Abstract
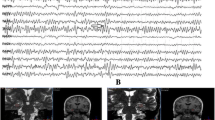
Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H MRS) is beneficial in the lateralization of the epileptogenic zone in temporal lobe epilepsy; however, its role in extratemporal and, especially, MRI-negative epilepsy has not been established. This study seeks to verify how 1H MRS could help in localizing the epileptogenic zone in patients with MRI-negative extratemporal epilepsy. Seven patients (8–23 years) with MRI-negative refractory focal epilepsy were studied using 1H MRS on a 1.5T MR system. Chemical shift imaging sequence in the transversal plane was directed towards the suspected epileptogenic zone localized by seizure semiology, scalp video/EEG, ictal SPECT and 18FDG-PET. Spectra were evaluated using the program CULICH, and the coefficient of asymmetry was used for quantitative lateralization. MRS detected lateralization in all patients and was able to localize pathology in five. The most frequent findings were decreased ratios of N-acetylaspartate to choline compounds characterized by increasing choline concentration. The localization of the 1H MRS abnormality correlated well with ictal SPECT and subdural mapping. In all cases, histopathological analysis revealed MRI-undetected focal cortical dysplasias. 1H MRS could be more sensitive for the detection of discrete malformations of cortical development than conventional MRI. It is valuable in the presurgical evaluation of patients without MRI-apparent lesions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garcia PA, Laxer KD, Ng T (1995) Application of spectroscopic imaging in epilepsy. Magn Reson Imaging 13:1181–1185
Zimmerman RA, Wang Z (1999) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Crit Rev Neurosurg 9:161–166
Bonavita S, Di Salle F, Tedeschi G (1999) Proton MRS in neurological disorders. Eur J Radiol 30:125–131
Ranjeva JP, Confort-Gouny S, Le Fur Y, Cozzone PJ (2000) Magnetic resonance spectroscopy of brain in epilepsy. Childs Nerv Syst 16:235–241
Cendes F, Caramanos Z, Andermann F, Dubeau F, Arnold DL (1997) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging and magnetic resonance imaging volumetry in the lateralization of temporal lobe epilepsy: a series of 100 patients. Ann Neurol 42:737–746
Hajek M, Dezortova M, Komarek V (1998) 1H MR spectroscopy in patients with mesial temporal epilepsy. Magn Reson Mater Phy 7:95–114
Hammen T, Stefan H, Eberhardt KE, W-Huk BH, Tomandl BF (2003) Clinical applications of 1H-MR spectroscopy in the evaluation of epilepsies-what do pathological spectra stand for with regard to current results and what answers do they give to common clinical questions concerning the treatment of epilepsies? Acta Neurol Scand 108:223–238
Hajek M, Komarek V, Dezortova M, Hlavnicka P, Smejkalova M, Faladova L, Hovorka J (1995) Determination of epileptogenic focus using 1H MR spectroscopy. (Cz) Ces Slov Neurol Neurochir 3:103–107
Hetherington HP, Pan JW, Spencer DD (2000) 1H and 31P spectroscopy and bioenergetics in the lateralization of seizures in temporal lobe epilepsy. J Magn Reson Imaging 16:477–483
Bernasconi A, Tasch E, Cendes F, Li LM, Arnold DL (2002) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging suggests progressive neuronal damage in human temporal lobe epilepsy. Prog Brain Res 135:297–304
Klose U, Jiru F (2005) Principles of MR spectroscopy and chemical shift imaging. In: Landini L (ed) Advanced image processing in magnetic resonance imaging (signal processing and communications). CRC, Boca Raton, pp 369–409
Garcia PA, Laxer KD, van der Grond J, Hugg JW, Matson GB, Weiner MW (1995) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging in patients with frontal lobe epilepsy. Ann Neurol 37:279–281
Stanley JA, Cendes F, Dubeau F, Andermann F, Arnold DL (1998) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging in patients with extratemporal epilepsy. Epilepsia 39:267–273
Lundbom N, Gaily E, Vuori K, Paetau R, Liukkonen E, Rajapakse JC, Valanne L, Hakkinen AM, Granstrom ML (2001) Proton spectroscopic imaging shows abnormalities in glial and neuronal cell pools in frontal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 42:1507–1514
Guye M, Ranjeva JP, Le Fur Y, Bartolomei F, Confort-Gouny S, Regis J, Chauvel P, Cozzone PJ (2005) 1H-MRS imaging in intractable epilepsies characterized by depth electrode recording. Neuroimage 26:1174–1183
Jiru F, Skoch A, Hajek M (2003) LCModel for quantitative single voxel spectroscopy and spectroscopic imaging: a comparison. Magn Reson Mater Phy 16 (Suppl 1):S211. Abstract
Jiru F, Skoch A, Klose U, Grodd W, Hajek M (2006) Error images for spectroscopic imaging by LCModel using Cramer-Rao bounds. Magn Reson Mater Phy 19:1–14
Jiru F, Dezortova M, Burian M, Hajek M (2003) The role of relaxation time corrections for the evaluation of long and short echo time 1H MR spectra of the hippocampus by NUMARIS and LCModel techniques. Magn Reson Mater Phy 16:135–143
