectroscopic ellipsometry in the infrared range. Thin Solid Films 313–314, 625–630 (1998)
S. Bruynooghe, F. Bertin, A. Chabli, J.-C. Blanchard, M. Couchaud, Infrared spectroscopic ellipsometry for residual water detection in annealed sol–gel thin layers. Thin Solid Films 313–314, 722–726 (1998)
M.A. Villegas, J.M. Fernández Navarro, Characterization of B2O3–SiO2 glasses prepared via sol-gels. J. Mater. Sci. 23, 2464–2478 (1988)
A.M. Efimov, Quantitative IR spectroscopy: applications to studying glass structure and properties. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 203, 1–11 (1996)
P. Broadhead, G.A. Newman, The vibrational spectra of orthoboric acid and its thermal decomposition products. J. Mol. Struct. 10, 157–172 (1971)
A.M. Efimov, Water related bands in the IR absorption spectra of silicate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 332, 93–114 (2003)
C. Gautan, Synthesis, structural and optical investigation of (Pb, Bi)TiO3 borosilicate glasses. Phys. Res. Intern., 2014, 1–7(2014). Article ID 606709
G. Lucovsky, M.J. Manitini, J.K. Srivastava, E.A. Irene, Low-temperature growth of silicon dioxide films: a study of chemical bonding by ellipsometry and infrared spectroscopy. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B5, 530–537 (1987)
A. Lehmann, L. Schumann, K. Hubner, Optical phonons in amorphous silicon oxides. II. Calculation of phonon spectra and interpretation of the IR transmission of SiO x . Phys. Stat. Solidi B121, 505–511 (1984)
C. Martinet, R.A.B. Devine, Analysis of the vibrational mode spectra of amorphous SiO2 films. J. Appl. Phys. 77, 4343–4348 (1995)
A.C. Angood, J.L. Koenig, Effect of nonrandom polymer chain orientation in the thickness direction on infrared absorption measurements. Macromolecules 2, 37–41 (1969)
F.L. Galeener, A.J. Leadbetter, M.W. Stringfellow, Comparison of the neutron, Raman, and infrared vibrational spectra of vitreous Si02, GeO2, and BeF2. Phys. Rev. B 27, 1052–1078 (1983)
S.W. de Leeuw, M.F. Thorpe, Coulomb splittings in glasses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 55, 2879–2882 (1985)
F.L. Galeener, G. Lukovsky, Longitudinal optical vibrations in glasses: GeO2 and SiO2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 37, 1476–1478 (1976)
D.W. Berreman, Infrared absorption at longitudinal optic frequency in cubic crystal films. Phys. Rev. 130, 2193–2198 (1963)
K. Hubner, L. Schumann, A. Lehmann, H.H. Vajen, G. Zuther, Detection of LO and TO phonons in amorphous SiO2 films by oblique incidence of IR light. Phys. Stat. Solidi B104, K1–K5 (1981)
J.E. Olsen, F. Shimura, Infrared reflection spectroscopy of the SiO2-silicon interface. J. Appl. Phys. 66, 1353–1358 (1989)
R.M. Almeida, Detection of LO modes in glass by infrared reflection spectroscopy at oblique incidence. Phys. Rev. B 45, 161–170 (1992)
I.I. Shaganov, T.S. Perova, A.R. Moore, K. Berwick, Spectroscopic characterisation of SiO and SiO2 solid films assignment and local field influence. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 12, 351–355 (2001)
R.A.B. Devine, Structural nature of the Si/SiO2 interface through infrared spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 68, 3108–3110 (1996)
G. Xiong, G. Lan, H. Wang, C. Huang, Infrared reflectance and Raman spectra of lithium triborate single crystal. J. Raman Spectrosc. 24, 785–789 (1993)
A.F. Perveev, G.A. Muranova, V.M. Zolotarev, Sov. Solid State Phys. 14, 2510 (1972)
I.I. Shaganov, Manifestation of local field effects in the properties of optical materials and coatings. Sov. J. Opt. Technol. 59, 1–11 (1992)
R.M. Levin, Water absorption and densification of phosphosilicate glass films. J. Electrochem. Soc. 129, 1765–1770 (1982)
T.S. Izumitani, Optical glass (American Institute of Physics, New York, 1986), p. 17
Acknowledgments
The Authors would also like to thank C. Beitia for ellipsometry results.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perova, T.S., Nolan-Jones, M., McGilp, J. et al. Borosilicate glass nanolayer as a spin-on dopant source: FTIR and spectroscopic ellipsometry investigations. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 27, 6292–6304 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4561-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4561-y