Abstract
Parrotfishes and surgeonfishes are major Caribbean herbivores that primarily graze reef algae and thereby play an important functional role in indirectly promoting coral recruitment and growth. Yet, an emerging body of research suggests that these nominal herbivores graze on a diverse array of other food sources and researchers have questioned whether they may target more nutrient-dense foods growing within or upon algae, such as cyanobacteria. In this study, we investigated the species-specific foraging rates of parrotfishes and surgeonfishes on Brown Chromis (Chromis multilineata) fecal pellets compared to other major dietary items. We found that almost 85% of observed fecal pellets were ingested by fishes and that over 90% of ingested fecal pellets were consumed by parrotfishes and surgeonfishes alone. While there were species-specific differences in the levels of feces consumption (coprophagy), we found that all three surgeonfishes (Acanthurus chirurgus, A. coeruleus, and A. tractus) and six of the nine of parrotfish species surveyed (Scarus coeruleus, S. iseri, S. taeniopterus, S. vetula, Sparisoma aurofrenatum, and S. viride) consumed C. multilineata feces. To better understand the nutritional value of this behavior, we analyzed the composition of proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, total calories, and micronutrients in C. multilineata fecal pellets and compared these to published values for other food sources targeted by these fishes. Our findings suggest that these fecal pellets may have higher values of proteins, carbohydrates, total calories, and important micronutrients, such as phosphorus, compared to various macroalgae and the epilithic algae matrix, though comparable or lower values compared to cyanobacteria. To our knowledge, this is the first study to document coprophagy by tropical herbivorous fishes in the Caribbean region. This research advances our understanding of the foraging ecology of nominally herbivorous fishes and highlights the importance of fish feces as a nutritional resource on coral reefs.
Graphical abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Herbivorous fishes play an important role in coral reef ecosystems by grazing algae that can otherwise outcompete corals, thereby indirectly promoting the recruitment, growth, and survivorship of reef-building corals (Hughes et al. 2007; Bonaldo et al. 2014; Adam et al. 2015). Parrotfishes (tribe Scarini within the Labridae) and surgeonfishes (Acanthuridae) are key herbivores that are abundant on many tropical reefs and predominantly graze upon algae (Lewis and Wainwright 1985; Bellwood et al. 2004; Adam et al. 2015). Many studies have focused on quantifying the grazing dynamics and nutritional ecology of parrotfishes and surgeonfishes to better understand the patterns and drivers of grazing by these critically important fishes. Parrotfishes and surgeonfishes can vary in their grazing behavior interspecifically, ontogenetically, and based on context-dependent factors, such as food and nutrient availability (Burkepile and Hay 2011; Bonaldo et al. 2014; Smith et al. 2018; Duran et al. 2019; Ruttenberg et al. 2019). In addition to algae, nominally herbivorous parrotfishes graze on a diverse array of other food sources such as cyanobacteria, sponges, and corals (Bruggemann et al. 1994a; Burkepile et al. 2019; Nicholson and Clements 2020; Rempel et al. 2020). Surgeonfishes have also been documented grazing on benthic cyanobacterial mats and invertebrates, such as sponges (Cissell et al. 2019; Duran et al. 2019).
Turf algae and the epilithic algal matrix (EAM), which represent a large portion of the diet of parrotfishes and surgeonfishes, also contain notable amounts of cyanobacteria, feces, microbes, and detritus (Lewis and Wainwright 1985; Wilson 2002; Mumby 2006; Bonaldo et al. 2014; Nicholson and Clements 2020). Therefore, researchers have questioned whether some nominally herbivorous fishes may be detritivores and microphages that target other food sources growing upon algae or within algae-covered substrates that may be more nutrient dense, such as cyanobacteria (Choat et al. 2001; Crossman et al. 2005; Clements et al. 2016; Nicholson and Clements 2020). In addition, one study documented parrotfishes and surgeonfishes eating the feces of other fishes (coprophagy) on Indo-Pacific reefs (Robertson 1982), though this coprophagous behavior has not been documented in other tropical regions. Another study found that a surgeonfish and other fishes consume the feces and vomit of a cetacean on subtropical reefs in Brazil (Sazima et al. 2003). Parrotfishes and surgeonfishes may have more varied diets and nutritional ecology than previously believed, playing important roles as detritivores and microphages. However, there has been surprisingly little research documenting the role of coprophagy in the foraging dynamics of these fishes. Coprophagy has clear documentation and significance in terrestrial ecosystems (e.g., Soave and Brand 1991; Hirakawa 2001; Nalepa et al. 2001). It may also play an important role in nutrient transfer in marine ecosystems, such as providing a source of iron in the mesopelagic (Le Mézo and Galbraith 2021), nitrogen and phosphorus in temperate littoral systems (Pinnegar and Polunin 2006), carbon and nitrogen for marine invertebrates (Frankenberg and Smith 1967), and as a possible source of detrital organic matter for marine zooplankton recycling (Turner and Ferrante 1979). However, there is little documentation of the nutritional significance and transfer of energy through coprophagy on tropical coral reefs (Bailey and Robertson 1982; Robertson 1982).
Coral reefs are typically nutrient-limited ecosystems. Algae are generally considered to be of low-nutritional quality in the diets of herbivorous fishes (Horn 1989; Harmelin-Vivien 2002; Lobato et al. 2014; Shantz et al. 2017) as they are relatively low in protein and contain carbohydrates that are difficult to digest for fishes with a limited capacity for hindgut fermentation, such as parrotfishes (Crossman et al. 2005; Clements et al. 2016). Moreover, due to the relatively low abundance of nitrogen and phosphorus in algae, the growth of herbivorous fishes can be limited by nitrogen and phosphorus rather than energy (Hood et al. 2005; Benstead et al. 2014; Shantz et al. 2017; Schiettekatte et al. 2020). Fish feces may be a rich source of some of these nutrients and the nutritional value of fish feces can be equal to, or higher than, that of non-fecal food sources (Bailey and Robertson 1982). Coprophagous fishes often graze upon the feces of planktivores and higher trophic level fishes more frequently than fishes at lower trophic levels (Bailey and Robertson 1982; Robertson 1982). Planktivorous fish feces may be a particularly rich nutritional food source as they can be high in amino acids (Crossman et al. 2005), and their protein and lipid content may equal to or exceed that of algae, which dominates the diet of parrotfishes and surgeonfishes (Bailey and Robertson 1982). Therefore, fish fecal material may play an important role in the nutritional ecology of herbivorous reef fishes and nutrient cycling on coral reefs (Robertson 1982; Meyer and Schultz 1985; Smriga et al. 2010).
While recent studies have highlighted the importance of fish waste products on nutrient and energy cycling in coral reef food webs (Allgeier et al. 2017; Gil and Hein 2017; Ezzat et al. 2019), the role of coprophagy as a nutritional resource for fishes on coral reefs has received little attention (Bailey and Robertson 1982; Robertson 1982). Coprophagy may be an additional nutrient cycling mechanism to consider when assessing dietary preferences and nutritional needs of these key herbivores on coral reefs.
