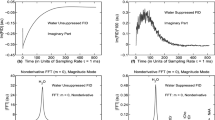
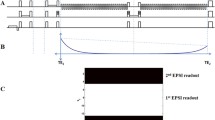
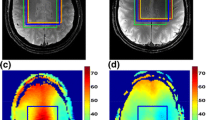
Abstract
1H MR spectroscopy is routinely used for lateralization of epileptogenic lesions. The present study deals with the role of relaxation time corrections for the quantitative evaluation of long (TE=135 ms) and short echo time (TE=10 ms) 1H MR spectra of the hippocampus using two methods (operator-guided NUMARIS and LCModel programs). Spectra of left and right hippocampi of 14 volunteers and 14 patients with epilepsy were obtained by PRESS (TR/TE=5000/135 ms) and STEAM (TR/TE=5000/10 ms) sequences with a 1.5-T imager. Evaluation was carried out using Siemens NUMARIS software and the results were compared with data from LCModel processing software. No significant differences between the two methods of processing spectra with TE=135 ms were found. The range of relaxation corrections was determined. Metabolite concentrations in hippocampi calculated from spectra with TE=135 ms and 10 ms after application of correction coefficients did not differ in the range of errors and agreed with published data (135 ms/10 ms: NAA=10.2±0.6/10.4±1.3 mM, Cho=2.4±0.1/2.7±0.3 mM, Cr=12.2±1.3/11.3±1.3 mM). When relaxation time corrections were applied, quantitative results from short and long echo time evaluation with LCModel were in agreement. Signal intensity ratios obtained from long echo time spectra by NUMARIS operator-guided processing also agreed with the LCModel results.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rudkin TM, Arnold DL (2002) MR Spectroscopy and the biochemical basis of neurological disease. In: Scott W (ed) Atlas magnetic resonance imaging of the brain and spine. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 2021–2040
De Graff RA (1998) In vivo NMR spectroscopy. Wiley, Chichester
Michaelis T, Merboldt KD, Bruhn H, Hänicke W, Frahm J (1993) Absolute concentrations of metabolites in the adult human brain in vivo: Quantification of localized proton MR Spectra. Radiology 187:219–227
Henriksen O (1995) In vivo quantitation of metabolite concentrations in the brain by means of proton MRS. NMR Biomed 8:139–148
Henriksen O (1994) MR spectroscopy in clinical research. Acta Radiol 35(2):96–116
Del Sole A, Gambini A, Falini A, Lecchi M, Lucignani G (2002) In vivo neurochemistry with emission tomography and magnetic resonance spectroscopy: clinical applications. Eur Radiol 12(10):2582–2599
Michaelis T, Merboldt KD, Hänicke W, Gyngell ML, Bruhn H, Frahm J (1991) On the identification of cerebral metabolites in localized 1 h nmr spectra of human brain in vivo. NMR Biomed 4(2):90–98
Behar KL, Rothman DL, Spencer DD, Petrof OAC (1994) Analysis of macromolecule resonances in 1H NMR spectra of human brain. Magn Reson Med 32(3):294–302
Seeger U, Mader I, Nagele T, Grodd W, Lutz O, Klose U (2001) Reliable detection of macromolecules in single-volume 1H NMR spectra of the human brain. Magn Reson Med 45(6):948–954
Provencher SW (1993) Estimation of metabolite concentrations from localized in vivo proton NMR spectra. Magn Reson Med 30:672–679
de Beer R, van Ormondt D (1992) Analysis of NMR data using time domain fitting procedures. In: Diehl P, Fluck E, Günther H, Kosfeld R, Seelig J (eds) NMR 26, In-vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy. 1. Probeheads and radiofrequency pulses, spectrum analysis. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 201–259
Mierisova S, Ala-Korpela M (2001) MR spectroscopy quantitation: A review of frequency domain methods. NMR Biomed 14(4):247–259
Simister RJ, Woermann FG, McLean MA, Bartlett PA, Barker GJ, Duncan JS (2002) A short-echo-time proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging study of temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 43(9):1021–1031
Hájek M, Dezortová M, Komárek V (1998) 1H MR spectroscopy in patients with mesial temporal epilepsy. Magma 7:95–114
Meiners LC (2002) Role of MR imaging in epilepsy. Eur Radiol 12:499–501
Gadian DG, Connelly A, Duncan JS, Cross JH, Kirkham FJ, Johnson CL, Vargha-Khadem F, Nevile BG, Jackson GD (1994) 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the investigation of intractable epilepsy. Acta Neurol Scand, Suppl 152:116–121
Ng TC, Comair YG, Xue M, So N, Majors A, Kolem H, Luders H, Modic M (1994) Temporal lobe epilepsy: Presurgical localization with proton chemical shift imaging. Radiology 193:465–472
