Abstract
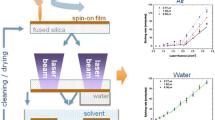
Laser-induced backside wet and dry etching (LIBWE and LIBDE) methods were developed for micromachining of transparent materials. Comparison of these techniques is helpful in understanding the etching mechanism but was not realized due to complications in setting up comparable experimental conditions. In our comparative investigations we used a solid tin film for dry and molten tin droplets for wet etching of fused-silica plates. A tin–fused-silica interface was irradiated through the sample by a KrF excimer laser beam (λ=248 nm, FWHM=25 ns); the fluence was varied between 400 and 2100 mJ/cm2. A significant difference between the etch depths of the two investigated methods was not found. The slopes of the lines fitted to the measured data (slLIBDE=0.111 nm/mJ cm−2, slLIBDE=0.127 nm/mJ cm−2) were almost similar. Etching thresholds for LIBDE and LIBWE were approximately 650 and 520 mJ/cm2, respectively. To compare the dependence of etch rates on the pulse number, target areas were irradiated at different laser fluences and pulse numbers. With increasing pulse number a linear rise of depth was found for wet etching while for dry etching the etch depth increase was nonlinear. Secondary ion mass spectroscopic investigations proved that this can be due to the reconstruction of a new thinner tin-containing surface layer after the first pulse.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Hanada, K. Sugioka, Y. Gomi, H. Yamaoka, O. Otsuki, I. Miyamoto, K. Midorikawa, Appl. Phys. A 79, 1001 (2004)
R. Böhme, K. Zimmer, Appl. Surf. Sci. 239(1), 109 (2004)
R. Böhme, D. Hirsch, K. Zimmer, Appl. Surf. Sci. 252(13), 4763 (2006)
J. Wang, H. Niino, A. Yabe, Appl. Surf. Sci. 154–155(1), 571 (2000)
J. Wang, H. Niino, A. Yabe, Appl. Phys. A 68(1), 111 (1999)
K. Zimmer, R. Böhme, B. Rauschenbach, Appl. Phys. A 79(8), 1883 (2004)
G. Kopitkovas, T. Lippert, C. David, A. Wokaun, J. Gobrecht, Microelectron. Eng. 67–68, 438 (2003)
Cs. Vass, B. Hopp, T. Smausz, F. Ignácz, Thin Solid Films 453–454(1), 121 (2004)
Cs. Vass, D. Sebők, B. Hopp, Appl. Surf. Sci. 252(13), 4768 (2006)
B. Hopp, Cs. Vass, T. Smausz, Appl. Surf. Sci. 253, 7922 (2007)
B. Hopp, Cs. Vass, T. Smausz, Zs. Bor, J. Phys. D 39, 4843 (2006)
J. Ihlemann, Appl. Phys. A 93(1), 65 (2008)
K. Zimmer, R. Böhme, Opt. Lasers Eng. 43(12), 1349 (2005)
G. Kopitkovas, T. Lippert, N. Murazawa, C. David, A. Wokaun, J. Gobrecht, R. Winfield, Appl. Surf. Sci. 254(4), 1073 (2007)
H. Niino, Y. Kawaguchi, T. Sato, A. Narazaki, T. Gumpenberger, R. Kurosaki, Appl. Surf. Sci. 252(13), 4387 (2006)
Cs. Vass, K. Osvay, B. Hopp, Z. Bor, Appl. Phys. A 87(4), 611 (2007)
R. Böhme, J. Zajadacz, K. Zimmer, B. Rauschenbach, Appl. Phys. A 80(2), 433 (2005)
X.M. Ding, Y. Kawaguchi, T. Sato, A. Narazaki, R. Kurosaki, H. Niino, J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 166(1–3), 129 (2004)
B. Hopp, T. Smausz, M. Bereznai, Appl. Phys. A 87, 77 (2007)
http://www.minerals.net/mineral/silicate/tecto/quartz/quartz.htm
J. Sullivan, J. Zhao, T.D. Bennett, Appl. Opt. 44(33), 7173 (2005)
K. Zimmer, R. Böhme, D. Hirsch, B. Rauschenbach, J. Phys. D 39, 4651 (2006)
T. Smausz, T. Csizmadia, N. Kresz, Cs. Vass, Zs. Márton, B. Hopp, Appl. Surf. Sci. 254, 1091 (2007)
R.G. Wilson, Int. J. Mass Spectrom. Ion Process. 143, 43 (1995)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hopp, B., Smausz, T., Vass, C. et al. Laser-induced backside dry and wet etching of transparent materials using solid and molten tin as absorbers. Appl. Phys. A 94, 899–904 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-009-5078-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-009-5078-5