Abstract
Key message
Heterologous expression of a nematode-responsive promoter in tomato successfully driven the RNAi constructs to impart root-knot nematode resistance.
Abstract
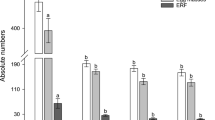
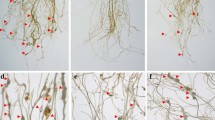
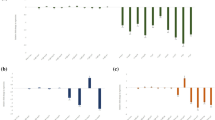
The root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita seriously afflicts the global productivity of tomatoes. Nematode management options are extremely reliant on chemical methods, however, only a handful of nematicides are commercially available. Additionally, nematodes have developed resistance-breaking phenotypes against the commercially available Mi gene-expressing tomatoes. Nematode resistance in crop plants can be enhanced using the bio-safe RNAi technology, in which plants are genetically modified to express nematode gene-specific dsRNA/siRNA molecules. However, the majority of the RNAi crops conferring nematode tolerance have used constitutive promoters, which have many limitations. In the present study, using promoter-GUS fusion, we functionally validated two nematode-inducible root-specific promoters (pAt1g74770 and pAt2g18140, identified from Arabidopsis thaliana) in the Solanum lycopersicum-M. incognita pathosystem. pAt2g18140 was found to be nematode-responsive during 10–21 days post-inoculation (dpi) and became non-responsive during the late infection stage (28 dpi). In contrast, pAt1g74770 remained nematode-responsive for a longer duration (10–28 dpi). Next, a number of transgenic lines were developed that expressed RNAi constructs (independently targeting the M. incognita integrase and splicing factor genes) driven by the pAt1g74770 promoter. M. incognita parasitic success (measured by multiplication factor ratio) in pAt1g74770:integrase and pAt1g74770:splicing factor RNAi lines were significantly reduced by 60.83–74.93% and 69.34–75.31%, respectively, compared to the control. These data were comparable with the RNAi lines having CaMV35S as the promoter. Further, a long-term RNAi effect was evident, because females extracted from transgenic lines were of deformed shape with depleted transcripts of integrase and splicing factor genes. We conclude that pAt1g74770 can be an attractive alternative to drive localized expression of RNAi constructs rather than using a constitutive promoter. The pAt1g74770-driven gene silencing system can be expanded into different plant–nematode interaction models.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sets supporting this article are included in the article and in the supplemental files.
References
Adam MAM, Phillips MS, Blok VC (2007) Molecular diagnostic key for identification of single juveniles of seven common and economically important species of root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne spp.). Plant Pathol 56:190–197
Ali MA, Azeem F, Abbas A, Joyia FA, Li H, Dababat AA (2017) Transgenic strategies for enhancement of nematode resistance in plants. Front Plant Sci 8:750
Banerjee S, Banerjee A, Gill SS, Gupta OP, Dahuja A, Jain PK, Sirohi A (2017) RNA interference: a novel source of resistance to combat plant parasitic nematodes. Front Plant Sci 8:834
Barbary A, Djian-Caporalino C, Palloix A, Castagnone-Sereno P (2015) Host genetic resistance to root-knot nematodes, Meloidogyne spp., in Solanaceae: from genes to the field. Pest Manag Sci 71:1591–1598
Bertioli DJ, Smoker M, Burrows PR (1999) Nematode-responsive activity of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter and its subdomains. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 12:189–196
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans J, Huggett J, Kubista M, Wittwer CT (2009) The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem 55:611–622
Byrd DW, Kirkpatrick JRT, Barker KR (1983) An improved technique for clearing and staining plant tissues for detection of nematodes. J Nematol 15:142–143
Cabot C, Martos S, Llugany M, Gallego B, Tolrà R, Poschenrieder C (2019) A role for zinc in plant defense against pathogens and herbivores. Front Plant Sci 10:1171
