Abstract
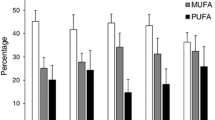
Food supply for deposit feeders varies from highly seasonal phytodetritus to a steady source of older organic matter, resulting in contrasting patterns of nutrient uptake and storage. To identify patterns in energy storage and feeding behaviour driven by different food conditions for the circumpolar deposit-feeding protobranch bivalve Yoldia hyperborea, we measured variations in cytological (digestive cell height) and biochemical (lipid class, fatty acid, glycogen, and protein content) components during controlled experiments. Three treatments with organisms in sediment with high refractory organic matter (12 % OM) were exposed to different feeding regimes resembling (a) the annual spring bloom settlement, (b) low food availability during winter, and (c) sporadic resuspension events. Yoldia exposed to a diatom-supplemented diet showed significantly higher mean values for digestive cell height (28.44 μm), glycogen (30.4 mg g−1 dry mass, DM), diatom-specific fatty acids, and total lipid (TL) levels (14.4 mg g−1 DM), but lower protein concentrations, than in non-supplemented treatments (digestive cell height 20.34 μm; glycogen 9.23 mg g−1 DM; TL 6.7 mg g−1 DM). All analyses showed no effect of resuspension events; thus, it was unlikely that resuspension improved sediment nutritional value. In the absence of recently deposited diatoms, Y. hyperborea did not increase nutrient storage, suggesting that significant amounts of older refractory OM are not used for growth or reproduction. The rapid storage of nutrients derived from diatoms demonstrates the role of seasonal episodic events of settling algae in the nutrition of subpolar Y. hyperborea and in the transfer of energy from the water column to the benthos.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AMPL:
-
Acetone-mobile polar lipids
- BAFA:
-
Bacterial fatty acids
- C/N:
-
Carbon-to-nitrogen ratio
- DM:
-
Dry mass
- FAME:
-
Fatty acid methyl esters
- MUFA:
-
Monounsaturated fatty acids
- PUFA:
-
Polyunsaturated fatty acids
- OC:
-
Organic carbon
- ON:
-
Organic nitrogen
- SAFA:
-
Saturated fatty acids
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- TAG:
-
Triacylglycerol
- TFA:
-
Total fatty acid
- TL:
-
Total lipid
References
Allen WV (1976) Biochemical aspects of lipid storage and utilization in animals. Am Zool 16:631–647
Ansell AD (1974) Seasonal changes in biochemical composition of the bivalve Nucula sulcata from the Clyde Sea area. Mar Biol 25:101–108
Barnes H, Heath JR (1966) The extraction of glycogen from marine invertebrate tissues. Helgol wiss Meeresunters 13:115–117
Beninger PG, Lucas A (1984) Seasonal variations in condition, reproductive activity and gross biochemical composition of two species of adult clam reared in a common habitat: Tapes decussatus (Jeffreys) and Tapes philippinarum (Adam & Reeve). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 79:19–37
Bodennec G, Arzul G, Erard-Le Denn E, Gentien P (1994) Gymnodinium sp. Dans l’étang de Diane (Corse), septembre–octobre 1993. Test biologiques et chimiques. Edition de l’IFREMER. Direction Environment et Aménagement Littoral, R INT DEL 94.07
Boon AR, Duineveld GCA, Berghuis EM, van der Weele JA (1998) Relationships between benthic activity and the annual phytopigment cycle in near-bottom water and sediments in the southern North Sea. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 46:1–13
Byrén L, Ejdung G, Elmgren R (2006) Uptake of sedimentary organic matter by the deposit-feeding Baltic amphipods Monoporeia affinis and Pontoporeia femorata. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 313:135–143
Cammen LM (1989) The relationship between ingestion rate of deposit feeders and sediment nutritional value. In: Lopez GR, Taghon GL, Levinton JS (eds) Ecology of marine deposit feeders. Lecture Notes on Coastal and Estuarine Studies No 31. Springer, New York, pp 201–222
Charles F, Amouroux JM, Grémare A (1999) Comparative study of the utilization of bacteria and microalgae by the suspension-feeding bivalve: Callista chione. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 79:577–584
Cheng I-J, Levinton JS, McCartney M, Martinez D, Weissburg MJ (1993) A bioassay approach to seasonal variation in the nutritional value of sediment. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 94:275–285
Dalsgaard J, St John M, Kattner G, Müller-Navarra D, Hagen W (2003) Fatty acid trophic markers in the pelagic marine environment. Adv Mar Biol 46:225–340
