Abstract
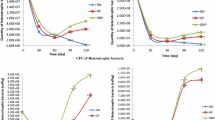
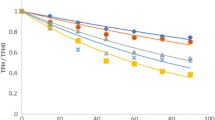
Ornithogenic soils that form in penguin rookeries contain high levels of organic carbon and nitrogen. On Seabee Hook, Cape Hallett, Antartica, ornithogenic soil was contaminated with hydrocarbons following establishment of a scientific research station. In these soils hydrocarbon biodegradation could be supported by available soil nitrogen. Hexadecane mineralization activity was detected in vitro in ornithogenic soil when incubated at 5 or 15°C. At 5°C the extent of hexadecane mineralization was higher in hydrocarbon-contaminated soil than in uncontaminated soil. Alkane-degrading bacteria isolated from Seabee Hook soil were identified as Rhodococcus or Gordonia spp. or an unclassified Corynebacterineae. The alkane degraders grew on n-alkanes from heptane (C8) to eicosane (C20) and pristane, and utilized uric acid or ammonium nitrate as nitrogen source. All of the isolates possessed urease activity. Results of this study indicate biodegradation of hydrocarbons may contribute to the natural attenuation of oil spills in ornithogenic surface soils in summer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aislabie J, McLeod M, Fraser R (1998) Potential for biodegradation of hydrocarbons in soil from the Ross Dependency, Antarctica. Appl. Microbiol Biotech 49:210–214. doi: 10.1007/s002530051160
Aislabie J, Fraser R, Duncan S, Farrell RL (2001) Effects of oil spills on microbial heterotrophs in Antarctic soils. Polar Biol 24:308–313. doi: 10.1007/s003000000210
Aislabie JM, Balks MR, Foght JM, Waterhouse EJ (2004) Hydrocarbon spills on Antarctic soils: effects and management. Environ Sci Tech 38:1265–1274. doi: 10.1021/es0305149
Aislabie J, Saul DJ, Foght JM (2006) Bioremediation of hydrocarbon-contaminated polar soils. Extremophiles 10:171–179. doi:10.1007/s00792-005-0498-4
Atlas RM (1979) Measurement of hydrocarbon biodegradation potentials and enumeration of hydrocarbon-utilizing microorganisms using carbon-14 hydrocarbon-spiked crude oil. In: Costerton JW, Colwell RR (eds.) Native aquatic bacteria: enumeration, activity, and ecology. ASTM STP 695. American Society for Testing and Materials, pp 196–204
Bej AK, Saul DJ, Aislabie J (2000) Cold tolerance of alkane-degrading bacteria isolated from soil near Scott Base, Antarctica. Polar Biol 23:100–105. doi: 10.1007/s003000050014
Blakemore LC, Searle PL, Daly BK (1987) Methods for chemical analysis of soils. New Zealand Soil Bureau Scientific Report 80, Wellington
Brosius J, Dull TL, Sleeter DD, Noller HF (1981) Gene organisation and primary structure of a ribosomal RNA operon from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol 148:107–127. doi: 10.1016/00222836(81)90508–8
Campbell IB, Claridge GGC (1987) Antarctica: soils, weathering processes and environment. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Delille D (2000) Response of Antarctic soil bacterial assemblages to contamination by diesel fuel and crude oil. Micro Ecol 40:159–168. doi: 10.1007/s002480000027
Delille D, Pelletier E, Delille B, Coulon F (2003) Effects of nutrient enrichments on the bacterial assemblage of Antarctic soils contaminated by diesel or crude oil. Polar Rec 39:1–10. doi: 10.1017/S0032247402002863
Duphorn K (1981) Physiographical and glaciogeological observations in northern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Geol Jahr B41:89–109
Eriksson M, Ka J-O, Mohn WW (2001) Effects of low temperature and freeze-thaw cycles on hydrocarbon biodegradation in Arctic tundra soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:5107–5112. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.11.5107–5112.2001
Ferguson SH, Franzmann PD, Revill AT, Snape I, Rayner JL (2003) The effects of nitrogen and water on mineralization of hydrocarbons in diesel-contaminated terrestrial Antarctic soils. Cold Reg Sci Tech 37:197–212. doi: 10.1016/S0165-232X(03)00041-7
