Abstract
Key message
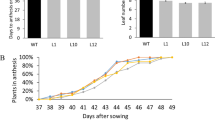
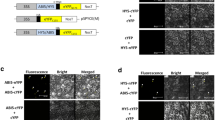
Our findings indicated that the SlERF.J2-IAA23 module integrates hormonal signals to regulate hypocotyl elongation and plant height in tomato.
Abstract
Light and phytohormones can synergistically regulate photomorphogenesis-related hypocotyl elongation and plant height in tomato. AP2/ERF family genes have been extensively demonstrated to play a role in light signaling and various hormones. In this study, we identified a novel AP2/ERF family gene in tomato, SlERF.J2. Overexpression of SlERF.J2 inhibits hypocotyl elongation and plant height. However, the plant height in the slerf.j2ko knockout mutant was not significantly changed compared with the WT. we found that hypocotyl cell elongation and plant height were regulated by a network involving light, auxin and gibberellin signaling, which is mediated by regulatory relationship between SlERF.J2 and IAA23. SlERF.J2 protein could bind to IAA23 promoter and inhibit its expression. In addition, light–dark alternation can activate the transcription of SlERF.J2 and promote the function of SlERF.J2 in photomorphogenesis. Our findings indicated that the SlERF.J2-IAA23 module integrates hormonal signals to regulate hypocotyl elongation and plant height in tomato.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data supporting the findings of this study are available within the paper and within its supplementary materials published online.
References
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. polyphenoloxidase in beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24(1):1–15
Audran-Delalande C, Bassa C, Mila I, Regad F, Zouine M, Bouzayen M (2012) Genome-wide identification, functional analysis and expression profiling of the Aux/IAA gene family in tomato. Plant Cell Physiol 53(4):659–672
Bai MY, Fan M, Oh E, Wang ZY (2012) A triple helix-loop-helix/basic helix-loop-helix cascade controls cell elongation downstream of multiple hormonal and environmental signaling pathways in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24(12):4917–4929
Bassa C, Mila I, Bouzayen M, Audran-Delalande C (2012) Phenotypes associated with down-regulation of Sl-IAA27 support functional diversity among Aux/IAA family members in tomato. Plant Cell Physiol 53(9):1583–1595
Cai XT, Xu P, Zhao PX, Liu R, Yu LH, Xiang CB (2014) Arabidopsis ERF109 mediates cross-talk between jasmonic acid and auxin biosynthesis during lateral root formation. Nat Commun 5:5833
Casal JJ (2013) Photoreceptor signaling networks in plant responses to shade. Annu Rev Plant Biol 64:403–427
Catala C, Rose JK, York WS, Albersheim P, Darvill AG, Bennett AB (2001) Characterization of a tomato xyloglucan endotransglycosylase gene that is down-regulated by auxin in etiolated hypocotyls. Plant Physiol 127(3):1180–1192
Chaabouni S, Jones B, Delalande C, Wang H, Li Z, Mila I, Frasse P, Latche A, Pech JC, Bouzayen M (2009) Sl-IAA3, a tomato Aux/IAA at the crossroads of auxin and ethylene signalling involved in differential growth. J Exp Bot 60(4):1349–1362
Chaiwanon J, Wang W, Zhu JY, Oh E, Wang ZY (2016) Information integration and communication in plant growth regulation. Cell 164(6):1257–1268
Chen G, Hackett R, Walker D, Taylor A, Lin Z, Grierson D (2004) Identification of a specific isoform of tomato lipoxygenase (TomloxC) involved in the generation of fatty acid-derived flavor compounds. Plant Physiol 136(1):2641–2651