Davis JP, Wilson J (1983) Seasonal changes in tissue weight and biochemical composition of the bivalve Nucula turgida in Dublin Bay with reference to gametogenesis. Neth J Sea Res 17:84–95
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
Emmett B, Thompson K, Popham J (1987) The reproductive and energy storage cycles of two populations of Mytilus edulis (Linné) from British Columbia. J Shellfish Res 6:29–36
Fernández-Reiriz MJ, Pérez-Camacho A, Delgado M, Labarta U (2007) Dynamics of biochemical components, lipid classes and energy values on gonadal development of R. philippinarum associated with the temperature and ingestion rate. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 147:1053–1059
Forbes TL, Lopez GR (1990) The effect of food concentration, body size and environmental oxygen tension on the growth of the deposit-feeding polychaete Capitella species I. Limnol Oceanogr 35:1535–1544
Gabbott PA (1983) Developmental and seasonal metabolic activities in marine molluscs. In: Hochachka PW (ed) The Mollusca. Academic Press, New York, pp 165–217
Garstecki T, Wickham SA, Arndt H (2002) Effects of experimental sediment resuspension on a coastal planktonic microbial food web. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 55:751–762
Gnaiger E, Bitterlich G (1984) Proximate composition and caloric content calculations from elemental CHN analysis: a stoichiometric concept. Oecologia 62:289–298
Gontikaki E, van Oevelen D, Soetaert K, Witte U (2011) Food web flows through a sub-arctic deep-sea benthic community. Prog Oceanogr 91:245–259
Gontikaki E, Polymenakou PN, Thornton B, Narayanaswamy BE, Black K, Tselepides A, Witte U (2012) Microbial response to organic matter enrichment in the oligotrophic Levantine Basin (Eastern Mediterranean). Geomicrobiol J 29:648–655
Graeve M, Kattner G, Piepenburg D (1997) Lipids in Arctic benthos: does the fatty acid and alcohol composition reflect feeding and trophic interactions? Polar Biol 18:56–61
Grant J, Cranford P, Emerson C (1997) Sediment resuspension rates, organic-matter quality and food utilization by sea scallops (Placopecten magellanicus) on Georges Bank. J Mar Res 55:965–994
Grémare A, Amouroux JM, Charles F, Dinet A, Riaux-Gobin C, Baudart J, Medernach L, Bodiou JY, Vétion G, Colomines JC, Albert P (1997) Temporal changes in the biochemical composition and nutritional value of the particulate organic-matter available to surface deposit feeders: a 2-year study. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 150:195–206
Hall JM, Parrish CC, Thompson RJ (2002) Eicosapentaenoic acid regulates scallop (Placopecten magellanicus) membrane fluidity in response to cold. Biol Bull 202:201–203
Heip CHR, Goosen NK, Herman PMJ, Kromkamp K, Middelburg JJ, Soetaert K (1995) Production and consumption of biological particles in temperate tidal estuaries. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 33:1–149
Holm-Hansen O, Riemann B (1978) Chlorophyll a determination: improvements in methodology. Oikos 30:438–447
Ibarrola I, Etxeberria M, Iglesias JIP, Urrutia MB, Angulo E (2000a) Acute and acclimated digestive responses of the cockle Cerastoderma edule (L.) to changes in the food quality and quantity II. Enzymatic, cellular and tissular responses of the digestive gland. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 252:199–219
Ibarrola I, Navarro E, Urrutia MB (2000b) Acute and acclimated digestive responses of the cockle Cerastoderma edule (L.) to changes in food quality and quantity I. Feeding and absorption of biochemical components. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 252:181–198
Jaramillo JR, Thompson RJ (2008) The reproductive response of the protobranch bivalve Yoldia hyperborea to an intermittent influx of phytodetritus. An experimental approach. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 357:57–63
Jumars PA, Mayer LM, Deming J, Baross J, Wheatcroft RA (1990) Deep-sea deposit-feeding strategies suggested by environmental and feeding constraints. Philos Trans R Soc Lond A 331:85–101
Laursen AK, Mayer LM, Townsend DW (1996) Liability of proteinaceous material in estuarine seston and subcellular fractions of phytoplankton. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 136:227–234
Legendre L, Michaud J (1999) Chlorophyll a to estimate the particulate organic carbon available as food to large zooplankton in the euphotic zone of oceans. J Plankton Res 21:2067–2083