Cendes F, Andermann F, Preul MC, Arnold DL (1994) Lateralization of temporal lobe epilepsy based on regional metabolic abnormalities in proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic images. Ann Neurol 35(2):211–216
Jírů F, Dezortová M, Burian M, Hájek M (1999) Calculation of metabolite concentrations in hippocampus from spectra measured with TE=10 and 135 ms. Magma 8 Suppl 1:235–236
Kreis R (1997) Quantitative localized 1H MR spectroscopy for clinical use. Prog Nucl Mag Res Sp 31:155–195
Hájek M (1995) Quantitative NMR spectroscopy. Comments on methodology of in vivo MR spectroscopy in medicine. Quart Magn Res Biol Med 3:165–193
Hájek M, Burian M, Dezortová M (2000) Application of LCModel for quality control and quantitative in vivo 1H MR spectroscopy by short echo time STEAM sequence. Magma 10:6–17
Christiansen P, Toft P, Larsson HBW, Stubgaard M, Henriksen O (1993) The concentration of N-acetyl aspartate, creatine + phosphocreatine, and choline in different parts of the brain in adulthood and senium. Magn Reson Imaging 11:799–806
Elster C, Link A, Schubert F, Seifert F, Walzel M, Rinneberg H (2000) Quantitative MRS: comparison of time domain and time domain frequency domain methods using a novel test procedure. Magn Reson Imaging 18(5):597–606
Auer DP, Gossl C, Schirmer T, Czisch M (2001) Improved analysis of 1H-MR spectra in the presence of mobile lipids. Magn Reson Med 46(3):615–618
Seeger U, Klose U, Mader I, Grodd W, Nagele T (2003) Parameterized evaluation of macromolecules and lipids in proton MR spectroscopy of brain diseases. Magn Reson Med 49(1):19–28
Hofmann L, Slotboom J, Jung B, Maloca P, Boesch C, Kreis R (2002) Quantitative 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy of human brain: Influence of composition and parameterization of the basis set in linear combination model-fitting. Magn Reson Med 48(3):440–453
Helms G (2001) Volume correction for edema in single-volume proton MR spectroscopy of contrast-enhancing multiple sclerosis lesions. Magn Reson Med 46(2):256–263
Alger JR, Symko SC, Bizzi A, Posse S, DesPres DJ, Armstrong MR (1993) Absolute quantitation of short TE brain 1H-MR spectra and spectroscopic imaging data. J Comput Assist Tomogr 17(2):191–199
Leary SM, Brex PA, MacManus DG, Parker GJ, Barker GJ, Miller DH, Thompson AJ (2000) A (1)H magnetic resonance spectroscopy study of aging in parietal white matter: implications for trials in multiple sclerosis. Magn Reson Imaging 18(4):455–459
Ala-Korpela M, Usenius JP, Keisala J, van den Boogaart A, Vainio P, Jokisaari J, Soimakallio S, Kauppinen R (1995) Quantification of metabolites from single-voxel in vivo 1H NMR data of normal human brain by means of time-domain data analysis. Magma 3:129–136
Isobe T, Matsumura A, Anno I, Yoshizawa T, Nagatomo Y, Itai Y, Nose T (2002) Quantification of cerebral metabolites in glioma patients with proton MR spectroscopy using T2 relaxation time correction. Magn Reson Imaging 20(4):343–349
Mascalchi M, Brugnoli R, Guerrini L, Belli G, Nistri M, Politi LS, Gavazzi C, Lolli F, Argenti G, Villari N (2002) Single-voxel long TE 1H-MR spectroscopy of the normal brainstem and cerebellum. J Magn Reson Imaging 16(5):532–537
Barker PB, Hearshen DO, Boska MD (2001) Single-voxel proton MRS of the human brain at 1.5T and 3.0T. Magn Reson Med 45(5):765–769
Chong VF, Rumpel H, Fan YF, Mukherji SK (2001) Temporal lobe changes following radiation therapy: Imaging and proton MR spectroscopic findings. Eur Radiol 11(2):317-324
Choi CG, Frahm J (1999) Localized proton MRS of the human hippocampus: metabolite concentrations and relaxation times. Magn Reson Med 41:204–207
Longo R, Bampo A, Vidimari R, Magnaldi S, Giorgini A (1995) Absolute quantitation of brain 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectra. Comparison of different approaches. Invest Radiol 30:199–203
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by grants CEZ:L17/98:00023001, IGA MZ CR: NF/7411–3 and NF/6794-3, and MSMT: LN00B122 and LN00A065, Czech Republic.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jírů, F., Dezortová, M., Burian, M. et al. The role of relaxation time corrections for the evaluation of long and short echo time 1H MR spectra of the hippocampus by NUMARIS and LCModel techniques. Magn Reson Mater Phy 16, 135–143 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-003-0018-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-003-0018-4