Abstract
Objectives
To investigate the technical feasibility of whole-body intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) imaging.
Materials and Methods
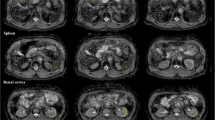
Whole-body MR images of eight healthy volunteers were acquired at 3T using a spin-echo echo-planar imaging sequence with eight b-values. Coronal parametrical whole-body maps of diffusion (D), pseudodiffusion (D*), and the perfusion fraction (Fp) were calculated. Image quality was rated qualitatively by two independent radiologists, and inter-reader reliability was tested with intra-class correlation coefficients (ICCs). Region of interest (ROI) analysis was performed in the brain, liver, kidney, and erector spinae muscle.
Results
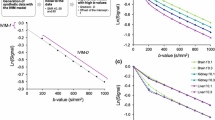
Depiction of anatomic structures was rated as good on D maps and good to fair on D* and Fp maps. Exemplary mean D (10−3 mm2/s), D* (10−3 mm2/s) and Fp (%) values (± standard deviation) of the renal cortex were as follows: 1.7 ± 0.2; 15.6 ± 6.5; 20.9 ± 4.4. Inter-observer agreement was “substantial” to “almost perfect” (ICC = 0.80 – 0.92). The coefficient of variation of D* was significantly lower with the proposed algorithm compared to the conventional algorithm (p < 0.001), indicating higher stability.
Conclusion
The proposed IVIM protocol allows computation of parametrical maps with good to fair image quality. Potential future clinical applications may include characterization of widespread disease such as metastatic tumours or inflammatory myopathies.
Key Points
• IVIM imaging allows estimation of tissue perfusion based on diffusion-weighted MRI.
• In this study, a clinically suitable whole-body IVIM algorithm is presented.
• Coronal parametrical whole-body maps showed good depiction of anatomic details.
• Potential future applications include detection of widespread metastatic or inflammatory disease.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Padhani AR, Liu G, Koh DM et al (2009) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging as a cancer biomarker: consensus and recommendations. Neoplasia 11:102–125
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Grenier P, Cabanis E, Laval-Jeantet M (1986) MR imaging of intravoxel incoherent motions: application to diffusion and perfusion in neurologic disorders. Radiology 161:401–407
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Aubin ML, Vignaud J, Laval-Jeantet M (1988) Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology 168:497–505
Le Bihan D (1988) Intravoxel incoherent motion imaging using steady-state free precession. Magn Reson Med Off J Soc Magn Res Med / Soc Magn Reson Med 7:346–351
Turner R, Le Bihan D, Maier J, Vavrek R, Hedges LK, Pekar J (1990) Echo-planar imaging of intravoxel incoherent motion. Radiology 177:407–414
Chiaradia M, Baranes L, Van Nhieu JT et al (2013) Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) MR imaging of colorectal liver metastases: are we only looking at tumor necrosis? J Magn Reso Imaging : JMRI. doi:10.1002/jmri.24172
Sasaki M, Sumi M, Van Cauteren M, Obara M, Nakamura T (2013) Intravoxel incoherent motion imaging of masticatory muscles: pilot study for the assessment of perfusion and diffusion during clenching. AJR Am J Roentgenol 201:1101–1107
Bisdas S, Koh TS, Roder C et al (2013) Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MR imaging of gliomas: feasibility of the method and initial results. Neuroradiology 55:1189–1196
Dyvorne HA, Galea N, Nevers T et al (2013) Diffusion-weighted imaging of the liver with multiple b values: effect of diffusion gradient polarity and breathing acquisition on image quality and intravoxel incoherent motion parameters–a pilot study. Radiology 266:920–929
Patel J, Sigmund EE, Rusinek H, Oei M, Babb JS, Taouli B (2010) Diagnosis of cirrhosis with intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion MRI and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI alone and in combination: preliminary experience. J Magn Reso Imaging : JMRI 31:589–600
Yamada I, Aung W, Himeno Y, Nakagawa T, Shibuya H (1999) Diffusion coefficients in abdominal organs and hepatic lesions: evaluation with intravoxel incoherent motion echo-planar MR imaging. Radiology 210:617–623
Andreou A, Koh DM, Collins DJ et al (2013) Measurement reproducibility of perfusion fraction and pseudodiffusion coefficient derived by intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MR imaging in normal liver and metastases. Eur Radiol 23:428–434
Sigmund EE, Vivier PH, Sui D et al (2012) Intravoxel incoherent motion and diffusion-tensor imaging in renal tissue under hydration and furosemide flow challenges. Radiology 263:758–769
Ichikawa S, Motosugi U, Ichikawa T, Sano K, Morisaka H, Araki T (2013) Intravoxel incoherent motion imaging of the kidney: alterations in diffusion and perfusion in patients with renal dysfunction. Magn Reson Imaging 31:414–417
Rheinheimer S, Stieltjes B, Schneider F et al (2012) Investigation of renal lesions by diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging applying intravoxel incoherent motion-derived parameters–initial experience. Eur J Radiol 81:e310–e316
Morvan D (1995) In vivo measurement of diffusion and pseudo-diffusion in skeletal muscle at rest and after exercise. Magn Reson Imaging 13:193–199
Qi J, Olsen NJ, Price RR, Winston JA, Park JH (2008) Diffusion-weighted imaging of inflammatory myopathies: polymyositis and dermatomyositis. J Magn Reso Imaging : JMRI 27:212–217
Gudbjartsson H, Patz S (1995) <Gudbjartsson_1995.pdf> Magn Reson Med Off J Soc Magn Res Med / Soc Magn Reson Med 34:910–914
Kundel HL, Polansky M (2003) Measurement of observer agreement. Radiology 228:303–308