In this study, we investigated species-specific patterns of coprophagy of planktivorous Brown Chromis (Chromis multilineata) feces by parrotfishes and surgeonfishes on Caribbean reefs. Additionally, we analyzed the nutritional value of C. multilineata feces compared to other food sources targeted by parrotfishes and surgeonfishes. Our objectives were to: (1) quantify species-specific consumption of C. multilineata fecal pellets relative to total bites across food sources by parrotfishes and surgeonfishes, (2) determine the frequency at which these fecal pellets are consumed by parrotfishes, surgeonfishes, and other reef fishes, and (3) compare the nutritional value of these fecal pellets (in terms of proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, total calories, and micronutrients) to known values from other food sources. To our knowledge, this is the first study to document coprophagy by herbivorous fishes in the Caribbean. This behavioral research, paired with the nutritional value of these ingested fecal pellets, advances our understanding of the grazing dynamics of nominally herbivorous fishes and the importance of nutrient cycling via the fish feces on coral reefs.
Material and methods
Study sites and species
We conducted this study from June to September 2019 on the Southern Caribbean island of Bonaire (Fig. S1). We surveyed four primary sites on the island’s leeward coast (Karpata, Tolo, Cliff, and Bachelor’s Beach), as well as two additional sites (Andrea I and Sweet Dreams) where we collected fish behavioral data for less abundant parrotfish species (described below). These sites were characterized by continuous fringing nearshore reefs. We conducted behavioral surveys of all three Caribbean surgeonfishes (Acanthurus chirurgus, A. coeruleus, and A. tractus—previously known as A. bahianus) and most reef-dwelling parrotfishes (Scarus coeruleus, S. guacamaia, S. iseri, S. taeniopterus, S. vetula, Sparisoma aurofrenatum, S. chrysopterum, S. rubripinne, and S. viride). The three largest Caribbean parrotfishes—S. coeruleus. S. guacamaia, and S. coelestinus—were rare across these study sites. Therefore, we conducted additional behavioral surveys of S. guacamaia and S. coeruleus at the sites Andrea I and Sweet Dreams to obtain at least 6 behavioral surveys per species. Scarus coelestinus were not included in this study since we did not encounter this species during any surveys.
Additionally, we monitored the defecated fecal pellets of C. multilineata—an abundant planktivore on Caribbean reefs—to track the frequency at which these fecal pellets were consumed by fishes. Chromis multilineata often forage high in the water column to feed on plankton (Hobson 1973). As a result, their fecal pellets fall through the water column before reaching the benthos (see supplementary video footage), providing opportunities for coprophagous fishes to target them (Bray et al. 1986). We chose to focus on the fecal pellets of C. multilineata based on behavioral observations of parrotfishes and surgeonfishes. We observed that one individual S. taeniopterus and one S. vetula each consumed one fecal pellet of a Sergeant Major damselfish (Abudefduf saxatilis) compared to 876 total instances of consumption of C. multilineata fecal pellets by parrotfishes and surgeonfishes. These findings suggest that although they may occasionally consume fecal pellets of other fish species, parrotfishes and surgeonfishes on Bonaire predominantly target C. multilineata feces.
Fish density surveys
To quantify the density of parrotfishes, surgeonfishes, and C. multilineata at each site, we used a roving diver method similar to Adam et al. (2015). We conducted timed swims while towing a Garmin GPS 72 receiver on a float to measure the distance traveled. We surveyed parrotfishes, surgeonfishes, and C. multilineata separately to ensure accurate counts of each taxa. During surveys, we recorded the species and fork length of all C. multilineata ≥ 3 cm, surgeonfishes ≥ 10 cm, and parrotfishes ≥ 15 cm within a 5 m wide belt (i.e., 2.5 m to either side of the observer). Some parrotfish species were less common at our study sites, while surgeonfishes and C. multilineata were more abundant. Therefore, we conducted 10 min surveys of surgeonfishes and C. multilineata, but 20–25 min surveys of parrotfishes to sample a sufficiently large area to accurately estimate the density of less common parrotfish species. Given the high abundance of C. multilineata, it was not feasible to record the exact length of every individual during the 10 min surveys. Therefore, we recorded the abundance of C. multilineata in bins of 3 to < 6 cm, 6 to < 8 cm, 8 to < 10 cm, and 10 to < 12 cm. We conducted four surveys of fish density per taxa per site across a range of depths from 4 to 18 m. We calculated the distance traveled between GPS points throughout the survey using the R package ‘geosphere’ (Hijmans 2019), then multiplied the survey distance by 5 m (the survey width) to calculate the total survey area.
Fecal pellet observations
To determine the proportion of C. multilineata fecal pellets that were consumed by different coprophagous fishes, we monitored fecal pellets using a similar protocol to that of Robertson (1982). We followed haphazardly selected C. multilineata individuals until they defecated between 9:00 and 16:00 (n = 135). Upon defecation, we recorded the depth of the fecal pellet in the water column (m) and the depth of the benthos (m) to calculate the distance above the benthos at which the individual defecated. Additionally, we calculated the rate at which fecal pellets sank (m s−1) by recording the time in seconds it took the fecal pellet to travel several meters or until it was consumed by a coprophage. We monitored each fecal pellet until it was consumed or reached the benthos and recorded whether the fecal pellet was inspected (approached but not consumed), tasted (ingested, then expelled), eaten, or not consumed. If the fecal pellet was inspected, tasted, or eaten, we recorded the species of the coprophagous fish (or genus in the case of a few difficult to distinguish Stegastes spp.). To minimize the potential effect of observers on fish behavior, we maintained at least a 2 m distance from focal fishes and fecal pellets.
Behavioral observations
To characterize the foraging patterns of parrotfishes and surgeonfishes, we conducted behavioral observations across study sites following Adam et al. (2015). We surveyed surgeonfishes ≥ 10 cm fork length and parrotfishes ≥ 15 cm, with the exception of the parrotfish S. iseri, for which we included individuals ≥ 10 cm due to their smaller length at sex change (Allsop and West 2003). Because parrotfishes are protogynous hermaphrodites and their diet may vary between initial and terminal phase individuals, we surveyed 6 initial phase and 6 terminal phase individuals of each species whenever possible. However, some parrotfish species and/or phases were rare across our study sites, therefore we surveyed a minimum of at least 6 individuals per species regardless of phase (see Table S1 for sample sizes). For surgeonfishes, we conducted 6 surveys per species. We conducted surveys between 9:00 and 16:00, a time frame during which parrotfishes and surgeonfishes are typically actively foraging and that is similar to that of previous studies of the foraging behavior of these fishes in the Western Atlantic (Bruggemann et al. 1994a; van Rooij et al. 1996; Bonaldo et al. 2006; Adam et al. 2015; Duran et al. 2019). Between 9:00 and 16:00, there appeared to be little relationship between the time of day on coprophagy rates (Fig. S2). We haphazardly selected focal fishes and allowed them approximately 2 min to acclimate to the diver prior to the survey. Thereafter, we followed the individual for 20 min and recorded the number of bites taken on feces and various non-fecal food sources. In a few rare instances, focal fishes swam out of sight prior to a full 20 min survey duration; we only included these data if the survey had lasted at least 15 min. To determine the defecation rates of C. multilineata, we haphazardly selected individuals ≥ 5 cm and observed them for 3 min (n = 50). We recorded the fork length of each fish to the nearest centimeter and total number of defecations during the survey period.