Legezynska J, Kedra M, Walkusz W (2012) When season does not matter: summer and winter trophic ecology of Arctic amphipods. Hydrobiologia 684:189–214
Linton DL, Taghon GL (2000a) Feeding, growth, and fecundity of Abarenicola pacifica in relation to sediment organic concentration. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 254:85–107
Linton DL, Taghon GL (2000b) Feeding, growth, and fecundity of Capitella sp. I in relation to sediment organic concentration. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 205:229–240
Lowe DM, Moore MN (1985) Cytological and cytochemical procedures. In: Bayne BL (ed) The effects of stress and pollution on marine animals. Praeger, New York, pp 179–204
MacIntyre HL, Geider RJ, Miller DC (1996) Microphytobenthos: the ecological role of the “secret garden” of unvegetated, shallow-water marine habitats. 1. Distribution, abundance and primary production. Estuaries 19:186–201
Mayer LM, Rice DL (1992) Early diagenesis of protein—a seasonal study. Limnol Oceanogr 37:280–295
Middelburg JJ, Barranguet C, Boschker HTS, Herman PMJ, Moens T, Heip CHR (2000) The fate of intertidal microphytobenthos carbon: an in situ C13-labeling study. Limnol Oceanogr 45:1224–1234
Morris L, Keough MJ (2003) Variation in the response of intertidal infaunal invertebrates to nutrient additions: field manipulations at two sites within Port Phillip Bay, Australia. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 250:35–49
Morton B (1983) Feeding and digestion in Bivalvia. In: Saleuddin ASM, Wilbur KM (eds) The Mollusca, vol 5; physiology, part 2. Academic Press, New York, pp 65–147
Murphy KJ, Mooney BD, Mann NJ, Nichols PD, Sinclair AJ (2002) Lipid, FA, and sterol composition of New Zealand green lipped mussel (Perna canaliculus) and Tasmanian blue mussel (Mytilus edulis). Lipids 37:587–595
Napolitano GE, Ackman RG (1992) Anatomical distributions and temporal variations of lipid classes in sea scallops Placopecten magellanicus (Gmelin) from Georges Bank (Nova Scotia). Comp Biochem Physiol B: Biochem Mol Biol 103:645–650
Oeckelmann KW (1958) Marine Lamellibranchiata. Meddelelser om Gronland 122:1–256
Owen G (1973) The fine structure and histochemistry of the digestive diverticula of the protobranchiate bivalve Nucula sulcata. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 183:249–264
Owen G (1974) Feeding and digestion in the Bivalvia. Adv Comp Physiol Biochem 5:1–35
Parrish CC (1987) Separation of aquatic lipid classes by chromarod thin-layer chromatography with measurement by latroscan flame ionization detection. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 44:722–731
Parrish CC (1998) Determination of total lipid, lipid classes and fatty acids in aquatic samples. In: Arts MT, Wainman BC (eds) Lipids in freshwater ecosystems. Springer, New York, pp 4–20
Parrish C (2009) Essential fatty acids in aquatic food webs. In: Kainz M, Brett MT, Arts MT (eds) Lipids in aquatic ecosystems. Springer, New York, pp 309–326
Parrish CC, Yang Z, Lau A, Thompson RJ (1996) Lipid composition of Yoldia hyperborea (Protobranchia), Nephtys ciliata (Nephthyidae) and Artacama proboscidea (Terebellidae) living at sub-zero temperatures. Comp Biochem Physiol B: Biochem Mol Biol 114:59–67
Parrish CC, Wells JS, Yang Z, Dabinett P (1998) Growth and lipid composition of scallop juveniles, Placopecten magellanicus, fed the flagellate Isochrysis galbana with varying lipid composition and the diatom Chaetoceros muelleri. Mar Biol 133:461–471
Parrish CC, Abrajano TA, Budge SM, Helleur RJ, Hudson ED, Pulchan K, Ramos C (2000) Lipid and phenolic biomarkers in marine ecosystems: analysis and applications. In: Wangersky P (ed) The handbook of environmental chemistry, vol 5D. Springer, Berlin, pp 193–223
Parrish CC, Thompson RJ, Deibel D (2005) Lipid classes and fatty acids in plankton and settling matter during the spring bloom in a cold ocean coastal environment. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 286:57–68
Parrish CC, Deibel D, Thompson RJ (2009) Effect of sinking spring phytoplankton blooms on lipid content and composition in suprabenthic and benthic invertebrates in a cold ocean coastal environment. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 391:33–51
Peck LS, Morris DJ, Clarke A, Holmes LJ (1986) Oxygen consumption and nitrogen excretion in the Antarctic brachiopod Liothyrella uva (Jackson, 1912) under simulated winter conditions. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 104:203–213
