Abstract
Key Message
We investigated the mechanism of the effect of different light qualities on the synthesis and regulation of mung bean sprouts. Light quality acts as a signal molecule, strongly enhancing polyphenol biosynthesis in sprouts.
Abstract
Mung bean (Vigna radiata) sprouts are a popular sprouting vegetable all over the world and are an excellent source of polyphenols with high antioxidant activity. This study investigated the effects of light qualities on the kinetic changes and metabolic regulation mechanism of light signal-mediating polyphenols in three mung bean sprout cultivars. Experimental results showed that three light qualities significantly enhanced the contents of caffeic acid, rutin, vitexin, genistin and delphinidin 3-glucoside. Interestingly, ferulic acid and vitexin responded selectively to blue light and red light, severally. Most genes involved in polyphenol biosynthesis were activated under different light quality conditions, resulting in an overaccumulation of phenylpropanoids. Pearson correlation analysis showed that PAL, F3H, F3’H and F3′5’H expression correlated highly with rutin, whereas ANS expression paralleled anthocyanin biosynthesis. Moreover, MYB111, MYB3, MYB4, MYB1 and MYC2 were critical regulators of polyphenol biosynthesis in mung bean sprouts. These changes were likely due to the changes in the expression of the photoreceptor genes CRY-D, PHOT2, PHYE and light response genes (PIF3 and HY5). Our results provide insights into polyphenol biosynthesis in sprouts and microgreens.
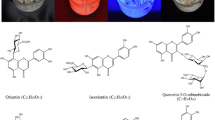
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Change history
20 December 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-022-02964-w
References
Appolloni E, Pennisi G, Zauli I, Carotti L, Paucek I, Quaini S, Orsini F, Gianquinto G (2022) Beyond vegetables: effects of indoor LED light on specialized metabolite biosynthesis in medicinal and aromatic plants, edible flowers, and microgreens. J Sci Food Agric 102(2):472–487. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.11513
Bubna GA, Lima RB, Zanardo DYL, dos Santos WD, Ferrarese MdLL, Ferrarese-Filho O (2011) Exogenous caffeic acid inhibits the growth and enhances the lignification of the roots of soybean (Glycine max). J Plant Physiol 168(14):1627–1633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2011.03.005
Choi J-H, Kim D-W, Park S-E, Lee H-J, Kim K-M, Kim K-J, Kim M-K, Kim S-J, Kim S (2015) Anti-thrombotic effect of rutin isolated from Dendropanax morbifera Leveille. J Biosci Bioeng 120(2):181–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2014.12.012
Craver JK, Gerovac JR, Lopez RG, Kopsell DA (2017) Light Intensity and Light Quality from Sole-source Light-emitting Diodes Impact Phytochemical Concentrations within Brassica Microgreens. J Am Soc Hort Sci 142(1):3–12. https://doi.org/10.21273/JASHS03830-16
del Río-Celestino M, Font R (2020) The Health Benefits of Fruits and Vegetables. Foods 9(3):369. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9030369
Deng Y, Lu S (2017) Biosynthesis and Regulation of Phenylpropanoids in Plants. CRC Crit Rev Plant Sci 36(4):257–290. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352689.2017.1402852
Ebert AW, Chang C-H, Yan M-R, Yang R-Y (2017) Nutritional composition of mung bean and soybean sprouts compared to their adult growth stage. Food Chem 237(15):15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.05.073
Gallego AM, Rojas LF, Parra O, Rodriguez HA, Mazo Rivas JC, Urrea AI, Atehortúa L, Fister AS, Guiltinan MJ, Maximova SN, Pabón-Mora N (2018) Transcriptomic analyses of cacao cell suspensions in light and dark provide target genes for controlled flavonoid production. Sci Rep 8(1):13575. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31965-7
Gan R-Y, Wang M-F, Lui W-Y, Wu K, Corke H (2016) Dynamic changes in phytochemical composition and antioxidant capacity in green and black mung bean (Vigna radiata) sprouts. Int J Food Sci Technol 51(9):2090–2098. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.13185
Ganesan K, Xu B (2018) A critical review on phytochemical profile and health promoting effects of mung bean (Vigna radiata). Food Sci Hum Wellness 7(1):11–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fshw.2017.11.002