Fecal sample collection
To analyze the nutritional quality of C. multilineata feces, we collected samples of fecal pellets. To do so, we swam in the water column following haphazardly selected C. multilineata individuals and opportunistically collected fecal samples in 2.0 mL sterilized vials. To avoid diver contamination and ensure the collection of intact fecal pellets, we positioned the vials below feces and allowed them to sink directly into the tube. We collected three fecal pellets per vial (n = 50 vials). We transported samples on ice to our field research facility, then immediately froze samples at − 18 °C. We used an Air Sea Containers Bio-Freeze Pack to transport frozen samples from Bonaire to our laboratory facility at California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo and kept samples frozen until we conducted fecal nutritional analyses.
Fecal nutritional analyses
Sample preparation
The C. multilineata fecal samples we collected originally contained three fecal pellets per vial (n = 50 vials); however, since individual pellets were small, we combined vials to yield enough material for nutritional analyses. To do so, we added 50 mL of deionized water to each vial for fecal homogenization and extraction and then combined the contents of five vials into sterile 50 mL Falcon centrifuge tubes (resulting in n = 10 sample vials, each containing 15 fecal pellets). We homogenized samples using a probe sonicator and centrifuged them at 4700 xg for 60 s, then pipetted and discarded excess water from the surface. We then flash froze wet samples in liquid nitrogen immediately before placing them in a Labconco lyophilizer at − 50 °C with a 20 mTorr vacuum for 24 h. After freeze-drying samples, we recorded the dry weight of samples to the nearest 0.0001 g.
Protein analysis
To determine feces protein content, we conducted a bicinchoninic acid (BCA) assay. This method uses the reduction of Cu+2 to Cu+1 by protein to produce a colorimetric reaction and can be more tolerant to interfering substances than the Lowry method (Smith et al. 1985). We first placed 20 mg aliquots of homogenized, dried fecal material from each sample vial in 1.5 mL Eppendorf tubes and added 0.6 mL of 1 M sodium hydroxide (NaOH). We homogenized samples by securing tubes horizontally and vortexing them at room temperature using an orbital shaker at medium speed for 12 h (Montgomery and Gerking 1980; Crossman et al. 2005). We centrifuged samples at 12,000 xg for 5 min and transferred 300 µL of supernatant from each sample into a new Eppendorf tube. We analyzed protein content using a Thermo Scientific™ Pierce™ Rapid Gold BCA Protein Assay Kit. We prepared and added kit working reagents to the BCA standard and samples in a flat-bottom 96-well plate and read absorbances in a spectrophotometer at OD 480 nm, then determined protein concentrations using the standard curve.
Lipid analysis
To determine feces lipid content, we conducted a colorimetric assay using the sulfo-phospho-vanillin (SPV) method (Chabrol and Charonnet 1937). This method is well-established for quantifying lipids and has been used in studies of marine fishes and invertebrates (Lu et al. 2008; Park et al. 2016). We extracted lipid content using an Abcam Chloroform-Free Lipid Extraction Kit. We placed 40–50 mg aliquots of fecal material in Eppendorf tubes (n = 10) and added 500 μL of the extraction buffer, then homogenized samples with a probe sonicator for 1–2 min. We kept samples on ice before and after sonication, then centrifuged them at 10,000 xg for 5 min at 4 °C. We collected the supernatant in microcentrifuge tubes and placed samples on an orbital shaker at room temperature for 15 min, then centrifuged them again at 10,000 xg for 5 min at room temperature. We collected the resulting supernatant and flash froze samples using liquid nitrogen. We resuspended the lipid extract in 50 μL of the kit’s suspension buffer and agitated it for 20 min at room temperature in a bath sonicator. We then determined lipid content using an Abcam Lipid Assay Kit. We prepared standards using dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and placed standards and samples in a 96-well plate with sulfuric acid before heating them for 10 min to prime the lipid. We added vanillin that reacted colorimetrically with the lipid in the acidic solution, read absorbances in a spectrophotometer at OD 540 nm, and determined lipid concentrations using the standard curve.
Ash content analysis
To determine feces ash content, we transferred 150 mg (± 5 mg) aliquots of wet sample into pre-labeled aluminum weigh boats (n = 10). We dried samples in a convection oven at 90 °C until samples reached a constant weight (3 h) and then immediately recorded the sample dry weight to the nearest 0.0001 g. We placed the dried samples in a muffle furnace for 5 h at 450 °C, similar to McDermid and Stuercke (2003). We let samples cool for 5 h to room temperature, then immediately re-weighed samples to the nearest 0.0001 g to determine ash content.
Carbohydrate and total caloric value calculations
To determine feces carbohydrate content, we calculated carbohydrates by difference as follows: carbohydrates = 100 − proteins − lipids − ash, where all variables are in % dry weight. This method is commonly used to determine total carbohydrates in food, including in fish feed nutrition studies (Southgate 1969; Opstvedt et al. 2003). Using the sample weight and percentage of proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates, we estimated the caloric values of fecal pellets using established conversion factors based on those broadly accepted by the USDA: carbohydrate, 4.0 kcal g−1; lipid, 9.0 kcal g−1; protein, 4.0 kcal g−1 (Atwater and Woods 1896; Maclean et al. 2003).
Micronutrient analysis
To quantify levels of several biologically important minor elements (calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus) and trace elements (copper, iron, and zinc) in feces, we sent 15 mg aliquots of homogenized, freeze-dried fecal material (n = 10) to the Michigan Elemental Analysis Lab at the University of Michigan for analysis using an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (Thermo Scientific iCAP Q ICP-MS). They digested the samples in 1 mL conc. Optima™ nitric acid (HNO3) using a CEM Mars 6 Microwave. Afterward, they diluted samples to 2% HNO3 (v v−1) and analyzed them using the kinetic energy discrimination (KED) mode with helium gas to overcome polyatomic interferences. The data were standardized based on sample weight and reported in percent dry weight or parts per million (ppm), depending on the element.
Nutritional value of other food sources
To compare the nutritional value of C. multilineata fecal pellets to the other food sources commonly targeted by parrotfishes and surgeonfishes, we conducted a literature search for published nutritional values for brown, green, and red algae, the epilithic and endolithic algae matrix (EAM), and cyanobacteria. We limited this search to articles examining wild, tropical algae of genera that occur in the Caribbean region, as well as studies of the EAM and cyanobacteria sampled from tropical regions (see Supplementary Material for a list of all articles). We compiled the values of total carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins (% dry weight) and the total caloric value (kcal g−1) (see Table S2 for sample sizes). In addition, we compiled published values on the content of magnesium, calcium, and phosphorus (% dry weight) and copper, iron, and zinc (parts per million) for brown, green, and red algae (see Table S3 for sample sizes). We were unable to find published values on the content of these micronutrients for the tropical EAM and cyanobacteria.
