Abstract
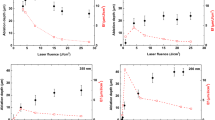
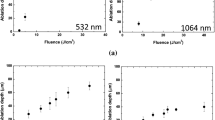
High refractory pressure-less sintered ternary composite ceramics of AlN-SiC-MoSi2 (ASMY), polished by mechanical grinding to a surface roughness R a ~40 nm, have been treated in vacuum by fs Ti:sapphire laser, operating at 800 nm wavelength, 100 fs pulse duration, and increasing fluence, to generate a “black ceramic material”, able to minimize solar radiation reflectance, in such a way that they could be used as the absorber material in an innovative conversion module of solar radiation into electrical energy. Disk specimens of approximately 3 cm in diameter and 3 mm thick have been treated by normal incident laser beam, generating a scanning pattern of parallel lines, at a lateral distance of about 80 μm, using a stage in motion, in the x, y, z directions, driven by a computer. The experimental conditions of laser treatment (energy fluence, speed of transition and lateral distance of steps) have been optimized to maximize the absorption properties of the patterned surface. In some samples this value was increased by about 15 %, compared to untreated surface, up to a value of final absorbance of about 95 %, all over the range of solar radiation spectrum (from UV to NIR). The morphological and chemical effects have been evaluated by SEM–EDS analysis. At higher fluence, we obtained the characteristic ablation craters and corresponding local material decomposition, while at lower fluence (over the ablation threshold) an ordered periodic nano-structure has been obtained, exploitable for its high capacity of entrapment of visible light. The laser treated ceramic specimen, characterized by very high absorption properties and reflectivity values lower than 4 %, has been used as active absorber material in a conversion module, installed in a solar test platform.






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Root mean squared \( R_{\rm q} = \sqrt{\frac{1}{n} \sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^{n} y_i^2} \), arithmetic average of absolute values \( R_{\rm a} = \frac{1}{n}\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^{n} {|y_{i} |} \), peak-valley distance \( \begin{aligned} R_{\rm t} = R_{\rm p} - R_{\rm v},\quad {\rm where}\; &R_{\rm p} = \text{peak value} \\ &R_{\rm v} = {\rm valley}\,\,{\rm value} \end{aligned} \).
References
International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), Technologies, cost analysis, concentrating solar power. Power Sect. 1(2/5), (2012)
C.E. Kennedy, Review of mid- to high-temperature solar selective absorber materials, Technical Report No. NREL/TP-520-31267, National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden, CO
E. Sani, L. Mercatelli, P. Sansoni, L. Silvestroni, D. Sciti, J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 4, 033104 (2012)
D. Ginley, M.A. Green, R. Collins, MRS Bull. 33, 355–364 (2008)
S. Chattopadhyay, Y.F. Huang, Y.J. Jen, A. Ganguly, K.H. Chen, L.C. Chen, Mater. Sci. Eng. Rep. 69(1–3), 1–35 (2010)
T.-H. Her, R.J. Finlay, C. Wu, S. Deliwala, E. Mazur, App. Phys. Lett. 73, 1673 (1998)
A.Y. Vorobyev, C. Guo, Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 7291–7294 (2011)
A.Y. Vorobyev, C. Guo, Laser Photonics Rev. 3, 385–407 (2013)
A.J. Pedraza, J.D. Fowlkes, D.H. Lowndes, App. Phys. Lett. 74, 2322 (1999)
M. Halbwax, T. Sarnet, P. Delaporte, M. Sentis, H. Etienne, F. Torregrosa, V. Vervisch, I. Perichaud, S. Martinuzzi, Thin Solid Films 516, 6791 (2008)
B.K. Nayak, V.V. Iyengar, M.C. Gupta, Prog. Photovolt Res. Appl. 19, 631–639 (2011)
M.D. Shirk, P.A. Molian, J. Laser Appl. 10, 18 (1998)
D. Ashkenasi, A. Rosenfeld, H. Varel, M. Wähmer, E.E.B. Campbell, Appl. Surf. Sci. 120, 65–80 (1997)
Q. Wu, Y. Ma, R. Fang, Y. Liao, Q. Yu, X. Chen, K. Wang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 1703–1705 (2003)
P. Rudolph, W. Kautek, Thin Solid Films 453–454, 537–541 (2004)
N. Yasumaru, K. Miyazaki, K. Kiuchi, Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 81, 933–937 (2005)
T. Tomita, K. Kinoshita, S. Matsuo, S. Hashimoto, Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 153115 (2007)
R. Wagner, J. Gottmann, A. Horn, E.W. Kreutz, Appl. Surf. Sci. 252, 8576–8579 (2006)
J. Gottmann, D. Wortmann, M. Horstmann-Jungemann, Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 5641–5646 (2009)
J. Bonse, J. Krüger, S. Höhm, A. Rosenfeld, J. Laser Appl. 24, 042006 (2012)
R. Wagner, J. Gottmann, J. Phys: Conf. Ser. 59, 333–337 (2007)
S.H. Kim, Ik-Bu Sohn, S. Jeong, Appl. Phys. A 102, 55–59 (2011)
S.H. Kim, Ik-Bu Sohn, S. Jeong, Appl. Phys. A 103, 1053–1057 (2011)
D. Sciti, S. Guicciardi, C. Melandri, A. Bellosi, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 86(10), 1720–1726 (2003)
M. Birnbaum, J. Appl. Phys. 36, 3688 (1965)
H.M. van Driel, J.E. Sipe, J.E. Young, Phys. Rev. Lett. 49, 1955–1959 (1982)
J.E. Sipe, J.F. Young, J.S. Preston, H.M. van Driel, Phys. Rev. B 27(2), 1141 (1983)
W. Kautek, P. Rudolph, G. Daminelli, J. Kruger, Appl. Phys. A 81, 65–70 (2005)
T. Tomita, R. Kumai, S. Matsuo, S. Hashimoto, M. Yamaguchi, Appl. Phys. A 97, 271–276 (2009)
E. Cappelli, S. Orlando, D. Sciti, D.M. Trucchi, Patent RM2012A000427 3 Sept 2012
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the European Community for the financial support of the European Project E2PHEST2US “Enhanced Energy Production of Heat and Electricity by a combined Solar Thermionic-Thermoelectric Unit System”—GA 241270 in the framework of the Seventh Framework Program, topic “Energy”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cappelli, E., Orlando, S., Sciti, D. et al. fs Laser surface nano-structuring of high refractory ceramics to enhance solar radiation absorbance. Appl. Phys. A 117, 243–251 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-014-8446-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-014-8446-8