Chaudhary S, Dutta TK, Tyagi N, Shivakumara TN, Papolu PK, Chobhe KA, Rao U (2019) Host-induced silencing of Mi-msp-1 confers resistance to root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita in eggplant. Transgenic Res 28:327–340
Coutu C, Brandle J, Brown D, Miki B, Simmonds J (2007) PORE: a modular binary vector series suited for both monocot and dicot plant transformation. Transgenic Res 16:771–781
De Schutter K, Taning CNT, Van Daele L, Van Damme EJM, Dubruel P, Smagghe G (2022) RNAi-based biocontrol products: market status, regulatory aspects, and risk assessment. Front Insect Sci 1:818037
Dutta TK, Banakar P, Rao U (2015a) The status of RNAi-based transgenic research in plant nematology. Front Microbiol 5:760
Dutta TK, Papolu PK, Banakar P, Choudhary D, Sirohi A, Rao U (2015b) Tomato transgenic plants expressing hairpin construct of a nematode protease gene conferred enhanced resistance to root-knot nematodes. Front Microbiol 6:260
Dutta TK, Papolu PK, Singh D, Sreevathsa R, Rao U (2020) Expression interference of a number of Heterodera avenae conserved genes perturbs nematode parasitic success in Triticum aestivum. Plant Sci 301:110670
Dutta TK, Vashisth N, Ray S, Phani V, Chinnusamy V, Sirohi A (2023a) Functional analysis of a susceptibility gene (HIPP27) in the Arabidopsis thaliana-Meloidogyne incognita pathosystem by using a genome editing strategy. BMC Plant Biol 23:390
Dutta TK, Santhoshkumar K, Veeresh A, Waghmare C, Mathur C, Sreevathsa R (2023b) RNAi-based knockdown of candidate gut receptor genes altered the susceptibility of Spodoptera frugiperda and S. litura larvae to a chimeric toxin Cry1AcF. PeerJ 11:e14716
Escobar C, De Meutter J, Aristizábal FA, Sanz-Alférez S, del Campo FF, Barthels N et al (1999) Isolation of the LEMMI9 gene and promoter analysis during a compatible plant-nematode interaction. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 12:440–449
Escobar C, Barcala M, Portillo M, Almoguera C, Jordano J, Fenoll C (2003) Induction of the Hahsp17.7G4 promoter by root-knot nematodes: involvement of heat-shock elements in promoter activity in giant cells. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 16:1062–1068
Eves-van den Akker S (2021) Plant–nematode interactions. Curr Opin Plant Biol 62:102035
Fairbairn DJ, Cavallaro AS, Bernard M, Mahalinga-Iyer J, Graham MW, Botella JR (2007) Host-delivered RNAi: an effective strategy to silence genes in plant parasitic nematodes. Planta 226:1525–1533
Fletcher SJ, Reeves PT, Hoang BT, Mitter N (2020) A perspective on RNAi-based biopesticides. Front Plant Sci 11:51
Goddijn OJ, Lindsey K, van der Lee FM, Klap JC, Sijmons PC (1993) Differential gene expression in nematode-induced feeding structures of transgenic plants harbouring promoter-gusA fusion constructs. Plant J 4:863–873
Goverse A, Biesheuvel J, Wijers GJ, Gommers FJ, Bakker J, Schots A, Helder J (1998) In planta monitoring of the activity of two constitutive promoters, CaMV 35S and TR2´, in developing feeding cells induced by Globodera rostochiensis using green fluorescent protein in combination with confocal laser scanning microscopy. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 52:275–284
Green J, Wang D, Lilley CJ, Urwin PE, Atkinson HJ (2012) Transgenic potatoes for potato cyst nematode control can replace pesticide use without impact on soil quality. PLoS ONE 7:e30973
Grunewald W, Karimi M, Wieczorek K, Van de Cappelle E, Wischnitzki E, Grundler F, Inze D, Beeckman T, Gheysen G (2008) A role for AtWRKY23 in feeding site establishment of plant-parasitic nematodes. Plant Physiol 148:358–368
Jammes F, Lecomte P, de Almeida-Engler J, Bitton F, Martin-Magniette ML, Renou JP et al (2005) Genome-wide expression profiling of the host response to root-knot nematode infection in Arabidopsis. Plant J 44:447–458
Jones HD (2021) Gene silencing or gene editing: the pros and cons. In: RNAi for plant improvement and protection. CABI, Wallingford, pp 47–53
Joshi I, Kumar A, Kohli D, Singh AK, Sirohi A, Subramaniam K, Chaudhury A, Jain PK (2020) Conferring root-knot nematode resistance via host-delivered RNAi-mediated silencing of four Mi-msp genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Sci 298:110592
