Abstract
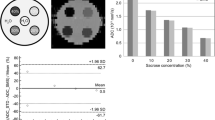
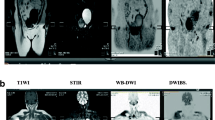
The purpose was to provide a diffusion-weighted whole-body magnetic resonance (MR) imaging sequence with background body signal suppression (DWIBS) at 3.0 Tesla. A diffusion-weighted spin-echo echo-planar imaging sequence was combined with the following methods of fat suppression: short TI inversion recovery (STIR), spectral attenuated inversion recovery (SPAIR), and spectral presaturation by inversion recovery (SPIR). Optimized sequences were implemented on a 3.0- and a 1.5-Tesla system and evaluated in three healthy volunteers and six patients with various lesions in the neck, chest, and abdomen on the basis of reconstructed maximum intensity projection images. In one patient with metastases of malignant melanoma, DWIBS was compared with 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET). Good fat suppression for all regions and diagnostic image quality in all cases could be obtained at 3.0 Tesla with the STIR method. In comparison with 1.5 Tesla, DWIBS images at 3.0 Tesla were judged to provide a better lesion-to-bone tissue contrast. However, larger susceptibility-induced image distortions and signal intensity losses, stronger blurring artifacts, and more pronounced motion artifacts degraded the image quality at 3.0 Tesla. A good correlation was found between the metastases as depicted by DWIBS and those as visualized by FDG-PET. DWIBS is feasible at 3.0 Tesla with diagnostic image quality.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takahara T, Imai Y, Yamashita T, Yasuda S, Nasu S, Van CM (2004) Diffusion weighted whole body imaging with background body signal suppression (DWIBS): technical improvement using free breathing, STIR and high resolution 3D display. Radiat Med 22:275–282
Sakurada A, Takahara T, Nasu S, Horie T, van Cauteren M, Imai Y (2006) Clinical significance of diffusion-weighted image in staging esophageal cancer. 14th Scientific Meeting and Exhibition, ISMRM: Abstracts, p 2226
Komori T, Narabayashi I, Matsumura K, Matsuki M, Kawachi M, Yamamoto M (2005) Comparison of radiography, FDG-PET/CT and body diffusion-weighted imaging for tumor evaluation in cancer patients on the same day. RSNA 2005, abstract
Zhang Y, Liang B, Gao L (2005) Preliminary study of a lymph nodes imaging: diffusion-weighted MRI with STIR-EPI. RSNA 2005, abstract
Goudarzi B, Kishimoto R, Yoshikawa K, Kandatsu S, Komatsu S, Ishikawa H, Shahnazi M, Tsujii H (2006) The diagnostic ability of diffusion-weighted imaging with background body signal suppression (DWIBS) in bone metastasis. 14th Scientific Meeting and Exhibition, ISMRM: Abstracts, p 548
Gibbs P, Pickles MD, Turnbull LW (2006) Diffusion imaging of the prostate at 3.0 tesla. Invest Radiol 41:185–188
Chiu FY, Jao JC, Chen CY, Liu GC, Jaw TS, Chiou YY, Hsu FO, Hsu JS (2005) Effect of intravenous gadolinium-DTPA on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images for evaluation of focal hepatic lesions. J Comput Assist Tomogr 29:176–180
Mürtz P, Flacke S, Träber F, van den Brink JS, Gieseke J, Schild HH (2002) Abdomen: diffusion-weighted MR imaging with pulse-triggered single-shot sequences. Radiology 224:258–264
Kawai Y, Sumi M, Nakamura T (2006) Turbo short tau inversion recovery imaging for metastatic node screening in patients with head and neck cancer. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:1283–1287
Müller MF, Prasad P, Siewert B, Nissenbaum MA, Raptopoulos V, Edelman RR (1994) Abdominal diffusion mapping with use of a whole-body echo-planar system. Radiology 190:475–478
Chow LC, Bammer R, Moseley ME, Sommer FG (2003) Single breath-hold diffusion-weighted imaging of the abdomen. J Magn Reson Imaging 18:377–382
Thoeny HC, De KF (2007) Extracranial applications of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Eur Radiol [Epub ahead of print]