de Lucas M, Daviere JM, Rodriguez-Falcon M, Pontin M, Iglesias-Pedraz JM, Lorrain S, Fankhauser C, Blazquez MA, Titarenko E, Prat S (2008) A molecular framework for light and gibberellin control of cell elongation. Nature 451(7177):480–484
de Wit M, Galvao VC, Fankhauser C (2016) Light-mediated hormonal regulation of plant growth and development. Annu Rev Plant Biol 67:513–537
Deng W, Yang Y, Ren Z, Audran-Delalande C, Mila I, Wang X, Song H, Hu Y, Bouzayen M, Li Z (2012) The tomato SlIAA15 is involved in trichome formation and axillary shoot development. New Phytol 194(2):379–390
Deng H, Chen Y, Liu Z, Liu Z, Shu P, Wang R, Hao Y, Su D, Pirrello J, Liu Y, Li Z, Grierson D, Giovannoni JJ, Bouzayen M, Liu M (2022) SlERF.F12 modulates the transition to ripening in tomato fruit by recruiting the co-repressor TOPLESS and histone deacetylases to repress key ripening genes. Plant Cell 34(4):1250–1272
Depuydt S, Hardtke CS (2011) Hormone signalling crosstalk in plant growth regulation. Curr Biol 21(9):R365-373
Dong X, Yan Y, Jiang B, Shi Y, Jia Y, Cheng J, Shi Y, Kang J, Li H, Zhang D, Qi L, Han R, Zhang S, Zhou Y, Wang X, Terzaghi W, Gu H, Kang D, Yang S, Li J (2020) The cold response regulator CBF1 promotes Arabidopsis hypocotyl growth at ambient temperatures. EMBO J 39(13):e103630
Exposito-Rodriguez M, Borges AA, Borges-Perez A, Perez JA (2008) Selection of internal control genes for quantitative real-time RT-PCR studies during tomato development process. Bmc Plant Biol 8:1–12
Feng S, Martinez C, Gusmaroli G, Wang Y, Zhou J, Wang F, Chen L, Yu L, Iglesias-Pedraz JM, Kircher S, Schafer E, Fu X, Fan LM, Deng XW (2008) Coordinated regulation of Arabidopsis thaliana development by light and gibberellins. Nature 451(7177):475–479
Fleet CM, Sun TP (2005) A DELLAcate balance: the role of gibberellin in plant morphogenesis. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8(1):77–85
Gibbs DJ, Md Isa N, Movahedi M, Lozano-Juste J, Mendiondo GM, Berckhan S, Marin-de la Rosa N, Vicente Conde J, Sousa Correia C, Pearce SP, Bassel GW, Hamali B, Talloji P, Tome DF, Coego A, Beynon J, Alabadi D, Bachmair A, Leon J, Gray JE, Theodoulou FL, Holdsworth MJ (2014) Nitric oxide sensing in plants is mediated by proteolytic control of group VII ERF transcription factors. Mol Cell 53(3):369–379
Guo H, Mao M, Deng Y, Sun L, Chen R, Cao P, Lai J, Zhang Y, Wang C, Li C, Li Y, Bai Q, Tan T, Yang J, Wang S (2022) Multi-omics analysis reveals that SlERF.D6 synergistically regulates SGAs and fruit development. Front Plant Sci 13:860577
Hellens RP, Allan AC, Friel EN, Bolitho K, Grafton K, Templeton MD, Karunairetnam S, Gleave AP, Laing WA (2005) Transient expression vectors for functional genomics, quantification of promoter activity and RNA silencing in plants. Plant Methods 1:13
Huang S, Raman AS, Ream JE, Fujiwara H, Cerny RE, Brown SM (1998) Overexpression of 20-oxidase confers a gibberellin-overproduction phenotype in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 118(3):773–781
Irfan M, Kumar P, Kumar V, Datta A (2022) Fruit ripening specific expression of beta-D-N-acetylhexosaminidase (beta-Hex) gene in tomato is transcriptionally regulated by ethylene response factor SlERF.E4. Plant Sci 323:111380
Job N, Datta S (2021) PIF3/HY5 module regulates BBX11 to suppress protochlorophyllide levels in dark and promote photomorphogenesis in light. New Phytol 230(1):190–204
Lau OS, Deng XW (2010) Plant hormone signaling lightens up: integrators of light and hormones. Curr Opin Plant Biol 13(5):571–577
Leivar P, Quail PH (2011) PIFs: pivotal components in a cellular signaling hub. Trends Plant Sci 16(1):19–28