Palmini A, Najm I, Avanzini G, Babb T, Guerrini R, Foldvary-Schaefer N et al (2004) Terminology and classification of the cortical dysplasias. Neurology 62 (Suppl 3):S2–S8
Nagae-Poetscher LM, Bonekamp D, Barker PB, Brant LJ, Kaufmann WE, Horska A (2004) Asymmetry and gender effect in functionally lateralized cortical regions: a proton MRS imaging study. J Magn Reson Imaging 19:27–33
Siegel AM, Jobst BC, Thadani VM, Rhodes CH, Lewis PJ, Roberts DW, Williamson PD (2000) Medically intractable, localization-related epilepsy with normal MRI: presurgical evaluation and surgical outcome in 43 patients. Epilepsia 42:883–888
Chapman K, Wyllie E, Najm I, Ruggieri P, Bingaman W, Lüders J, Kotagal P, Lachhwani D, Dinner D, Lüders HO (2005) Seizure outcome after epilepsy surgery in patients with normal preoperative MRI. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76:710–713
Blume WT, Ganapathy GR, Munoz D, Lee DH (2004) Indices of resective surgery effectiveness for intractable nonlesional focal epilepsy. Epilepsia 45:46–53
Tassi L, Colombo N, Garbelli R, Francione S, Lo Russo G, Mai R et al (2002) Focal cortical dysplasia: neuropathological subtypes, EEG, neuroimaging and surgical outcome. Brain 125:1719–1732
Bernasconi A (2003) Advanced MRI analysis methods for detection of focal cortical dysplasia. Epileptic Disord 5:81–84
Kuzniecky R, Hetherington H, Pan J, Hugg J, Palmer C, Gilliam F et al (1997) Proton spectroscopic imaging at 4.1 Tesla in patients with malformations of cortical development and epilepsy. Neurology 48:1018–1024
Li LM, Cendes F, Bastos AC, Andermann F, Dubeau F, Arnold DL (1998) Neuronal metabolic dysfunction in patients with cortical developmental malformations: a proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging study. Neurology 50:755–759
Kaminaga T, Kobayashi M, Abe T (2001) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in disturbances of cortical development. Neuroradiology 43:575–580
Simone IL, Federico F, Tortorella C, De Blasi R, Bellomo R, Lucivero V et al (1999) Metabolic changes in neuronal migration disorders: evaluation by combined MRI and proton MR spectroscopy. Epilepsia 40:872–879
Woermann FG, McLean MA, Bartlett PA, Barker GJ, Duncan JS (2001) Quantitative short echo time proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging study of malformations of cortical development causing epilepsy. Brain 124:427–436
Palmini A, Andermann F, Olivier A, Tampieri D, Robitaille Y, Andermann E, Wright G (1991) Focal neuronal migration disorders and intractable partial epilepsy: a study of 30 patients. Ann Neurol 30:741–749
Sisodiya SM (2004) Surgery for focal cortical dysplasia. Brain 127:2383–2384
Urbach H (2005) Imaging of the epilepsies. Eur Radiol 15(3):494–500
Duncan JS (2002) Neuroimaging methods to evaluate the etiology and consequences of epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 50:131–140
Henry TR, Van Heertum RL (2003) Positron emission tomography and single photon emission computed tomography in epilepsy care. Semin Nucl Med 33:88–104
Petroff OAC, Errante LD, Kim JH (2003) N-acetyl-aspartate, total creatine, and myo-inositol in the epileptogenic human hippocampus. Neurology 60:1646–1651
Boulanger Y, Labell M, Khiat A (2000) Role of phospholipase A2 on the variation of the choline signal intensity observed by 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy in brain diseases. Brain Res Rev 33:380–389
Yegin A, Akbas SH, Ozben T, Korgun DK (2002) Secretory phospholipase A2 and phospholipids in neural membranes in an experimental epilepsy model. Acta Neurol Scand 106:258–262
Lawson JA, Birchansky S, Pacheco E, Jayakar P, Resnick TJ, Dean P, Duchowny MS (2005) Distinct clinicopathologic subtypes of cortical dysplasia of Taylor. Neurology 64:55–61
Colombo N, Citterio A, Galli C, Tassi L, Lo Russo G, Scialfa G, Spreafico R (2003) Neuroimaging of focal cortical dysplasia: neuropathological correlations. Epileptic Disord 5 (Suppl 2):S67–72
Acknowledgements
Supported by grants from the Grant Agency of Czech Republic, no. 309/02/D076, Internal Grant Agency of Ministry of Health, Czech Republic, no. NF/7411-3 and NR/8843-4, Ministry of Education, Youth and Sport, Czech Republic LC554, and research projects no. 00000064203-4, 111300003, 111300004 and MZO 00023001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Pavel Krsek and Milan Hajek contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krsek, P., Hajek, M., Dezortova, M. et al. 1H MR spectroscopic imaging in patients with MRI-negative extratemporal epilepsy: correlation with ictal onset zone and histopathology. Eur Radiol 17, 2126–2135 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-007-0594-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-007-0594-1