Abstract
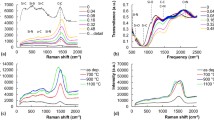
A comparative study of hardness of thin films of hydrogenated amorphous silicon (a-Si:H) and hydrogen-free amorphous silicon (a-Si) was carried out to reveal the role of hydrogen in the plastic properties of amorphous silicon. In addition, the effect of hydrogen on hardness was established by changing hydrogen concentration in the material using post-deposition processing of the samples. The hydrogen concentration in a-Si:H was decreased by thermal annealing. In a-Si hydrogen was introduced by plasma hydrogenation. The values of hardness of the as-prepared a-Si and a-Si:H films were determined by nanoindentation using depth profiling. Low-depth indentation was applied to evaluate the effect of post-hydrogenation. The results obtained show that the presence of hydrogen in the amorphous silicon network leads to the increase in hardness. The conducted experiments demonstrate that plasma hydrogenation can be used as an effective tool to increase the hardness of amorphous silicon. Hardness of a-Si:H of about 12.3–12.7 GPa is as high as of crystalline silicon, suggesting a-Si:H can be a substitute for crystalline silicon in some MEMS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.J. Demkowicz, A.S. Argon, Phys. Rev. B 72, 245205 (2005)
M.J. Demkowicz, A.S. Argon, Phys. Rev. B 72, 245206 (2005)
A.S. Argon, M.J. Demkowicz, Metall. Mater. Trans. 39A, 1762 (2008)
B. Haberl, J.E. Bradby, S. Ruffel, J.S. Williams, P. Munroe, J. Appl. Phys. 100, 013520 (2006)
S. Ruffel, J.E. Bradby, J.S. Williams, D. Munoz-Paniagua, S. Tadayyon, L.L. Coatsworth, P.R. Norton, Nanotechnology 20, 135603 (2009)
V. Kulikovsky, V. Vorlicek, P. Bohac, M. Stranyanek, R. Ctvrtlik, A. Kurdyumov, Thin Solid Films 516, 5368 (2008)
S. Roorda, W.C. Sinke, J.M. Poate, D.C. Jacobson, S. Dierker, B.S. Dennis, D.J. Eaglesham, F. Spaepen, P. Fuoss, Phys. Rev. B 44, 3702 (1991)
Z.E. Smith, S. Wagner, Phys. Rev. B 32, 5510 (1985)
W.C. Oliver, G.M. Pharr, J. Mater. Res. 7, 1564 (1992)
A.C. Fischer-Cripps, Surf. Coat. Technol. 200, 4153 (2006)
B. Bhushan (ed.), Handbook of Nanotechnology (Springer, Berlin, 2004), pp. 770, 775
D.M. Follstaedt, J.A. Knapp, S.M. Myers, J. Mater. Res. 19, 338 (2004)
B. Bhushan, X. Li, J. Mater. Res. 12, 59 (1997)
B. Pantchev, P. Danesh, E. Liarokapis, B. Shmidt, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 43, 454 (2004)
J. Gonzalez-Hernandez, S.S. Chao, D. Martin, R. Tsu, Proc. SPIE 254, 126 (1985)
S. Jin, H. Mavoori, J. Kim, V.A. Aksyuk, Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 2321 (2004)
W.J. Arora, A.J. Nichol, H.I. Smith, G. Barbastathis, Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 053108 (2006)
W.L. Chan, E. Chason, J. Appl. Phys. 101, 121301 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Danesh, P., Pantchev, B., Wiezorek, J. et al. Effect of hydrogen on hardness of amorphous silicon. Appl. Phys. A 102, 131–135 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-010-6026-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-010-6026-0