Li QF, He JX (2016) BZR1 interacts with HY5 to mediate brassinosteroid- and light-regulated cotyledon opening in Arabidopsis in darkness. Mol Plant 9(1):113–125
Licausi F, Ohme-Takagi M, Perata P (2013) APETALA2/Ethylene Responsive Factor (AP2/ERF) transcription factors: mediators of stress responses and developmental programs. New Phytol 199(3):639–649
Liu Q, Guo X, Chen G, Zhu Z, Yin W, Hu Z (2016) Silencing SlGID2, a putative F-box protein gene, generates a dwarf plant and dark-green leaves in tomato. Plant Physiol Biochem 109:491–501
Liu M, Chen Y, Chen Y, Shin JH, Mila I, Audran C, Zouine M, Pirrello J, Bouzayen M (2018) The tomato Ethylene Response Factor Sl-ERF.B3 integrates ethylene and auxin signaling via direct regulation of Sl-Aux/IAA27. New Phytol 219(2):631–640
Lorrain S, Allen T, Duek PD, Whitelam GC, Fankhauser C (2008) Phytochrome-mediated inhibition of shade avoidance involves degradation of growth-promoting bHLH transcription factors. Plant J 53(2):312–323
Muller M, Munne-Bosch S (2015) Ethylene response factors: a key regulatory hub in hormone and stress signaling. Plant Physiol 169(1):32–41
Murase K, Hirano Y, Sun TP, Hakoshima T (2008) Gibberellin-induced DELLA recognition by the gibberellin receptor GID1. Nature 456(7221):459–463
Nagpal P, Ellis CM, Weber H, Ploense SE, Barkawi LS, Guilfoyle TJ, Hagen G, Alonso JM, Cohen JD, Farmer EE, Ecker JR, Reed JW (2005) Auxin response factors ARF6 and ARF8 promote jasmonic acid production and flower maturation. Development 132(18):4107–4118
Nicot N, Hausman JF, Hoffmann L, Evers D (2005) Housekeeping gene selection for real-time RT-PCR normalization in potato during biotic and abiotic stress. J Exp Bot 56(421):2907–2914
Osterlund MT, Hardtke CS, Wei N, Deng XW (2000) Targeted destabilization of HY5 during light-regulated development of Arabidopsis. Nature 405(6785):462–466
Pattison RJ, Catala C (2012) Evaluating auxin distribution in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) through an analysis of the PIN and AUX/LAX gene families. Plant J 70(4):585–598
Saladie M, Rose JK, Cosgrove DJ, Catala C (2006) Characterization of a new xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase (XTH) from ripening tomato fruit and implications for the diverse modes of enzymic action. Plant J 47(2):282–295
Schomburg FM, Bizzell CM, Lee DJ, Zeevaart JA, Amasino RM (2003) Overexpression of a novel class of gibberellin 2-oxidases decreases gibberellin levels and creates dwarf plants. Plant Cell 15(1):151–163
Shi L, Olszewski NE (1998) Gibberellin and abscisic acid regulate GAST1 expression at the level of transcription. Plant Mol Biol 38(6):1053–1060
Shi QM, Yang X, Song L, Xue HW (2011) Arabidopsis MSBP1 is activated by HY5 and HYH and is involved in photomorphogenesis and brassinosteroid sensitivity regulation. Mol Plant 4(6):1092–1104
Shimada A, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Nakatsu T, Nakajima M, Naoe Y, Ohmiya H, Kato H, Matsuoka M (2008) Structural basis for gibberellin recognition by its receptor GID1. Nature 456(7221):520–523
Stephenson PG, Fankhauser C, Terry MJ (2009) PIF3 is a repressor of chloroplast development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(18):7654–7659
Su L, Bassa C, Audran C, Mila I, Cheniclet C, Chevalier C, Bouzayen M, Roustan JP, Chervin C (2014) The auxin Sl-IAA17 transcriptional repressor controls fruit size via the regulation of endoreduplication-related cell expansion. Plant Cell Physiol 55(11):1969–1976
Sun TP (2010) Gibberellin-GID1-DELLA: a pivotal regulatory module for plant growth and development. Plant Physiol 154(2):567–570
