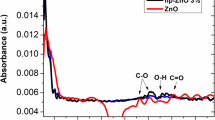
Abstract
In this work we present the optimization of zinc oxide (ZnO) film properties for a thin-film transistor (TFT) application. Thin films, 50±10 nm, of ZnO were deposited by Pulsed Laser Deposition (PLD) under a variety of growth conditions. The oxygen pressure, laser fluence, substrate temperature and annealing conditions were varied as a part of this study. Mobility and carrier concentration were the focus of the optimization. While room-temperature ZnO growths followed by air and oxygen annealing showed improvement in the (002) phase formation with a carrier concentration in the order of 1017–1018/cm3 with low mobility in the range of 0.01–0.1 cm2/V s, a Hall mobility of 8 cm2/V s and a carrier concentration of 5×1014/cm3 have been achieved on a relatively low temperature growth (250 °C) of ZnO. The low carrier concentration indicates that the number of defects have been reduced by a magnitude of nearly a 1000 as compared to the room-temperature annealed growths. Also, it was very clearly seen that for the (002) oriented films of ZnO a high mobility film is achieved.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Bayraktaroglu, K. Leedy, R. Neidhard, IEEE Electron Device Lett. 29(9), 1024 (2008)
A. Bashir, P.H. Wobkenberg, J. Smith, J.M. Ball, G. Adamopoulos, D.D.C. Bradley, T.D. Anthopoulos, Adv. Mater. 21, 2226 (2009)
J.F. Wager, Science 300(5623), 1245 (2003)
S. Choopun, R.D. Vispute, W. Noch, A. Balsamo, R.P. Sharma, T. Venkatesan, A. Iliadis, D.C. Look, Appl. Phys. Lett. 75, 3947 (1999)
E.M. Kaidashev, M. Lorenz, H. von Wenckstern, A. Rahm, H.-C. Semmelhack, K.-H. Han, G. Benndorf, C. Bundesmann, H. Hochmuth, M. Grundmann, Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 3901 (2003)
Ü. Özgür, Y.I. Alivov, C. Liu, A. Teke, M.A. Reshchikov, S. Doğan, V. Avrutin, S.-J. Cho, H. Morkoç, J. Appl. Phys. 98, 041301 (2005)
C. Klingshirn, Phys. Status Solidi (b) 244, 3027–3073 (2007)
S.L. King, J.G.E. Gardeniers, I.W. Boyd, Appl. Surf. Sci. 96–98, 81l (1996)
A.Og. Dikovska, P.A. Atanasov, C. Vasileva, I.G. Dimitrov, T.R. Stoyanchov, J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 7, 1329 (2003)
M. Gupta, F.R. Chowdhury, V. Sauer, S.S. Yap, T.W. Reenaas, Y.Y. Tsui, Proc. SPIE 8007, 80070J (2011)
M.W. Allen, M.M. Alkaisi, S.M. Durbin, Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 103520 (2006)
M.W. Allen, S.M. Durbin, Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 053512 (2007)
R. Yogamalar, R. Srinivasan, A. Vinu, K. Ariga, A.C. Bose, Solid State Commun. 149, 1919 (2009)
J.B. Franklin, B. Zou, P. Petrov, D.W. McComb, M.P. Ryan, M.A. McLachlan, J. Mater. Chem. 21, 8178 (2011)
A.M. Ma, M. Gupta, F.R. Chowdhury, M. Shen, K. Bothe, K. Shankar, Y. Tsui, D.W. Barlage, Solid State Electron. 76, 104 (2012)
Y.W. Heo, D.P. Norton, S.J. Pearton, J. Appl. Phys. 98, 073502 (2005)
J. Liu, Y. Zhao, Y.J. Jiang, C.M. Lee, Y.L. Liu, G.G. Siu, Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 231907 (2010)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) of Canada and the Canadian Institute for Photonic Innovations (CIPI) and Nanobridge. Fabrication was completed at the University of Alberta Nanofab. XRD and SEM characterization tools were provided by Integrated Nanosystems Research Facility (INRF) and Alberta Centre for Surface Engineering and Science (ACSES) both are at the University of Alberta.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, M., Chowdhury, F.R., Barlage, D. et al. Optimization of pulsed laser deposited ZnO thin-film growth parameters for thin-film transistors (TFT) application. Appl. Phys. A 110, 793–798 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-012-7154-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-012-7154-5