Abdel Razek A, Soliman NY, Elkhamary S, Alsharaway MK, Tawfik A (2006) Role of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in cervical lymphadenopathy. Eur Radiol 16:1468–1477
Koh DM, Scurr E, Collins DJ, Pirgon A, Kanber B, Karanjia N, Brown G, Leach MO, Husband JE (2006) Colorectal hepatic metastases: quantitative measurements using single-shot echo-planar diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Eur Radiol 16:1898–1905
Hayashida Y, Yakushiji T, Awai K, Katahira K, Nakayama Y, Shimomura O, Kitajima M, Hirai T, Yamashita Y, Mizuta H (2006) Monitoring therapeutic responses of primary bone tumors by diffusion-weighted image: initial results. Eur Radiol 16:2637–2643
Kozlowski P, Chang SD, Jones EC, Berean KW, Chen H, Goldenberg SL (2006) Combined diffusion-weighted and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI for prostate cancer diagnosis-correlation with biopsy and histopathology. J Magn Reson Imaging 24:108–113
Rubesova E, Grell AS, De MV, Metens T, Chao SL, Lemort M (2006) Quantitative diffusion imaging in breast cancer: a clinical prospective study. J Magn Reson Imaging 24:319–324
Squillaci E, Manenti G, Cova M, Di RM, Miano R, Palmieri G, Simonetti G (2004) Correlation of diffusion-weighted MR imaging with cellularity of renal tumours. Anticancer Res 24:4175–4179
Kim T, Murakami T, Takahashi S, Hori M, Tsuda K, Nakamura H (1999) Diffusion-weighted single-shot echoplanar MR imaging for liver disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol 173:393–398
Issa B (2002) In vivo measurement of the apparent diffusion coefficient in normal and malignant prostatic tissues using echo-planar imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 16:196–200
Guo Y, Cai YQ, Cai ZL, Gao YG, An NY, Ma L, Mahankali S, Gao JH (2002) Differentiation of clinically benign and malignant breast lesions using diffusion-weighted imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 16:172–178
Guo AC, Cummings TJ, Dash RC, Provenzale JM (2002) Lymphomas and high-grade astrocytomas: comparison of water diffusibility and histologic characteristics. Radiology 224:177–183
Gauvain KM, McKinstry RC, Mukherjee P, Perry A, Neil JJ, Kaufman BA, Hayashi RJ (2001) Evaluating pediatric brain tumor cellularity with diffusion-tensor imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 177:449–454
de Bazelaire CM, Duhamel GD, Rofsky NM, Alsop DC (2004) MR imaging relaxation times of abdominal and pelvic tissues measured in vivo at 3.0 T: preliminary results. Radiology 230:652–659
Gold GE, Han E, Stainsby J, Wright G, Brittain J, Beaulieu C (2004) Musculoskeletal MRI at 3.0 T: relaxation times and image contrast. AJR Am J Roentgenol 183:343–351
Träber F, Block W, Layer G, Braucker G, Gieseke J, Kretzer S, Hasan I, Schild HH (1996) Determination of 1H relaxation times of water in human bone marrow by fat-suppressed turbo spin echo in comparison to MR spectroscopic methods. J Magn Reson Imaging 6:541–548
Reeder SB, Wintersperger BJ, Dietrich O, Lanz T, Greiser A, Reiser MF, Glazer GM, Schoenberg SO (2005) Practical approaches to the evaluation of signal-to-noise ratio performance with parallel imaging: application with cardiac imaging and a 32-channel cardiac coil. Magn Reson Med 54:748–754
Nasu K, Kuroki Y, Sekiguchi R, Kazama T, Nakajima H (2006) Measurement of the apparent diffusion coefficient in the liver: is it a reliable index for hepatic disease diagnosis? Radiat Med 24:438–444
Nasu K, Kuroki Y, Sekiguchi R, Nawano S (2006) The effect of simultaneous use of respiratory triggering in diffusion-weighted imaging of the liver. Magn Reson Med Sci 5:129–136
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mürtz, P., Krautmacher, C., Träber, F. et al. Diffusion-weighted whole-body MR imaging with background body signal suppression: a feasibility study at 3.0 Tesla. Eur Radiol 17, 3031–3037 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-007-0717-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-007-0717-8