Tatematsu K, Kumagai S, Muto H, Sato A, Watahiki MK, Harper RM, Liscum E, Yamamoto KT (2004) MASSUGU2 encodes Aux/IAA19, an auxin-regulated protein that functions together with the transcriptional activator NPH4/ARF7 to regulate differential growth responses of hypocotyl and formation of lateral roots in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 16(2):379–393
Voegele A, Linkies A, Muller K, Leubner-Metzger G (2011) Members of the gibberellin receptor gene family GID1 (GIBBERELLIN INSENSITIVE DWARF1) play distinct roles during Lepidium sativum and Arabidopsis thaliana seed germination. J Exp Bot 62(14):5131–5147
Von Arnim A, Deng XW (1996) Light control of seedling development. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 47:215–243
Wang ZY, Bai MY, Oh E, Zhu JY (2012) Brassinosteroid signaling network and regulation of photomorphogenesis. Annu Rev Genet 46:701–724
Weijers D, Wagner D (2016) Transcriptional responses to the auxin hormone. Annu Rev Plant Biol 67:539–574
Xie Q, Hu Z, Zhu Z, Dong T, Zhao Z, Cui B, Chen G (2014) Overexpression of a novel MADS-box gene SlFYFL delays senescence, fruit ripening and abscission in tomato. Sci Rep 4:4367
Xie Z, Nolan TM, Jiang H, Yin Y (2019) AP2/ERF transcription factor regulatory networks in hormone and abiotic stress responses in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 10:228
Xu N, Chu Y, Chen H, Li X, Wu Q, Jin L, Wang G, Huang J (2018) Rice transcription factor OsMADS25 modulates root growth and confers salinity tolerance via the ABA-mediated regulatory pathway and ROS scavenging. PLoS Genet 14(10):e1007662
Zhang L, Kang J, Xie Q, Gong J, Shen H, Chen Y, Chen G, Hu Z (2020) The basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor bHLH95 affects fruit ripening and multiple metabolisms in tomato. J Exp Bot 71(20):6311–6327
Zhao MJ, Yin LJ, Liu Y, Ma J, Zheng JC, Lan JH, Fu JD, Chen M, Xu ZS, Ma YZ (2019) The ABA-induced soybean ERF transcription factor gene GmERF75 plays a role in enhancing osmotic stress tolerance in Arabidopsis and soybean. Bmc Plant Biol 19(1):506
Zhu Z, Liang H, Chen G, Li F, Wang Y, Liao C, Hu Z (2019) The bHLH transcription factor SlPRE2 regulates tomato fruit development and modulates plant response to gibberellin. Plant Cell Rep 38(9):1053–1064
Zouine M, Fu Y, Chateigner-Boutin AL, Mila I, Frasse P, Wang H, Audran C, Roustan JP, Bouzayen M (2014) Characterization of the tomato ARF gene family uncovers a multi-levels post-transcriptional regulation including alternative splicing. PLoS ONE 9(1):e84203
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31872121), and the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing of China (csts2019jcyj-msxmX0094), and the Innovation project of people returned from studying abroad of Chongqing (cx2019158).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZH and QX designed and managed the research work and improved the manuscript. YC, HY designed the experiments and analyzed the data. YC, BT, FL, GC performed the experiments. YC wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have read and approved this version of the article, and due care has been taken to ensure the integrity of this work. All the authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Sukhpreet Sandhu.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Yang, H., Tang, B. et al. The AP2/ERF transcription factor SlERF.J2 functions in hypocotyl elongation and plant height in tomato. Plant Cell Rep 42, 371–383 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-022-02963-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-022-02963-x