Abstract
Objectives
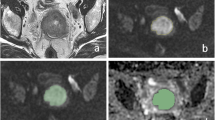
To investigate the feasibility of whole-tumor histogram analysis of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) MRI for predicting occult lymph node metastasis (LNM) in early-stage oral tongue squamous cell cancer (OTSCC).
Materials and methods
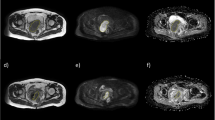
This retrospective study included 55 early-stage OTSCC (cT1-2N0M0) patients; 34 with pathological LNM and 21 without. Eight whole-tumor histogram features were extracted from quantitative apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps and two semi-quantitative DCE parametric maps (wash-in and wash-out). The clinicopathological factors and histogram features were compared between the two groups. Stepwise logistic regression was used to identify independent predictors. Receiver operating characteristic curves were generated to assess the performances of significant variables and a combined model for predicting occult LNM.
Results
MRI-determined depth of invasion and ADCentropy was significantly higher in the LNM group, with respective areas under the curve (AUCs) of 0.67 and 0.69, and accuracies of 0.73 and 0.73. ADC10th. ADCuniformity and wash-inskewness were significantly lower in the LNM group, with respective AUCs of 0.68, 0.71, and 0.69, and accuracies of 0.65, 0.71, and 0.64. Histogram features from wash-out maps were not significantly associated with cervical node status. In the logistic regression analysis, ADC10th, ADCuniformity, and wash-inskewness were independent predictors. The combined model yielded the best predictive performance, with an AUC of 0.87 and an accuracy of 0.82.
Conclusions
Whole-tumor histogram analysis of ADC and wash-in maps is a feasible tool for preoperative evaluation of cervical node status in early-stage OTSCC.
Key Points
• Histogram analysis of parametric maps from DWI and DCE-MRI may assist the prediction of occult LNM in early-stage OTSCC.
• ADC 10th , ADC uniformity , and wash-in skewness were independent predictors.
• The combined model exhibited good predictive performance, with an accuracy of 0.82.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ADC:
-
Apparent diffusion coefficient
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- DCE:
-
Dynamic contrast-enhanced
- DOI:
-
Depth of invasion
- DWI:
-
Diffusion-weighted imaging
- ICC:
-
Intraclass correlation coefficient
- LNM:
-
Lymph node metastasis
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- OTSCC:
-
Oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- ROI:
-
Region of interest
References
Chi AC, Day TA, Neville BW (2015) Oral cavity and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma–an update. CA Cancer J Clin 65:401–421
Huang SH, Hwang D, Lockwood G, Goldstein DP, O’Sullivan B (2009) Predictive value of tumor thickness for cervical lymph-node involvement in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity: a meta-analysis of reported studies. Cancer 115:1489–1497
Greenberg JS, El Naggar AK, Mo V, Roberts D, Myers JN (2003) Disparity in pathologic and clinical lymph node staging in oral tongue carcinoma. Implication for therapeutic decision making Cancer 98:508–515
Oh LJ, Phan K, Kim SW, Low TH, Gupta R, Clark JR (2020) Elective neck dissection versus observation for early-stage oral squamous cell carcinoma: systematic review and meta-analysis. Oral Oncol 105:104661
Surov A, Meyer HJ, Gawlitza M et al (2017) Correlations between DCE MRI and histopathological parameters in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Transl Oncol 10:17–21
Bonello L, Preda L, Conte G et al (2016) Squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity and oropharynx: what does the apparent diffusion coefficient tell us about its histology? Acta Radiol 57:1344–1351
Chawla S, Kim S, Loevner LA et al (2011) Prediction of disease-free survival in patients with squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck using dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:778–784
Xie T, Zhao Q, Fu C et al (2019) Differentiation of triple-negative breast cancer from other subtypes through whole-tumor histogram analysis on multiparametric MR imaging. Eur Radiol 29:2535–2544
Gong ML, Li L, Li K, Li SJ, Wen M (2020) Relationship of ADC histogram parameters with pathological grade and lymph node metastasis of prostate cancer. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue 26:881–887
Li J, Zhou Y, Wang X, Yu Y, Zhou X, Luan K (2021) Histogram analysis of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging as a biomarker to predict lymph node metastasis in T3 stage rectal carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res 13:2983–2993
Chen YL, Li R, Chen TW et al (2019) Whole-tumour histogram analysis of pharmacokinetic parameters from dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI in resectable oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma can predict T-stage and regional lymph node metastasis. Eur J Radiol 112:112–120
Kelly HR, Curtin HD (2017) Chapter 2 Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck-imaging evaluation of regional lymph nodes and implications for management. Semin Ultrasound CT MR 38:466–478
Shrout PE, Fleiss JL (1979) Intraclass correlations: uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol Bull 86:420–428
Lambin P, Rios-Velazquez E, Leijenaar R et al (2012) Radiomics: extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. Eur J Cancer 48:441–446