Statistical analysis
We conducted statistical analyses using R v3.6.2 and the ‘tidyverse’ package suite (R Core Team 2019; Wickham et al. 2019; RStudio Team 2020). We conducted a correlation test to analyze the relationship between defecation rate and fork length (cm) of C. multilineata. We conducted a binomial logistic regression analysis to examine if there were significant differences in the proportion of the total number of bites by fishes on C. multilineata feces in response to the distance above the benthos at which the C. multilineata defecated (m), the rate at which the feces sank (m s−1), and the interaction between these variables.
To evaluate the difference in the proportion of fecal pellets consumed by different parrotfish and surgeonfish species after accounting for differences in the proportional abundance of these fishes, we used a simulation-based test. We generated 1000 random samples of the proportion of feces consumed by each fish species from simulation based on their proportional abundance. We compared the distribution of possible proportions of coprophagy from the simulated data to the actual observed proportions. For the test, we restricted our comparisons to parrotfishes and surgeonfishes for which we conducted density surveys, not other fish taxa. However, observations of coprophagy by other fish taxa were rare. Of the 135 fecal pellets we monitored, a total of 104 were consumed by parrotfishes and surgeonfishes and only 10 were consumed by other fish taxa.
To analyze species-specific differences in coprophagous behavior, we used Kruskal–Wallis tests to compare: (1) the percentage of bites on fecal pellets relative to total bites and (2) the bite rate on fecal pellets (bites per minute) by parrotfish and surgeonfish species. To determine which species differed significantly, we conducted post hoc comparisons using Dunn’s tests. For these analyses, we used the ‘stats’ and ‘dunn.test’ R packages (Dinno 2017; R Core Team 2019).
Results
Species-specific rates of coprophagy
Chromis multilineata were abundant across our study sites, with an average density that ranged from 1.6 (± 0.3 SE) to 3.1 (± 1.1 SE) individuals per m2. Based on observations, we estimated that C. multilineata had an average defecation rate of 5.6 (± 1.3 SE) fecal pellets per hour (n = 50 behavioral surveys). We found no relationship between C. multilineata defecation rate and fork length (correlation test, p value > 0.05), but the range of fish fork lengths for individuals we observed was small (6–8 cm).
We followed 135 C. multilineata fecal pellets and observed that 84.4% were consumed, 3.7% were tasted but not ingested, 0.7% were inspected, and 11.1% were not inspected or consumed prior to reaching the benthos. Of the 114 fecal pellets consumed by fishes, 91.2% were consumed by parrotfishes or surgeonfishes alone, while 8.8% were consumed by other fishes (Abudefduf saxatilis, Pomacanthus paru, Stegastes partitus, S. planifrons, and other Stegastes spp.). The parrotfish S. taeniopterus and surgeonfish A. coeruleus were more frequent coprophages, where of the total 114 observed instances of coprophagy of C. multilineata fecal pellets, 44.7% were by S. taeniopterus and 26.3% were by A. coeruleus. We observed that coprophagous fishes regularly swam high in the water column to consume descending fecal pellets (see supplementary video footage). The range of depths at which we observed feces being defecated by C. multilineata spanned from approximately 3 to 14 m above the benthos, while the range at which we observed feces being consumed spanned from approximately 5 to 18 m above the benthos. Based on our observations, we estimate that fecal pellets sank at an average rate of 0.02 m s−1 (± 0.001 SE). We found no evidence of a significant difference in the likelihood of feces being consumed based on the distance above the benthos at which C. multilineata defecated (m), rate that feces sank (m s−1), or the interaction between these variables (p value > 0.05).
Based on observations of C. multilineata fecal pellets, as well as surveys of the foraging behavior of parrotfishes and surgeonfishes, we found that all three surgeonfishes (Acanthurus chirurgus, A. coeruleus, and A. tractus) and many parrotfish species surveyed (Scarus coeruleus, S. iseri, S. taeniopterus, S. vetula, Sparisoma aurofrenatum, and S. viride) consumed C. multilineata feces (Fig. S3). For some species, coprophagy was rare; we observed S. coelestinus consuming fecal pellets during surveys of their foraging behavior but not during our fecal pellet observations, and we only observed S. vetula engaging in coprophagy during fecal pellet observations but not during foraging behavioral surveys. Several parrotfish species were not observed engaging in coprophagy using either survey method (S. guacamaia, S. chrysopterum, and S. rubripinne).
Analysis of coprophagy based on fecal pellet observations
There was a significant difference in the observed proportion of feces consumed by different parrotfish and surgeonfish species than predicted from the distribution of possible simulated proportions based on species proportional abundance (Fig. 1). Our findings suggest that S. taeniopterus and A. coeruleus consumed a greater proportion of feces (Simulation-based test, p value < 0.001 and 0.031, respectively) and that S. coeruleus, S. guacamaia, S. chrysopterum, S. rubripinne, and S. viride consumed a lesser proportion of feces than predicted after accounting for the relative density of parrotfish and surgeonfish species (p value < 0.001 for all, Fig. S4).
Analysis of coprophagy based on fish behavioral observations
Based on surveys of the foraging behavior of parrotfishes and surgeonfishes (Fig. 2), there was a significant difference in the median percentage of bites on fecal pellets compared to total bites across food sources among species (Kruskal–Wallis test, X2 = 58.313, df = 11, p value < 0.001). Our results suggest that A. coeruleus, S. iseri, S. taeniopterus, and S. aurofrenatum had a significantly higher percentage of bites on feces compared to S. guacamaia, S. vetula, and S. chrysopterum (Dunn’s test, adj. p value < 0.05 for all; Table S4). Additionally, S. taeniopterus had a significantly higher percentage of bites on feces compared to S. viride (Dunn’s test, adj. p value = 0.044). There was also a significant difference in the median bite rate (bites per minute) on fecal pellets among species (Kruskal–Wallis test, X2 = 58.285, df = 11, p value < 0.001). Our findings suggest that A. coeruleus, S. iseri, and S. taeniopterus had significantly higher bite rates on fecal pellets compared to S. guacamaia, S. vetula, S. chrysopterum, and S. viride (Dunn’s test, adj. p value < 0.05 for all; Table S5).
a Median percentage of bites by parrotfishes and surgeonfishes on Chromis multilineata fecal pellets compared to other food sources. b Median coprophagy rates (bites per min) by parrotfishes and surgeonfishes. We used bootstrapping to generate 95% confidence intervals based on 1000 sampling iterations (n = 6–12 20 min behavioral observations per species)
Nutritional value of feces
We estimated that the C. multilineata fecal pellets contained a median protein content of 16.6% dry weight. This was greater than the median of reported values for brown, green, and red algae, as well as the EAM, though lower than that of cyanobacteria (Fig. 3; Table S6). We estimated that the median lipid content of fecal pellets was 2.4% dry weight, which was similar to the median of reported values for brown, green, and red algae, as well as the EAM, but lower than that of cyanobacteria. Based on calculations of percent carbohydrates in feces, we estimated the median carbohydrate content in fecal pellets to be 75.1% dry weight, which was far higher than values of all other food items considered. Based on calculations of fecal pellet caloric value, we estimated that they had a median of 3.9 kcal g−1, which was higher than the median for brown, green, and red algae (2.4, 1.9, and 1.9 kcal g−1, respectively) and the EAM (1.0 kcal g−1), but lower than that of cyanobacteria (6.0 kcal g−1).