Foght J, Aislabie J, Turner S, Brown CE, Ryburn J, Saul DJ, Lawson W (2004) Culturable bacteria in subglacial sediment and ice from two Southern Hemisphere glaciers. Microb Ecol 47:329–340. doi: 10.1007/s00248-003-1036-5
Gilmore WY (2001) United States Antarctic program environmental assessment and remediation. Environmental site assessment, Hallett Station, Cape Hallett, Antarctica
Goodfellow M, Maldonado LA (2006) The families Dietziaceae, Gordoniaceae, Nocardiaceae and Tsukamurellaceae. Prokaryotes 3:843–888. doi: 10.1007/0-387-30743-5_32
Guthridge GG (1983) Hallett Station, Antarctica, 1956–1973. Ant J US 18(4):1–8
Hofstee EH, Balks MR, Campbell DI (2006a) Soils of Seabee Hook, Cape Hallett, Northern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Ant Sci 18:473–486. doi: 1017/S0954102006000526
Hofstee EH, Campbell DI, Balks MR, Aislabie J (2006b) Groundwater characteristics at Seabee Hook, Cape Hallett, Antarctica. Ant Sci 18:487–495. doi: 1017/S0954102006000538
Kennicutt MC, Sweet ST, Fraser WR, Stackton WL, Culver M (1991) Grounding of the Bahia Paraiso at Arthur Harbor, Antarctica. Distribution and fate of oil spill related hydrocarbons. Environ Sci Technol 24:620–624
Koren O, Knezevic V, Ron EZ, Rosenberg E (2003) Petroleum pollution bioremediation using water-insoluble uric acid as the nitrogen source. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:6337–6339. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.10.6337-6339.2003
Ruberto LAM, Vazquez S, Lobalbo A, MacCormack WP (2005) Psychrotolerant hydrocarbon-degrading Rhodococcus strains isolated from polluted Antarctic soils. Ant Sci 17:47–56. doi: 1017/S0954102005002415
Saul DJ, Aislabie JM, Brown CE, Harris L, Foght JM (2005) Hydrocarbon contamination changes the bacterial diversity of soil from around Scott Base, Antarctica. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 53:141–155. doi:10.1016/j.femsec.2004.11.007
Sparling G, Dragten R, Aislabie J, Fraser R (1998) Atrazine mineralization in New Zealand topsoils and subsoils: influence of edaphic factors and numbers of atrazine-degrading microbes. Aust J Soil Res 36:557–570. doi: 10.1071/SR97065
Speir TW, Cowling JC (1984) Ornithogenic soils of the cape bird adelie penguin rookeries, Antarctica. Polar Biol 2:199–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00263625
US EPA (1987) Testing methods for evaluating soil waste: physical/chemical methods, 3rd edn. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response, Washington
Whyte LG, Hawari J, Zhou E, Bournonniére L, Inniss WE, Greer CW (1998) Biodegradation of variable-chain-length at low temperatures by a psychrotrophic Rhodococcus sp. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:2578–2584
Whyte LG, Schultz A, van Beilen JB, Luz AP, Pellizari V, Labbé D, Greer CW (2002) Prevalence of alkane monooxygenase genes in Arctic and Antarctic hydrocarbon-contaminated and pristine soils. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 41:141–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2002.tb00975
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by funding from the Foundation for Research, Science and Technology, New Zealand (C09X0307). Antarctica New Zealand provided logistic support. Rachel Brown and Gus McAllister of Antarctica New Zealand provided field support. Soil analyses were carried out in the Environmental Chemistry Laboratory, Landcare Research, New Zealand. 16S rDNA sequences were analysed by Sacha Jordan, University of Auckland, New Zealand
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aislabie, J., Ryburn, J. & Sarmah, A. Hexadecane mineralization activity in ornithogenic soil from Seabee Hook, Cape Hallett, Antarctica. Polar Biol 31, 421–428 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-007-0368-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-007-0368-x