Joshi I, Kumar A, Kohli D, Bhattacharya R, Sirohi A, Chaudhury A, Jain PK (2022) Gall-specific promoter, an alternative to the constitutive CaMV35S promoter, drives host-derived RNA interference targeting Mi-msp2 gene to confer effective nematode resistance. Front Plant Sci 13:1007322
Kakrana A, Kumar A, Satheesh V, Abdin MZ, Subramaniam K, Bhattacharya RC, Srinivasan R, Sirohi A, Jain PK (2017) Identification, validation and utilization of novel nematode-responsive root-specific promoters in Arabidopsis for inducing host-delivered RNAi mediated root-knot nematode resistance. Front Plant Sci 8:2049
Kaloshian I, Teixeira M (2019) Advances in plant-nematode interactions with emphasis on the notorious nematode genus Meloidogyne. Phytopathology 109:1988–1996
Koch A, Wassenegger M (2021) Host-induced gene silencing—mechanisms and applications. New Phytol 231:54–59
Koulagi R, Banerjee S, Gawade BH, Singh AK, Jain PK, Praveen S, Subramaniam K, Sirohi A (2020) Host-delivered RNA interference in tomato for mediating resistance against Meloidogyne incognita and Tomato leaf curl virus. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult (PCTOC) 143:345–361
Kumar A, Kakrana A, Sirohi A, Subramaniam K, Srinivasan R, Abdin MZ, Jain PK (2017) Host-delivered RNAi-mediated root-knot nematode resistance in Arabidopsis by targeting splicing factor and integrase genes. J Gen Plant Pathol 83:91–97
Lilley CJ, Urwin PE, Johnston KA, Atkinson HJ (2004) Preferential expression of a plant cystatin at nematode feeding sites confers resistance to Meloidogyne incognita and Globodera pallida. Plant Biotechnol J 2:3–12
Lilley CJ, Wang D, Atkinson HJ, Urwin PE (2011) Effective delivery of a nematode-repellent peptide using a root-cap-specific promoter. Plant Biotechnol J 9:151–161
Lilley CJ, Davies LJ, Urwin PE (2012) RNA interference in plant parasitic nematodes: a summary of the current status. Parasitology 139:630–640
Mani V, Reddy CS, Lee SK, Park S, Ko HR, Kim DG, Hahn BS (2020) Chitin biosynthesis inhibition of Meloidogyne incognita by RNAi-mediated gene silencing increases resistance to transgenic tobacco plants. Int J Mol Sci 21:6626
Moreira VJV, Lourenço-Tessutti IT, Basso MF, Lisei-de-Sa ME, Morgante CV, Paes-de-Melo B, Grossi-de-Sa MF (2022) Minc03328 effector gene downregulation severely affects Meloidogyne incognita parasitism in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta 255:44
Moreira VJV, Pinheiro DH, Lourenço-Tessutti IT, Basso MF, Lisei-de-Sa ME, Silva M, Grossi-de-Sa MF (2023) In planta RNAi targeting Meloidogyne incognita Minc16803 gene perturbs nematode parasitism and reduces plant susceptibility. J Pest Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-023-01623-7
Onyango SO, Roderick H, Tripathi JN, Collins R, Atkinson HJ, Oduor RO, Tripathi L (2016) The ZmRCP-1 promoter of maize provides root tip specific expression of transgenes in plantain. J Biol Res Thessaloniki 23:4
Opperman CH, Taylor CG, Conkling MA (1994) Root-knot nematode directed expression of a plant root-specific gene. Science 263:221–223
Papadopoulou N, Devos Y, Álvarez-Alfageme F, Lanzoni A, Waigmann E (2020) Risk assessment considerations for genetically modified RNAi plants: EFSA’s activities and perspective. Front Plant Sci 11:445
Papolu PK, Dutta TK, Tyagi N, Urwin PE, Lilley CJ, Rao U (2016) Expression of a cystatin transgene in eggplant provides resistance to root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne incognita. Front Plant Sci 7:1122
Peremarti A, Twyman RM, Go S, Naqvi S, Farré G, Sabalza M et al (2010) Promoter diversity in multigene transformation. Plant Mol Biol 73:363–378
Phani V, Gowda MT, Dutta TK (2023) Grafting vegetable crops to manage plant-parasitic nematodes: a review. J Pest Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-023-01658-w
Rosso MN, Jones JT, Abad P (2009) RNAi and functional genomics in plant parasitic nematodes. Annu Rev Phytopathol 47:207–232
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108
Severino FE, Brandalise M, Costa CS, Wilcken SRS, Maluf MP, Goncalves W et al (2012) CaPrx, a Coffea arabica gene encoding a putative class III peroxidase induced by root-knot nematode infection. Plant Sci 191–192:35–42
Sharma A, Sharma D, Verma SK (2019) Zinc binding proteome of a phytopathogen Xanthomonas translucens pv. undulosa. R Soc Open Sci 6:190369