Macronutrient levels (% dry weight) and total caloric values of Chromis multilineata fecal pellets compared to values from the literature of other food sources targeted by parrotfishes and surgeonfishes (see Table S2 for sample sizes). EAM values include the epilithic algae matrix, endolithic algae matrix, turf algae, and associated detritus. The boxplots show the median and interquartile range (IQR), with whiskers extending to values up to 1.5 times the IQR and outlying data displayed as individual points. Ash content values are presented in Table S6
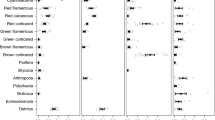
In addition to these macronutrients, coprophagous fishes may also derive nutritional value from minor and trace elements in fish feces. We found that concentrations of several minor elements (calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus) and trace elements (copper, iron, and zinc) in the C. multilineata fecal pellets were well above the median values reported for a range of tropical algal species (Fig. 4; Table S7). The median levels of calcium, copper, magnesium, phosphorus, and zinc were higher in fecal pellets compared to the median of reported values for tropical brown, green, and red algae. Median concentrations of iron in fecal pellets were also greater than values for green algae, though similar to that of red algae and less than that of brown algae.
Minor elements (% dry weight) and trace elements (parts per million) in Chromis multilineata fecal pellets compared to values from the literature of other food sources targeted by parrotfishes and surgeonfishes (see Table S3 for sample sizes). The boxplots show the median and interquartile range (IQR), with whiskers extending to values up to 1.5 times the IQR and outlying data displayed as individual points
Discussion
This study provides the first documentation and quantitative analyses of coprophagous behavior of nominally herbivorous fishes in the Caribbean, as well as early insights into the potential nutritional values of this behavior. We found that consumption of fish feces was prevalent among Caribbean parrotfishes and surgeonfishes, where six of the nine parrotfish species surveyed and all three surgeonfish species actively consumed the feces of an abundant planktivore, Chromis multilineata. While other species were observed consuming C. multilineata feces, we found that over 90% of ingested fecal pellets were consumed by parrotfishes and surgeonfishes alone. Similar to our results, a previous study that found that over 90% of fecal pellets from zooplanktivorous fishes were consumed by reef fishes in the Indo-Pacific and nearly 97% of ingested fecal pellets were consumed by herbivores and detritivores alone (Robertson 1982). Furthermore, we observed that several species regularly swam high in the water column to forage on descending fecal pellets as they slowly sank. Since parrotfishes and surgeonfishes typically graze on EAM, some macroalgae, and other food items on the reef benthos (Adam et al. 2015; Dromard et al. 2015; Duran et al. 2019), this foraging behavior strongly suggests that these species are actively targeting these feces.
Such high consumption rates, broad utilization, and active targeting of fecal pellets across a range of species suggest that these fishes are deriving some nutritional benefit beyond what they obtain through their nominally herbivorous diets. We found that these C. multilineata fecal pellets were rich in macronutrients such as protein and some potentially limiting micronutrients, similar to findings from previous studies of Chromis spp. fecal pellets in other tropical and temperate reefs (Bailey and Robertson 1982; Geesey et al. 1984; Pinnegar and Polunin 2006). While there are species-specific differences in levels of coprophagy, these planktivore feces were targeted by a wide variety of parrotfish and surgeonfish species on Bonaire. Our observations of high levels of coprophagy of planktivore feces by herbivorous fishes in the Caribbean are similar to those of a previous study in the Indo-Pacific (Robertson 1982), suggesting that these feces may be an important source of nutrition for herbivorous fishes in other regions.
Parrotfishes and surgeonfishes have long been recognized for their important functional role in grazing upon and removing turf algae and macroalgae from coral substrate and rubble, a behavior which is believed to mediate competition between coral and algae. However, recent work suggests that these herbivores vary significantly in their foraging behavior interspecifically, ontogenetically, and as a function of resource availability and habitat type (Adam et al. 2015; Smith et al. 2018; Duran et al. 2019). The prevailing hypothesis has been that parrotfishes and surgeonfishes primarily target algae. Yet, recent studies suggest that these nominal herbivores may target detritus and protein-rich microscopic autotrophs—such as cyanobacteria—within or upon the algal-covered substrate or epiphytic on algae (Crossman et al. 2001; Clements et al. 2016; Mendes et al. 2018; Cissell et al. 2019; Nicholson and Clements 2020), as well as other food items such as corals and sponges (Burkepile et al. 2019; Rempel et al. 2020). Our findings suggest that fecal pellets may be another important but overlooked component in the diets of these fishes.
A previous study by Robertson (1982) found that coprophagy is widespread among herbivorous and detritivorous coral reef fishes in the Indo-Pacific and suggested that ‘high-quality’ feces may be a more nutritious energy source than algae. Moreover, that study found that the feces of zooplanktivorous fishes—including a few Chromis spp.—were more frequently consumed than those of corallivores and herbivores. Interestingly, based on behavioral surveys, we found that 99.8% of the fecal pellets consumed by parrotfishes and surgeonfishes were from a single planktivorous species, C. multilineata. Since our behavioral data strongly suggest that herbivores on Bonaire were targeting the fecal pellets of this planktivore, we examined their nutritional content and compared our results to published values for brown, green, and red algae, as well as the EAM and cyanobacteria. Our analyses of macronutrients reveal that these planktivore feces may have higher protein levels than those reported for all food types except cyanobacteria, higher total caloric energy than all algal food types, and higher levels of carbohydrates than all food sources examined. These findings are similar to those of Dethier and colleagues that suggested that feces of a marine invertebrate may have higher protein content than algae (Dethier et al. 2019). Additionally, Bailey and Robertson (1982) found that the feces of the planktivore Chromis atripectoralis were rich in protein, lipids, and total calories compared to the feces of other coral reef fishes. The comparatively high protein levels and total caloric energy in fecal pellets we sampled suggest that C. multilineata feces, like cyanobacteria and the EAM, may be targeted to supplement the relatively lower-quality algae-based diets of parrotfishes and surgeonfishes.
