Abstract
Objectives
To investigate the diagnostic performance of diffusion tensor imaging in patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD).
Methods
We examined a total of 126 PD patients (68 males/58 females, mean age: 62.0 ±7.6 years) and 91 healthy controls (43 males/48 females, mean age: 59.8 ±7.2 years). Images were acquired on a 3 Tesla magnetic resonance scanner. The Camino software was used to normalize and parcellate diffusion-weighted images into 90 cerebral regions based on the automatic anatomical labelling template. The minimum, median, and maximum values of the mean/radial/axial diffusivity/fractional anisotropy were determined. The diagnostic performance was assessed by receiver operating characteristic analysis. The associations of imaging parameters with disease severity were tested using Pearson’s correlation coefficients after adjustment for disease duration.
Results
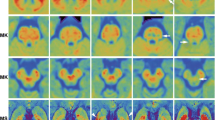
Compared with healthy controls, PD patients showed increased diffusivity in multiple cortical regions that extended beyond the basal ganglia. An area under curve of 85 % was identified for the maximum values of mean diffusivity in the ipsilateral middle temporal gyrus. The most significant intergroup difference was 26.8 % for the ipsilateral inferior parietal gyrus.
Conclusion
The measurement of water diffusion from the parcellated cortex may be clinically useful for the assessment of PD patients.
Key Points
• Increased diffusivity was identified in multiple cortical regions of Parkinson’s disease patients.
• The area under the receiver operating curve was 85 % in the middle temporal gyrus.
• The ipsilateral inferior parietal gyrus showed the most significant change.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lang AE, Lozano AM (1998) Parkinson's disease. First of two parts. N Engl J Med 339:1044–1053
Lang AE, Lozano AM (1998) Parkinson's disease. Second of two parts. N Engl J Med 339:1130–1143
Adler CH, Beach TG, Hentz JG et al (2014) Low clinical diagnostic accuracy of early vs advanced Parkinson disease: clinicopathologic study. Neurology 83:406–412
Tessitore A, Amboni M, Cirillo G et al (2012) Regional gray matter atrophy in patients with Parkinson disease and freezing of gait. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:1804–1809
Choi SH, Jung TM, Lee JE, Lee SK, Sohn YH, Lee PH (2012) Volumetric analysis of the substantia innominata in patients with Parkinson's disease according to cognitive status. Neurobiol Aging 33:1265–1272
Carlesimo GA, Piras F, Assogna F, Pontieri FE, Caltagirone C, Spalletta G (2012) Hippocampal abnormalities and memory deficits in Parkinson disease: a multimodal imaging study. Neurology 78:1939–1945
Chang CC, Chang WN, Lui CC et al (2011) Clinical significance of the pallidoreticular pathway in patients with carbon monoxide intoxication. Brain 134:3632–3646
Wang J, Wai Y, Lin WY et al (2010) Microstructural changes in patients with progressive supranuclear palsy: a diffusion tensor imaging study. J Magn Reson Imaging 32:69–75
Menke RA, Scholz J, Miller KL et al (2009) MRI characteristics of the substantia nigra in Parkinson's disease: a combined quantitative T1 and DTI study. NeuroImage 47:435–441
Karagulle Kendi AT, Lehericy S, Luciana M, Ugurbil K, Tuite P (2008) Altered diffusion in the frontal lobe in Parkinson disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:501–505
Zhang Y, Schuff N, Jahng GH et al (2007) Diffusion tensor imaging of cingulum fibers in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease. Neurology 68:13–19
Acosta-Cabronero J, Alley S, Williams GB, Pengas G, Nestor PJ (2012) Diffusion tensor metrics as biomarkers in Alzheimer's disease. PLoS One 7, e49072
Gattellaro G, Minati L, Grisoli M et al (2009) White matter involvement in idiopathic Parkinson disease: a diffusion tensor imaging study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:1222–1226
Vaillancourt DE, Spraker MB, Prodoehl J et al (2009) High-resolution diffusion tensor imaging in the substantia nigra of de novo Parkinson disease. Neurology 72:1378–1384
Cochrane CJ, Ebmeier KP (2013) Diffusion tensor imaging in parkinsonian syndromes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurology 80:857–864
Kikuchi A, Baba T, Hasegawa T et al (2013) Hypometabolism in the supplementary and anterior cingulate cortices is related to dysphagia in Parkinson's disease: a cross-sectional and 3-year longitudinal cohort study. BMJ open 3
Chan LL, Rumpel H, Yap K et al (2007) Case control study of diffusion tensor imaging in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78:1383–1386
Chen Z, Ma L, Lou X, Zhou Z (2010) Diagnostic value of minimum apparent diffusion coefficient values in prediction of neuroepithelial tumor grading. J Magn Reson Imaging 31:1331–1338
Murakami R, Hirai T, Sugahara T et al (2009) Grading astrocytic tumors by using apparent diffusion coefficient parameters: superiority of a one- versus two-parameter pilot method. Radiology 251:838–845
Lo CY, Wang PN, Chou KH, Wang J, He Y, Lin CP (2010) Diffusion tensor tractography reveals abnormal topological organization in structural cortical networks in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 30:16876–16885
Ng SH, Hsu WC, Wai YY et al (2013) Sex dimorphism of cortical water diffusion in normal aging measured by magnetic resonance imaging. Front Aging Neurosci 5:71