Shirasu K, Lahaye T, Tan MW, Zhou F, Azevedo C, Schulze-Lefert P (1999) A novel class of eukaryotic zinc-binding proteins is required for disease resistance signaling in barley and development in C. elegans. Cell 99:355–366
Shivakumara TN, Chaudhary S, Kamaraju D, Dutta TK, Papolu PK, Banakar P, Sreevathsa R, Singh B, Manjaiah KM, Rao U (2017) Host-induced silencing of two pharyngeal gland genes conferred transcriptional alteration of cell wall-modifying enzymes of Meloidogyne incognita vis-à-vis perturbed nematode infectivity in eggplant. Front Plant Sci 8:473
Siddique S, Endres S, Atkins JM, Szakasits D, Wieczorek K, Hofmann J et al (2009) Myo-inositol oxygenase genes are involved in the development of syncytia induced by Heterodera schachtii in Arabidopsis roots. New Phytol 184:457–472
Siddique S, Wieczorek K, Szakasits D, Kreil DP, Bohlmann H (2011) The promoter of a plant defensin gene directs specific expression in nematode induced syncytia in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Physiol Biochem 49:1100–1107
Sindhu AS, Maier TR, Mitchum MG, Hussey RS, Davis EL, Baum TJ (2009) Effective and specific in planta RNAi in cyst nematodes: expression interference of four parasitism genes reduces parasitic success. J Exp Bot 60:315–324
Southey JF (1986) Laboratory methods for work with plant and soil nematodes. Fisheries and Food Great Britain: Ministry of Agriculture, London, p 202
Sukno S, Shimerling O, Mccuiston J, Tsabary G, Shani Z, Shoseyov O et al (2006) Expression and regulation of the Arabidopsis thaliana Cel1 endo 1,4 beta glucanase gene during compatible plant-nematode interactions. J Nematol 38:354–361
Urwin PE, Lilley CJ, McPherson MJ, Atkinson HJ (1997) Resistance to both cyst and root-knot nematodes conferred by transgenic Arabidopsis expressing a modified plant cystatin. Plant J 12:455–461
Ventura V, Frisio DG (2021) The economics of RNAi-based innovation: from the innovation landscape to consumer acceptance. In: RNAi for plant improvement and protection. CABI, Wallingford, pp 159–166
Vercauteren I, van der Schueren E, Van Montagu M, Gheysen G (2001) Arabidopsis thaliana genes expressed in the early compatible interaction with root knot nematodes. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 14:288–299
Vieira P, Gleason C (2019) Plant-parasitic nematode effectors-insights into their diversity and new tools for their identification. Curr Opin Plant Biol 50:37–43
Wheatley MS, Yang Y (2021) Versatile applications of the CRISPR/Cas toolkit in plant pathology and disease management. Phytopathology 111:1080–1090
Yadav BC, Veluthambi K, Subramaniam K (2006) Host-generated double stranded RNA induces RNAi in plant-parasitic nematodes and protects the host from infection. Mol Biochem Parasitol 148:219–222
Zschiesche W, Barth O, Daniel K, Böhme S, Rausche J, Humbeck K (2015) The zinc-binding nuclear protein HIPP 3 acts as an upstream regulator of the salicylate-dependent plant immunity pathway and of flowering time in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol 207:1084–1096
Acknowledgements
We profusely thank the staffs of National Phytotron Facility, IARI for maintenance of our transgenic lines.
Funding
The present research was funded by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) via National Agricultural Innovative Project (NAIP/C4/C1092) and National Agricultural Science Fund (NFBSFARA/RNA-3022/2012-13).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: YET, TKD, AS; methodology: YET, TKD; formal analysis: TKD; resources: PKJ, KS; writing—original draft: TKD; writing—review and editing: AS; Supervision: AS.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that no competing interests is associated with this manuscript.
Additional information
Communicated by Marcelo Menossi.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Thorat, Y.E., Dutta, T.K., Jain, P.K. et al. A nematode-inducible promoter can effectively drives RNAi construct to confer Meloidogyne incognita resistance in tomato. Plant Cell Rep 43, 3 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-023-03114-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-023-03114-6