While previous studies have examined the nutritional value of some of the food sources targeted by herbivores on coral reefs (Bruggemann et al. 1994a, b; Crossman et al. 2001), there are still knowledge gaps in the nutritional content of the EAM, cyanobacteria, and sessile invertebrates such as sponges and corals that these fishes are known to target. A recent review questioned whether algal resources are sufficient to support the high biomass of herbivorous fishes found on coral reefs (Clements et al. 2016). This work highlights the importance of integrating anatomical and biochemical analyses in addition to feeding observations to understand the dietary targets and nutritional ecology of nominally herbivorous fishes more fully.
Our findings suggest that planktivore fecal pellets are not only rich in macronutrients such as proteins and carbohydrates but may also be an important source of micronutrients. Coral reefs are commonly nutrient-poor ecosystems and may be limited in nutrients essential for metabolic processes (Howarth 1988; Watanabe et al. 1997). For example, the availability of some micronutrients, such as phosphorus and iron, may be limiting to the growth of reef organisms (Howarth 1988; Schiettekatte et al. 2020). Furthermore, elements such as copper and zinc are critical for enzyme function and metabolic pathways and must be obtained in part from dietary intake (Hilton 1989; Watanabe et al. 1997). The feces of planktivores may be an important source of micronutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus for herbivorous species that consume a nutrient-poor diet (Pinnegar and Polunin 2006). We found higher levels of calcium, copper, phosphorus, and zinc in C. multilineata feces compared to reported values for brown, green, and red macroalgae. The median phosphorus levels of these fecal pellets were over 25 times that of any algae taxa; this is notable as the growth of corals, reef algae, and other organisms may be limited by these nutrients (Howarth 1988). The high levels of phosphorus and calcium in fecal pellets may also drive the high levels of coprophagy we observed, since these elements cannot solely be taken up from the environment via gills and therefore are required from the diet (Sundell and Björnsson 1988; Hilton 1989; Flik and Verbost 1993). Furthermore, these micronutrients interact with one another in complex ways based on presence and quantity within a diet, therefore acting as important supplements (Hilton 1989). A previous study reported higher levels of phosphorus, copper, iron, and zinc in C. multilineata feces from St. Croix compared to values we observed from Bonaire (Geesey et al. 1984), suggesting that the feces of this planktivore may be a rich source of nutrients in other areas of the Caribbean. Broadly, these findings suggest that coprophagy may supply an important source of micronutrients, particularly for herbivorous fishes.
While this study provides the first documentation of coprophagy by herbivorous fishes in the Caribbean and insights into the nutritional benefits of this behavior, additional research is needed to investigate the importance of coprophagy in nutrient cycling on coral reefs. A recent study suggests that fish growth can be limited by available nitrogen and phosphorus, particularly for herbivores and detritivores (Schiettekatte et al. 2020). Fish excretion may provide an important supply of nutrients in marine ecosystems, including nitrogen and phosphorus (Meyer and Schultz 1985; Allgeier et al. 2014; Schiettekatte et al. 2020), but little work has explored the importance of fish egestion in these processes (Bailey and Robertson 1982; Geesey et al. 1984; Pinnegar and Polunin 2006). Our findings support that fish feces may play an undervalued role in nutrient cycling on coral reefs. Future work evaluating patterns of coprophagy and assimilation of these nutrients across fish ontogenetic stages will provide further insight into the importance of this behavior for fish nutrition and bioenergetics.
While coprophagy has been observed by coral reef fishes, including parrotfishes and surgeonfishes in the Indo-Pacific (Robertson 1982) and a surgeonfish in subtropical reefs in Brazil (Sazima et al. 2003), this process has not been well-documented in the vast majority of coral reef ecosystems. As a result, we are uncertain if this behavior is unique to Bonaire—an island where C. multilineata are abundant—or occurs throughout other areas of the Caribbean. Future work should examine how common this behavior is in other coral reef ecosystems, as well as whether the degree of coprophagous behavior is dependent in part on the availability of high-quality fecal pellets, such as that of planktivorous fishes. Additionally, while we observed that most parrotfishes and all surgeonfishes engaged in coprophagy, S. taeniopterus and A. coeruleus had particularly high levels of coprophagy. Gut content and stable isotope analyses suggest that A. coeruleus may have a higher consumption of fleshy macroalgae, algal turf, detritus, and invertebrates compared to other surgeonfishes and parrotfishes (Dromard et al. 2015). In contrast, research suggests that S. taeniopterus may have more dietary overlap with parrotfishes such as S. iseri, S. vetula, and S. viride, consuming more fleshy macroalgae and coral in addition to algal turf and detritus (Dromard et al. 2015; Smith et al. 2018), as well as benthic cyanobacterial mats (Cissell et al. 2019). Future work examining the nutritional value of the various food sources targeted by parrotfish and surgeonfish species (e.g., specific carbohydrate, amino acid, and lipid profiles) and assimilation of nutrients may help to reveal why certain species are more coprophagous than others.
Our novel observations of coprophagy by nominally herbivorous fishes in the Caribbean suggest that fish feces may be an important, yet previously understudied food resource for parrotfishes and surgeonfishes. While there were species-specific differences in the proportional levels of coprophagy and rates of fecal pellet consumption, we observed that most parrotfish species and all three surgeonfish species engaged in this behavior to some degree. Additionally, our findings suggest that these fecal pellets may have higher nutritional values of proteins, total calories, and certain micronutrients compared to macroalgae and the EAM. This study highlights the potential nutritional benefits of coprophagy and improves our understanding of the foraging ecology of nominally herbivorous fishes.
Data availability
All data and scripts are available in a publicly accessible GitHub repository (https://github.com/hannahrempel/coprophagy_2022). Data are also available from the NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI Accession 0,242,462) at https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/archive/accession/0242462.
References
Adam TC, Kelley M, Ruttenberg BI, Burkepile DE (2015) Resource partitioning along multiple niche axes drives functional diversity in parrotfishes on Caribbean coral reefs. Oecologia 179:1173–1185
Allgeier JE, Layman CA, Mumby PJ, Rosemond AD (2014) Consistent nutrient storage and supply mediated by diverse fish communities in coral reef ecosystems. Glob Change Biol 20:2459–2472
Allgeier JE, Burkepile DE, Layman CA (2017) Animal pee in the sea: consumer-mediated nutrient dynamics in the world’s changing oceans. Glob Change Biol 23:2166–2178
Allsop DJ, West SA (2003) Constant relative age and size at sex change for sequentially hermaphroditic fish. J Evol Biol 16:921–929
Atwater WO, Woods CD (1896) The chemical composition of American food materials. U.S Department of Agriculture, Washington, D.C.