Alexander DC, Pierpaoli C, Basser PJ, Gee JC (2001) Spatial transformations of diffusion tensor magnetic resonance images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 20:1131–1139
Modrego PJ, Fayed N, Artal J, Olmos S (2011) Correlation of findings in advanced MRI techniques with global severity scales in patients with Parkinson disease. Acad Radiol 18:235–241
Litvan I, Bhatia KP, Burn DJ et al (2003) SIC task force appraisal of clinical diagnostic criteria for parkinsonian disorders. Mov Disord 18:467–486
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2000) Voxel-based morphometry--the methods. NeuroImage 11:805–821
Cook PA, Bai Y, Nedjati-Gilani S, Seunarine KK, Hall MG, Parker GJ, Alexander DC (2006) Camino: open-source diffusion-mri reconstruction and processing 14th scientific meeting of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, Seattle, WA, USA, p 2759
Schulz JB, Skalej M, Wedekind D et al (1999) Magnetic resonance imaging-based volumetry differentiates idiopathic Parkinson's syndrome from multiple system atrophy and progressive supranuclear palsy. Ann Neurol 45:65–74
Geng DY, Li YX, Zee CS (2006) Magnetic resonance imaging-based volumetric analysis of basal ganglia nuclei and substantia nigra in patients with Parkinson's disease. Neurosurgery 58:256–262, discussion 256–262
Burton EJ, McKeith IG, Burn DJ, Williams ED, O'Brien JT (2004) Cerebral atrophy in Parkinson's disease with and without dementia: a comparison with Alzheimer's disease, dementia with Lewy bodies and controls. Brain 127:791–800
Gonzalez-Redondo R, Garcia-Garcia D, Clavero P et al (2014) Grey matter hypometabolism and atrophy in Parkinson's disease with cognitive impairment: a two-step process. Brain 137:2356–2367
Cunnington R, Egan GF, O'Sullivan JD, Hughes AJ, Bradshaw JL, Colebatch JG (2001) Motor imagery in Parkinson's disease: a PET study. Mov Disord 16:849–857
Matsui H, Udaka F, Miyoshi T et al (2006) Frontal assessment battery and brain perfusion image in Parkinson's disease. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol 19:41–45
Braak H, Del Tredici K (2008) Invited Article: Nervous system pathology in sporadic Parkinson disease. Neurology 70:1916–1925
Zhang H, Schneider T, Wheeler-Kingshott CA, Alexander DC (2012) NODDI: practical in vivo neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging of the human brain. NeuroImage 61:1000–1016
Jensen JH, Helpern JA (2010) MRI quantification of non-Gaussian water diffusion by kurtosis analysis. NMR Biomed 23:698–710
Basser PJ, Pierpaoli C (1996) Microstructural and physiological features of tissues elucidated by quantitative-diffusion-tensor MRI. J Magn Reson B 111:209–219
Choe BY, Park JW, Lee KS et al (1998) Neuronal laterality in Parkinson's disease with unilateral symptom by in vivo 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Investig Radiol 33:450–455
Lyoo CH, Ryu YH, Lee MS (2010) Topographical distribution of cerebral cortical thinning in patients with mild Parkinson's disease without dementia. Mov Disord 25:496–499
Summerfield C, Junque C, Tolosa E et al (2005) Structural brain changes in Parkinson disease with dementia: a voxel-based morphometry study. Arch Neurol 62:281–285
Aarsland D, Andersen K, Larsen JP, Lolk A, Nielsen H, Kragh-Sorensen P (2001) Risk of dementia in Parkinson's disease: a community-based, prospective study. Neurology 56:730–736
Acknowledgements
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Jiun-Jie Wang. The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. This study has received funding by the Ministry of Science and Technology Taiwan (103-2325-B-182-001 and 104-2314-B-182-042) and the Chang-Gung Memorial Hospital (CMRPD3D0011-3, CIRPD1E0061 and CMRPD1C0291-3). One of the authors has significant statistical expertise. Institutional review board approval was obtained. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects (including patients) in this study. Some study subjects or cohorts have been previously reported in (10.3389/fnagi.2013.00071). 77 healthy controls have been previously reported (10.3389/fnagi.2013.00071). The prior article discussed the change of water diffusion in the ageing process whereas this manuscript focused on the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease.
Methodology: prospective, case-control study, performed at one institution.
The imaging facility was supported by the Imaging Core Laboratory of Institute for Radiological Research and Center for Advanced Molecular Imaging and Translation. The authors would like to thank the Neuroscience Research Center, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Imaging Core Laboratory of Institute for Radiological Research, Chang Gung University/Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Linkou and the Healthy Aging Research Center, Chang Gung University for providing support. The funding source had no involvement in the collection, analysis, and interpretation data; in the writing of the report; and in the decision to submit the paper for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Chin-Song Lu and Shu-Hang Ng contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, CS., Ng, SH., Weng, YH. et al. Alterations of diffusion tensor MRI parameters in the brains of patients with Parkinson’s disease compared with normal brains: possible diagnostic use. Eur Radiol 26, 3978–3988 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-016-4232-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-016-4232-7