Yoon JH, Lee JM, Yu MH, Kiefer B, Han JK, Choi BI (2013) Evaluation of hepatic focal lesions using diffusion-weighted MR imaging: comparison of apparent diffusion coefficient and intravoxel incoherent motion-derived parameters. J Magn Reso Imaging : JMRI. doi:10.1002/jmri.24158
Ichikawa S, Motosugi U, Ichikawa T, Sano K, Morisaka H, Araki T (2013) Intravoxel incoherent motion imaging of focal hepatic lesions. J Magn Reso Imaging : JMRI 37:1371–1376
Chow AM, Gao DS, Fan SJ et al (2012) Liver fibrosis: an intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) study. J Magn Reso Imaging : JMRI 36:159–167
Guiu B, Petit JM, Capitan V et al (2012) Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a 3.0-T MR study. Radiology 265:96–103
Klauss M, Lemke A, Grunberg K et al (2011) Intravoxel incoherent motion MRI for the differentiation between mass forming chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic carcinoma. Investig Radiol 46:57–63
Dopfert J, Lemke A, Weidner A, Schad LR (2011) Investigation of prostate cancer using diffusion-weighted intravoxel incoherent motion imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 29:1053–1058
Sigmund EE, Cho GY, Kim S et al (2011) Intravoxel incoherent motion imaging of tumor microenvironment in locally advanced breast cancer. Magn Reson Med Off J Soc Magn Res Med / Soc Magn Reson Med 65:1437–1447
Bokacheva L, Kaplan JB, Giri DD et al (2013) Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MRI at 3.0 T differentiates malignant breast lesions from benign lesions and breast parenchyma. J Magn Reson Imaging: JMRI. doi:10.1002/jmri.24462
Federau C, Meuli R, O’Brien K, Maeder P, Hagmann P (2013) Perfusion measurement in brain gliomas with intravoxel incoherent motion MRI. AJNR American journal of neuroradiology. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A3686
Federau C, O’Brien K, Meuli R, Hagmann P, Maeder P (2013) Measuring brain perfusion with intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM): initial clinical experience. J Magn Reso Imaging : JMRI. doi:10.1002/jmri.24195
Kim HS, Suh CH, Kim N, Choi CG, Kim SJ (2013) Histogram analysis of intravoxel incoherent motion for differentiating recurrent tumor from treatment effect in patients with glioblastoma: initial clinical experience. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A3719
Kwee TC, Takahara T, Ochiai R, Nievelstein RA, Luijten PR (2008) Diffusion-weighted whole-body imaging with background body signal suppression (DWIBS): features and potential applications in oncology. Eur Radiol 18:1937–1952
Bammer R (2003) Basic principles of diffusion-weighted imaging. Eur J Radiol 45:169–184
Takahara T, Imai Y, Yamashita T, Yasuda S, Nasu S, Van Cauteren M (2004) Diffusion weighted whole body imaging with background body signal suppression (DWIBS): technical improvement using free breathing, STIR and high resolution 3D display. Radiat Med 22:275–282
Cohen AD, Schieke MC, Hohenwalter MD, Schmainda KM (2014) The effect of low b-values on the intravoxel incoherent motion derived pseudodiffusion parameter in liver. Magn Reson Med Off J Soc Magn Res Med / Soc Magn Reson Med. doi:10.1002/mrm.25109
Lemke A, Stieltjes B, Schad LR, Laun FB (2011) Toward an optimal distribution of b values for intravoxel incoherent motion imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 29:766–776
Concia M, Sprinkart AM, Penner AH et al (2013) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the pancreas: diagnostic benefit from an intravoxel incoherent motion model-based 3 b-value analysis. Investig Radiol. doi:10.1097/RLI.0b013e3182a71cc3
Penner AH, Sprinkart AM, Kukuk GM et al (2013) Intravoxel incoherent motion model-based liver lesion characterisation from three b-value diffusion-weighted MRI. Eur Radiol 23:2773–2783
Lemke A, Laun FB, Simon D, Stieltjes B, Schad LR (2010) An in vivo verification of the intravoxel incoherent motion effect in diffusion-weighted imaging of the abdomen. Magn Reson Med Off J Soc Magn Res Med / Soc Magn Reson Med 64:1580–1585
Kong XZ (2014) Association between in-scanner head motion with cerebral white matter microstructure: a multiband diffusion-weighted MRI study. PeerJ 2:e366
Chang HC, Guhaniyogi S, Chen NK (2014) Interleaved diffusion-weighted improved by adaptive partial-Fourier and multiband multiplexed sensitivity-encoding reconstruction. Magn Reson Med Off J Soc Magn Res Med / Soc Magn Reson Med. doi:10.1002/mrm.25318
Niederkohr RD, Rosenberg J, Shabo G, Quon A (2007) Clinical value of including the head and lower extremities in 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging for patients with malignant melanoma. Nucl Med Commun 28:688–695
Querellou S, Keromnes N, Abgral R et al (2010) Clinical and therapeutic impact of 18F-FDG PET/CT whole-body acquisition including lower limbs in patients with malignant melanoma. Nucl Med Commun 31:766–772
Malattia C, Damasio MB, Madeo A et al (2013) Whole-body MRI in the assessment of disease activity in juvenile dermatomyositis. Ann Rheum Dis. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202915
Acknowledgements
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Andreas Boss. The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. The authors state that this work has not received any funding. No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper. Institutional review board approval was obtained. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects (patients) in this study. Methodology: prospective, experimental, performed at one institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Filli, L., Wurnig, M.C., Luechinger, R. et al. Whole-body intravoxel incoherent motion imaging. Eur Radiol 25, 2049–2058 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3577-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3577-z