Bailey TG, Robertson DR (1982) Organic and caloric levels of fish feces relative to its consumption by coprophagous reef fishes. Mar Biol 69:45–50
Bellwood DR, Hughes TP, Folke C, Nyström M (2004) Confronting the coral reef crisis. Nature 429:827–833
Benstead JP, Hood JM, Whelan NV, Kendrick MR, Nelson D, Hanninen AF, Demi LM (2014) Coupling of dietary phosphorus and growth across diverse fish taxa: a meta-analysis of experimental aquaculture studies. Ecology 95:2768–2777
Bonaldo RM, Krajewski JP, Sazima C, Sazima I (2006) Foraging activity and resource use by three parrotfish species at Fernando de Noronha Archipelago, tropical West Atlantic. Mar Biol 149:423–433
Bonaldo R, Hoey A, Bellwood D (2014) The ecosystem roles of parrotfishes on tropical reefs. In: Hughes R, Hughes D, Smith I (eds) Oceanography and Marine Biology. CRC Press, pp 81–132
Bray RN, Purcell LJ, Miller AC (1986) Ammonium excretion in a temperate-reef community by a planktivorous fish, Chromis punctipinnis (Pomacentridae), and potential uptake by young giant kelp, Macrocystis pyrifera (Laminariales). Mar Biol 90:327–334
Bruggemann JH, Begeman J, Bosma EM, Verburg P, Breeman AM (1994a) Foraging by the stoplight parrotfish Sparisoma viride. II. Intake and assimilation of food, protein and energy. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 106:57–71
Bruggemann JH, Kuyper MWM, Breeman AM (1994b) Comparative analysis of foraging and habitat use by the sympatric Caribbean parrotfish Scarus vetula and Sparisoma viride (Scaridae). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 112:51–66
Burkepile DE, Hay ME (2011) Feeding complementarity versus redundancy among herbivorous fishes on a Caribbean reef. Coral Reefs 30:351–362
Burkepile DE, Adam TC, Roycroft M, Ladd MC, Munsterman KS, Ruttenberg BI (2019) Species-specific patterns in corallivory and spongivory among Caribbean parrotfishes. Coral Reefs 38:417–423
Chabrol E, Charonnet R (1937) Une novelle reaction pouŕl letude des lipides. Presse Med 45:1713
Choat J, Clements K, Robbins W (2001) The trophic status of herbivorous fishes on coral reefs - I: Dietary analyses. Mar Biol 140:613–623
Cissell EC, Manning JC, McCoy SJ (2019) Consumption of benthic cyanobacterial mats on a Caribbean coral reef. Sci Rep 9:1–7
Clements KD, German DP, Piché J, Tribollet A, Choat JH (2016) Integrating ecological roles and trophic diversification on coral reefs: multiple lines of evidence identify parrotfishes as microphages. Biol J Linn Soc 1–23
Crossman DJ, Choat HJ, Clements KD, Hardy T, McConochie J (2001) Detritus as food for grazing fishes on coral reefs. Limnol Oceanogr 46:1596–1605
Crossman D, Choat J, Clements K (2005) Nutritional ecology of nominally herbivorous fishes on coral reefs. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 296:129–142
Dethier MN, Hoins G, Kobelt J, Lowe AT, Galloway AWE, Schram JB, Raymore M, Duggins DO (2019) Feces as food: The nutritional value of urchin feces and implications for benthic food webs. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 514–515:95–102
Dinno A (2017) dunn.test: Dunn’s Test of Multiple Comparisons Using Rank Sums. R package version 1.3.5.
Dromard CR, Bouchon-Navaro Y, Harmelin-Vivien M, Bouchon C (2015) Diversity of trophic niches among herbivorous fishes on a Caribbean reef (Guadeloupe, Lesser Antilles), evidenced by stable isotope and gut content analyses. J Sea Res 95:124–131
Duran A, Adam TC, Palma L, Moreno S, Collado-Vides L, Burkepile DE (2019) Feeding behavior in Caribbean surgeonfishes varies across fish size, algal abundance, and habitat characteristics. Mar Ecol 40:e12561
Ezzat L, Lamy T, Maher R, Munsterman K, Landfield K, Schmeltzer E, Gaulke C, Burkepile D, Vega Thurber R (2019) Surgeonfish feces increase microbial opportunism in reef-building corals. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 631:81–97
Flik G, Verbost PM (1993) Calcium transport in fish gills and intestine. J Exp Biol 184:17–29
Frankenberg D, Smith KL (1967) Coprophagy in Marine Animals. Limnol Oceanogr 12:443–450
Geesey GG, Alexander GV, Bray RN, Miller AC (1984) Fish fecal pellets are a source of minerals for inshore reef communities. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 15:19–25
Gil MA, Hein AM (2017) Social interactions among grazing reef fish drive material flux in a coral reef ecosystem. Proc Natl Acad Sci 114:4703–4708
Harmelin-Vivien M (2002) Energetics and fish diversity on coral reefs. In: Sale P (ed) Coral Reef Fishes: Dynamics and Diversity in a Complex Ecosystem. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, pp 265–274
Hijmans RJ (2019) geosphere: Spherical Trigonometry. R package version 1.5–10.
Hilton JW (1989) The interaction of vitamins, minerals and diet composition in the diet of fish. Aquaculture 79:223–244
Hirakawa H (2001) Coprophagy in leporids and other mammalian herbivores. Mammal Rev 31:61–80
Hobson ES (1973) Diel feeding migrations in tropical reef fishes. Helgoländer Wiss Meeresunters 24:361–370
Hood JM, Vanni MJ, Flecker AS (2005) Nutrient recycling by two phosphorus-rich grazing catfish: the potential for phosphorus-limitation of fish growth. Oecologia 146:247–257
Horn M (1989) Biology of marine herbivorous fishes. In: Barnes H (ed) Oceanography and Marine Biology: An Annual. CRC Press, pp 167–272
Howarth RW (1988) Nutrient limitation of net primary production in marine ecosystems. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 19:89–110
Hughes TP, Rodrigues MJ, Bellwood DR, Ceccarelli D, Hoegh-Guldberg O, McCook L, Moltschaniwskyj N, Pratchett MS, Steneck RS, Willis B (2007) Phase shifts, herbivory, and the resilience of coral reefs to climate change. Curr Biol 17:360–365
Le Mézo PK, Galbraith ED (2021) The fecal iron pump: Global impact of animals on the iron stoichiometry of marine sinking particles. Limnol Oceanogr 66:201–213
Lewis SM, Wainwright PC (1985) Herbivore abundance and grazing intensity on a Caribbean coral reef. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 87:215–228
Lobato FL, Barneche DR, Siqueira AC, Liedke AMR, Lindner A, Pie MR, Bellwood DR, Floeter SR (2014) Diet and Diversification in the Evolution of Coral Reef Fishes. PLOS ONE 9:e102094
Lu Y, Ludsin SA, Fanslow DL, Pothoven SA (2008) Comparison of three microquantity techniques for measuring total lipids in fish. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 65:2233–2241
Maclean WC, Harnly JM, Chen J, Chevassus-Agnes S, Gilani G, Livesey G, Mathioudakis B, Muñoz de Chávez M, Devasconcellos MT, Warwick P (2003) Food energy - methods of analysis and conversion factors. Food & Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome
McDermid KJ, Stuercke B (2003) Nutritional composition of edible Hawaiian seaweeds. J Appl Phycol 15:513–524
Mendes TC, Ferreira CEL, Clements KD (2018) Discordance between diet analysis and dietary macronutrient content in four nominally herbivorous fishes from the Southwestern Atlantic. Mar Biol 165:180