Gillies RJ, Kinahan PE, Hricak H (2016) Radiomics: images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology 278:563–577
Yang C, Huang M, Li S et al (2020) Radiomics model of magnetic resonance imaging for predicting pathological grading and lymph node metastases of extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Lett 470:1–7
Chen W, Wang S, Dong D et al (2019) Evaluation of lymph node metastasis in advanced gastric cancer using magnetic resonance imaging-based radiomics. Front Oncol 9:1265
Hu W, Wang H, Wei R et al (2020) MRI-based radiomics analysis to predict preoperative lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Gland Surg 9:1214–1226
Xiao M, Ma F, Li Y et al (2020) Multiparametric MRI-based radiomics nomogram for predicting lymph node metastasis in early-stage cervical cancer. J Magn Reson Imaging 52:885–896
Cui X, Wang N, Zhao Y et al (2019) Preoperative prediction of axillary lymph node metastasis in breast cancer using radiomics features of DCE-MRI. Sci Rep 9:2240
Wang T, Gao T, Yang J et al (2019) Preoperative prediction of pelvic lymph nodes metastasis in early-stage cervical cancer using radiomics nomogram developed based on T2-weighted MRI and diffusion-weighted imaging. Eur J Radiol 114:128–135
Yuan Y, Ren J, Tao X (2021) Machine learning-based MRI texture analysis to predict occult lymph node metastasis in early-stage oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Eur Radiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-021-07731-1
Koh DM, Collins DJ (2007) Diffusion-weighted MRI in the body: applications and challenges in oncology. AJR Am J Roentgenol 188:1622–1635
Meyer HJ, Leifels L, Hamerla G, Höhn AK, Surov A (2018) ADC-histogram analysis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Associations with different histopathological features including expression of EGFR, VEGF, HIF-1α, Her 2 and p53. A preliminary study. Magn Reson Imaging 54:214–217
Surov A, Meyer HJ, Winter K, Richter C, Hoehn AK (2018) Histogram analysis parameters of apparent diffusion coefficient reflect tumor cellularity and proliferation activity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 9:23599–23607
Ren J, Qi M, Yuan Y, Tao X (2021) Radiomics of apparent diffusion coefficient maps to predict histologic grade in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral tongue and floor of mouth: a preliminary study. Acta Radiol 62:453–461
Ren J, Yuan Y, Wu Y, Tao X (2018) Differentiation of orbital lymphoma and idiopathic orbital inflammatory pseudotumor: combined diagnostic value of conventional MRI and histogram analysis of ADC maps. BMC Med Imaging 18:6
Kang Y, Choi SH, Kim YJ et al (2011) Gliomas: Histogram analysis of apparent diffusion coefficient maps with standard- or high-b-value diffusion-weighted MR imaging–correlation with tumor grade. Radiology 261:882–890
Ren JL, Yuan Y, Li XX, Shi YQ, Tao XF (2018) Histogram analysis of apparent diffusion coefficient maps in the prognosis of patients with locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: comparison of different region of interest selection methods. Eur J Radiol 106:7–13
De Robertis R, Maris B, Cardobi N et al (2018) Can histogram analysis of MR images predict aggressiveness in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors? Eur Radiol 28:2582–2591
Lee JY, Cheng KL, Lee JH et al (2019) Detection of local recurrence in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma using voxel-based color maps of initial and final area under the curve values derived from DCE-MRI. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 40:1392–1401
Meyer HJ, Hamerla G, Leifels L, Höhn AK, Surov A (2019) Histogram analysis parameters derived from DCE-MRI in head and neck squamous cell cancer - associations with microvessel density. Eur J Radiol 120:108669
Chawla S, Kim SG, Loevner LA et al (2020) Prediction of distant metastases in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck using DWI and DCE-MRI. Head Neck 42:3295–3306
Artese L, Rubini C, Ferrero G, Fioroni M, Santinelli A, Piattelli A (2001) Microvessel density (MVD) and vascular endothelial growth factor expression (VEGF) in human oral squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res 21:689–695
Xu C, Yuan J, Kang L et al (2020) Significance of depth of invasion determined by MRI in cT1N0 tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Sci Rep 10:4695
Funding
This work was supported by funds from the National Scientific Foundation of China (91859202, 81771901) and the Shanghai Municipal Health Commission (20194Y0104).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Guarantor
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Prof. Xiaofeng Tao.
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Statistics and biometry
One of the authors has significant statistical expertise.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval was obtained.
Methodology
• retrospective
• diagnostic or prognostic study
• performed at one institution
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, J., Yuan, Y. & Tao, X. Histogram analysis of diffusion-weighted imaging and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI for predicting occult lymph node metastasis in early-stage oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Eur Radiol 32, 2739–2747 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-021-08310-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-021-08310-0