Abstract
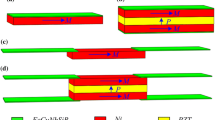
In this paper, we investigate the resonance magnetoelectric (ME) effect in the middle supported multilayer composites consisting of high-permeability Fe-based nanocrystalline soft magnetic alloy Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si13.5B9 (FeCuNbSiB), Nickel (Ni), and piezoelectric Pb(Zr1−x Ti x )O3 (PZT). The coupling effect between positive magnetostrictive FeCuNbSiB and negative magnetostrictive Ni results in the build-in magnetic bias due to their different magnetic permeability and coercivity. As a result, a giant resonance ME voltage coefficient (α ME,r ) at zero DC magnetic bias field (H dc) and multi-peaks of α ME,r for FeCuNbSiB/Ni/PZT/Ni/FeCuNbSiB composite are observed. The experimental results show that the giant zero-biased α ME,r strongly depends on the thickness of FeCuNbSiB ribbon. The maximum zero-biased α ME,r is up to 86 V/cm Oe for FeCuNbSiB/Ni/PZT/Ni/FeCuNbSiB with four-layer FeCuNbSiB ribbons, which is ∼500 times higher than that of the previously reported NKNLS-NZF/Ni/NKNLS-NZF trilayer composite. Compared with the peak α ME,r and the optimum H dc of Ni/PZT/Ni composite, the largest peak α ME,r of FeCuNbSiB/Ni/PZT/Ni/FeCuNbSiB composite with four-layer FeCuNbSiB ribbons increases ∼185 %, and the optimum H dc decreases ∼300 Oe, respectively. Based on the nonlinear magnetostrictive constitutive relation and the magnetoelectric equivalent circuit, a theoretical model of α ME,r versus H dc is built under free boundary conditions. Calculated zero-biased α ME,r and α ME,r versus H dc are in good agreement with the experimental data. This laminate composite shows promising applications for high-sensitivity power-free magnetic field sensors, zero-biased ME transducers and small-size energy harvesters.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ME:
-
Magnetoelectric
- FeCuNbSiB:
-
Fe-based nanocrystalline soft magnetic alloy Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si13.5B9
- Ni:
-
Nickel
- PZT:
-
Piezoelectric material Pb(Zr1−x Ti x )O3
- α ME,r :
-
Resonance ME voltage coefficient
- H dc :
-
DC magnetic bias field
- FNPNF:
-
Laminate composite of FeCuNbSiB/Ni/PZT/Ni/FeCuNbSiB
- NPN:
-
Laminate composite of Ni/PZT/Ni
- F:
-
Layers of FeCuNbSiB ribbons
- d 33,m1 :
-
The piezomagnetic coefficient of FeCuNbSiB
- d 33,m2f :
-
The piezomagnetic coefficient of Ni with flux concentration
- d 33,m2n :
-
The piezomagnetic coefficient of Ni without flux concentration
References
M. Laletin, N. Paddubnaya, G. Srinivasan, C.P. De Vreugd, M.I. Bichurin, V.M. Petrov, D.A. Filippov, Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 222507 (2005)
S.X. Dong, J.F. Li, D. Viehland, J. Cheng, L.E. Cross, Appl. Phys. Lett. 85(16) (2004)
D.A. Pan, S.G. Zhang, J.J. Tian, J.S. Sun, A.A. Volinsky, L.J. Qiao, Appl. Phys. A 98, 449–454 (2010)
J. Zhai, S. Dong, Z. Xing, J. Li, D. Viehland, Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 083507 (2006)
J.Y. Zhai, Z. Xing, S.X. Dong, J.F. Li, D. Viehland, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 91, 351–358 (2008)
S.X. Dong, J.Y. Zhai, F. Bai, J.F. Li, D. Viehland, Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 062502 (2005)
S.X. Dong, J.Y. Zhai, Z.P. Xing, J.F. Li, D. Viehland, Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 102901 (2005)
L. Chen, P. Li, Y.M. Wen, D. Wang, J. Alloys Compd. 509(14), 4811 (2011)
P. Li, Y. Wen, L. Bian, Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 022503 (2007)
P. Li, Y. Wen, P. Liu, X. Li, C. Jia, Sens. Actuators A 157, 100 (2010)
X.Z. Dai, Y.M. Wen, P. Li, J. Yang, M. Li, Sens. Actuators A 166, 94–101 (2011)
J. Yang, Y.M. Wen, P. Li, X.Z. Dai, Sens. Actuators A 168, 358–364 (2011)
S.X. Dong, J.Y. Zhai, J.F. Li, D. Viehland, J. Appl. Phys. 100, 124108 (2006)
S.X. Dong, J.Y. Zhai, J.F. Li, D. Viehland, Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 122903 (2006)
C.S. Park, K.H. Cho, M. Ali Arat, J. Evey, S. Priya, J. Appl. Phys. 107, 094109 (2010)
L. Chen, P. Li, Y.M. Wen, Smart Mater. Struct. 19, 115003 (2010)
V.M. Petrov, G. Srinivasan, Phys. Rev. B 78, 184421 (2008)
S.K. Mandal, G. Sreenivasulu, V.M. Petrov, G. Srinivasan, Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 192502 (2010)
S.C. Yang, C.S. Park, K.H. Cho, S. Priya, J. Appl. Phys. 108, 093706 (2010)
S.K. Mandal, G. Sreenivasulu, V.M. Petrov, G. Srinivasan, Phys. Rev. B 84, 014432 (2011)
G. Sreenivasulu, S.K. Mandal, S. Bandekar, V.M. Petrov, G. Srinivasan, Phys. Rev. B 84, 144426 (2011)
E. Lage, C. Kirchhof, V. Hrkac, L. Kienle, R. Jahns, R. Knöche, E. Quandt, D. Meyners, Nat. Mater. 11, 523–529 (2012)
T. Leineweber, H. Kronrniiller, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 176, 145–154 (1997)
C. Prados, I. Panagiotopoulus, G.C. Hadjipanayis, IEEE Trans. Magn. 33(5) (1997)
J.G. Wan, J.M. Liu, J. Appl. Phys. 93, 9916 (2003)
X.J. Zheng, X.E. Liu, J. Appl. Phys. 97, 053901 (2005)
C. Lei, L. Ping, W. Yu-Mei, W. Dong, Acta Phys. Sin. 60(6), 067501 (2011)
A. Aharoni, J. Appl. Phys. 83(6) (1998)
S.X. Dong, J.F. Li, D. Viehland, IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 50, 1253 (2003)
F. Yang, Y.M. Wen, P. Li, L.X. Bian, Sens. Actuators A 141, 12935 (2008)
C.W. Nan, G. Liu, Y. Lin, Appl. Phys. Lett. 83(21) (2003)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 50830202 and 61071042) and the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program) (No. 2012AA040602).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, C., Li, P., Wen, Y. et al. Investigation of magnetostrictive/piezoelectric multilayer composite with a giant zero-biased magnetoelectric effect. Appl. Phys. A 113, 413–421 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-013-7557-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-013-7557-y