Meyer JL, Schultz ET (1985) Migrating haemulid fishes as a source of nutrients and organic matter on coral reefs. Limnol Oceanogr 30:146–156
Montgomery WL, Gerking SD (1980) Marine macroalgae as foods for fishes: an evaluation of potential food quality. Environ Biol Fishes 5:143–153
Mumby PJ (2006) The impact of exploiting grazers (Scaridae) on the dynamics of Caribbean coral reefs. Ecol Appl 16:747–769
Nalepa CA, Bignell DE, Bandi C (2001) Detritivory, coprophagy, and the evolution of digestive mutualisms in Dictyoptera. Insectes Soc 48:194–201
Nicholson GM, Clements KD (2020) Resolving resource partitioning in parrotfishes (Scarini) using microhistology of feeding substrata. Coral Reefs 39:1313–1327
Opstvedt J, Aksnes A, Hope B, Pike IH (2003) Efficiency of feed utilization in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) fed diets with increasing substitution of fish meal with vegetable proteins. Aquaculture 221:365–379
Park J, Jeong HJ, Yoon EY, Moon SJ, Park J, Jeong HJ, Yoon EY, Moon SJ (2016) Easy and rapid quantification of lipid contents of marine dinoflagellates using the sulpho-phospho-vanillin method. Algae 31:391–401
Pinnegar JK, Polunin NVC (2006) Planktivorous damselfish support significant nitrogen and phosphorus fluxes to Mediterranean reefs. Mar Biol 148:1089–1099
R Core Team (2019) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria
Rempel HS, Bodwin KN, Ruttenberg BI (2020) Impacts of parrotfish predation on a major reef-building coral: quantifying healing rates and thresholds of coral recovery. Coral Reefs 39:1441–1452
Robertson D (1982) Fish feces as fish food on a Pacific coral reef. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 7:253–265
RStudio Team (2020) RStudio: Integrated Development for R. RStudio, PBC, Boston, MA
Ruttenberg BI, Adam TC, Duran A, Burkepile DE (2019) Identity of coral reef herbivores drives variation in ecological processes over multiple spatial scales. Ecol Appl 29:e01893
Sazima I, Sazima C, Silva JM (2003) The cetacean offal connection: Feces and vomits of spinner dolphins as a food source for reef fishes. Bull Mar Sci 72:151–160
Schiettekatte NMD, Barneche DR, Villéger S, Allgeier JE, Burkepile DE, Brandl SJ, Casey JM, Mercière A, Munsterman KS, Morat F, Parravicini V (2020) Nutrient limitation, bioenergetics and stoichiometry: A new model to predict elemental fluxes mediated by fishes. Funct Ecol 34:1857–1869
Shantz AA, Ladd MC, Burkepile DE (2017) Algal nitrogen and phosphorus content drive inter- and intraspecific differences in herbivore grazing on a Caribbean reef. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 497:164–171
Smith PK, Krohn RI, Hermanson GT, Mallia AK, Gartner FH, Provenzano MD, Fujimoto EK, Goeke NM, Olson BJ, Klenk DC (1985) Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem 150:76–85
Smith KM, Quirk-Royal BE, Drake-Lavelle K, Childress MJ (2018) Influences of ontogenetic phase and resource availability on parrotfish foraging preferences in the Florida Keys, FL (USA). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 603:175–187
Smriga S, Sandin SA, Azam F (2010) Abundance, diversity, and activity of microbial assemblages associated with coral reef fish guts and feces: Microbial assemblages associated with coral reef fish guts. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 73:31–42
Soave O, Brand CD (1991) Coprophagy in animals: a review. Cornell Vet 81:357–364
Southgate DAT (1969) Determination of carbohydrates in foods. I Available Carbohydrate. J Sci Food Agric 20:326–330
Sundell K, Björnsson BT (1988) Kinetics of calcium fluxes across the intestinal mucosa of the marine teleost, Gadus Morhua, measured using an in vitro perfusion method. J Exp Biol 140:171–186
Turner JT, Ferrante JG (1979) Zooplankton Fecal Pellets in Aquatic Ecosystems. Bioscience 29:670–677
van Rooij JM, de Jong E, Vaandrager F, Videler JJ (1996) Resource and habitat sharing by the stoplight parrotfish, Sparisoma viride, a Caribbean reef herbivore. Environ Biol Fishes 47:81–91
Watanabe T, Kiron V, Satoh S (1997) Trace minerals in fish nutrition. Aquaculture 151:185–207
Wickham H, Averick M, Bryan J, Chang W, McGowan L, François R, Grolemund G, Hayes A, Henry L, Hester J, Kuhn M, Pedersen T, Miller E, Bache S, Müller K, Ooms J, Robinson D, Seidel D, Spinu V, Takahashi K, Vaughan D, Wilke C, Woo K, Yutani H (2019) Welcome to the Tidyverse. J Open Source Softw 4:1686
Wilson S (2002) Nutritional value of detritus and algae in blenny territories on the Great Barrier Reef. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 271:155–169
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to E. Barton and P. Vanderbloomer for assistance with field data collection and the Stichting Nationale Parken Bonaire for logistical support. We are thankful for Dr. M.S. Edwards’ advice regarding the analysis of fish feces nutritional quality and thank Dr. A. Dial at the University of Michigan Elemental Analysis Lab for performing the micronutrient analyses. The feedback of reviewers and the editor helped to improve this manuscript. We thank Dive Friends Bonaire for their donation of SCUBA tanks for this study, as well as the Balaba and Everlove families for in-kind donations to support travel and accommodations. This project was funded by the California Polytechnic State University Baker/Koob Endowment Award, Bill & Linda Frost Fund, Dr. Earl H. Myers & Ethel M. Myers Oceanographic & Marine Biology Trust, Harvard Travellers Club Permanent Fund, and the American Museum of Natural History Lerner-Gray Memorial Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.S.R., A.K.S., J.C.V.W., and B.I.R. contributed to the study design, H.S.R. and A.K.S. secured funding for this study, H.S.R. and B.I.R. collected field data, H.S.R. and A.K.S. performed laboratory analyses, H.S.R, A.K.S., and K.N.B analyzed the data, H.S.R. and A.K.S. wrote the original draft of the paper, and all authors contributed to writing and approved the final draft for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This research was conducted under permits from the Openbaar Lichaam Bonaire (Archive No. 2018012755) and the Rijkswaterstaat Zee en Delta (RWS-2018/51358). On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that this research was conducted in compliance with ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Tropical Editor Andrew Hoey
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (MP4 130047 KB)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Rempel, H.S., Siebert, A.K., Van Wert, J.C. et al. Feces consumption by nominally herbivorous fishes in the Caribbean: an underappreciated source of nutrients?. Coral Reefs 41, 355–367 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-022-02228-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-022-02228-9