Phillips NW (1984) Role of different microbes and substrates as potential suppliers of specific, essential nutrients to marine detritivores. Bull Mar Sci 35:283–298
Porter ET, Mason RP, Sanford LP (2010) Effect of tidal resuspension on benthic-pelagic coupling in an experimental ecosystem study. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 413:33–53
Pusceddu A, Fiordelmondo C, Danovaro R (2005) Sediment resuspension effects on the benthic microbial loop in experimental microcosms. Microb Ecol 50:602–613
Ramskov T, Forbes VE (2008) Life history and population dynamics of the opportunistic polychaete Capitella sp. I in relation to sediment organic matter. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 369:181–192
Rice D, Rhoads DC (1989) Early diagenesis of organic matter and the nutritional value of sediment. In: Lopez GR, Taghon GL, Levinton JS (eds) Ecology of marine deposit feeders. Lecture Notes on Coastal and Estuarine Studies No 31. Springer, New York, pp 60–97
Sargent JR, Parkes RJ, Mueller-Harvey I, Henderson RJ (1987) Lipid biomarkers in marine ecology. In: Sleigh MA (ed) Microbes in the sea. Ellis Horwood Ltd., Chichester, pp 119–138
Schratzberger M, Forster RM, Goodsir F, Jennings S (2008) Nematode community dynamics over an annual production cycle in the central North Sea. Mar Environ Res 66:508–519
Stead RA, Thompson RJ (2003) The effect of the sinking spring diatom bloom on digestive processes of the cold-water protobranch Yoldia hyperborea. Limnol Oceanogr 48:157–167
Stead RA, Thompson RJ (2006) The influence of an intermittent food supply on the feeding behaviour of Yoldia hyperborea (Bivalvia: Nuculanidae). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 332:37–48
Stead RA, Thompson RJ, Jaramillo JR (2003) Absorption efficiency, ingestion rate, gut passage time and scope for growth in suspension- and deposit-feeding Yoldia hyperborea. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 252:159–172
Sun MY, Carroll ML, Ambrose WG, Clough LM, Zou L, Lopez GR (2007) Rapid consumption of phytoplankton and ice algae by Arctic soft-sediment benthic communities: evidence using natural and C-13-labeled food materials. J Mar Res 65:561–588
Thompson RJ, MacDonald BA (1990) The role of environmental conditions in the seasonal synthesis and utilisation of biochemical energy reserves in the giant scallop, Placopecten magellanicus. Can J Zool 68:750–756
Thompson RJ, Ratcliffe NA, Bayne BL (1974) Effects of starvation on structure and function in the digestive gland of the mussel (Mytilus edulis L.). J Mar Biol Assoc UK 54:699–712
Thompson RJ, Deibel D, Redden AM, McKenzie CH (2008) Vertical flux and fate of particulate matter in a Newfoundland fjord at sub-zero water temperatures during spring. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 357:33–49
Venturini N, Pires-Vanin AMS, Salhi M, Bessonart M, Muniz P (2011) Polychaete response to fresh food supply at organically enriched coastal sites: repercussion on bioturbation potential and trophic structure. J Mar Syst 88:526–541
Wassmann P (1991) Dynamics of primary production and sedimentation in shallow fjords and polls of western Norway. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 29:87–154
Wlodarska-Kowalczuk M (2007) Molluscs in Kongsfjorden (Spitsbergen, Svalbard): a species list and patterns of distribution and diversity. Polar Res 26:48–63
Zimmerman AR, Canuel EA (2001) Bulk organic matter and lipid biomarker composition of Chesapeake Bay surficial sediments as indicators of environmental processes. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 53:319–341
Acknowledgments
We thank the crew of the RV ‘Karl and Jackie’ for their help during the collection of specimens, and J. Deveraux, D. Au, and D. Whitten for their technical assistance with the refrigerated holding tanks. We thank P. Snelgrove, D. Deibel, and G. Lopez for their valuable input during discussion and C.C. Parrish for help with the lipid analyses. This work was funded by an NSERC Research grant (to R.J.T.), an NSERC collaborative grant (to R.J.T. et al.), and CIDA/MUN scholarships (to R.A.S. and S.V.P.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stead, R.A., Richoux, N.B., Pereda, S.V. et al. Influence of an intermittent food supply on energy storage by the subpolar deposit feeder Yoldia hyperborea (Bivalvia: Nuculanidae). Polar Biol 36, 1333–1345 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-013-1353-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-013-1353-1