Gu L, Wu Y, Li M, Wang F, Li Z, Yuan F, Zhang Z (2021) Over-immunity mediated abnormal deposition of lignin arrests the normal enlargement of the root tubers of Rehmannia glutinosa under consecutive monoculture stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 165:36–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.05.010
Heng Y, Jiang Y, Zhao X, Zhou H, Wang X, Deng Xing W, Xu D (2019) BBX4, a phyB-interacting and modulated regulator, directly interacts with PIF3 to fine tune red light-mediated photomorphogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 116(51):26049–26056. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1915149116
Kadomura-Ishikawa Y, Miyawaki K, Noji S, Takahashi A (2013) Phototropin 2 is involved in blue light-induced anthocyanin accumulation in Fragaria x ananassa fruits. J Plant Res 126(6):847–857. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-013-0582-2
Lee S-W, Seo JM, Lee M-K, Chun J-H, Antonisamy P, Arasu MV, Suzuki T, Al-Dhabi NA, Kim S-J (2014) Influence of different LED lamps on the production of phenolic compounds in common and Tartary buckwheat sprouts. Ind Crops Prod 54:320–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.01.024
Li C, Qi L, Zhang S, Dong X, Jing Y, Cheng J, Feng Z, Peng J, Li H, Zhou Y, Wang X, Han R, Duan J, Terzaghi W, Lin R, Li J (2022) Mutual upregulation of HY5 and TZP in mediating phytochrome A signaling. Plant Cell 34(1):633–654. https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koab254
Lillo C, Lea US, Ruoff P (2008) Nutrient depletion as a key factor for manipulating gene expression and product formation in different branches of the flavonoid pathway. Plant, Cell Environ 31(5):587–601. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2007.01748.x
Liu Z, Zhang Y, Wang J, Li P, Zhao C, Chen Y, Bi Y (2015) Phytochrome-interacting factors PIF4 and PIF5 negatively regulate anthocyanin biosynthesis under red light in Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant Sci 238:64–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.06.001
Liu H, Chen Y, Hu T, Zhang S, Zhang Y, Zhao T, Yu H, Kang Y (2016) The influence of light-emitting diodes on the phenolic compounds and antioxidant activities in pea sprouts. J Funct Foods 25:459–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2016.06.028
Liu Y, Fang S, Yang W, Shang X, Fu X (2018) Light quality affects flavonoid production and related gene expression in Cyclocarya paliurus. J Photochem Photobiol, B 179:66–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.01.002
Liu C, Yao X, Li G, Huang L, Xie Z (2020) Transcriptomic profiling of purple broccoli reveals light-induced anthocyanin biosynthetic signaling and structural genes. PeerJ 8:e8870. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.8870
Lu Y, Chang X, Guo X (2019) Dynamic Changes of Ascorbic Acid, Phenolics Biosynthesis and Antioxidant Activities in Mung Beans (Vigna radiata) until Maturation. Plants (basel, Switzerland) 8(3):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8030075
Mastropasqua L, Dipierro N, Paciolla C (2020) Effects of Darkness and Light Spectra on Nutrients and Pigments in Radish, Soybean Mung Bean and Pumpkin Sprouts. Antioxidants 9(6):558. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9060558
Mondal SK, Roy S (2018) Genome-wide sequential, evolutionary, organizational and expression analyses of phenylpropanoid biosynthesis associated MYB domain transcription factors in Arabidopsis. J Biomol Struct Dyn 36(6):1577–1601. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2017.1329099
Naing AH, Kim CK (2018) Roles of R2R3-MYB transcription factors in transcriptional regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in horticultural plants. Plant Mol Biol 98(1):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-018-0771-4
Nawae W, Yoocha T, Narong N, Paemanee A, Ketngamkum Y, Romyanon K, Toojinda T, Tangphatsornruang S, Pootakham W (2021) Transcriptome sequencing revealed the influence of blue light on the expression levels of light-stress response genes in Centella asiatica. PLoS ONE 16(11):e0260468. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0260468
Neelam KA, Sharma KK (2020) Phenylpropanoids and its derivatives: biological activities and its role in food, pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 60(16):2655–2675. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2019.1653822
Palma CFF, Castro-Alves V, Rosenqvist E, Ottosen C-O, Strid Å, Morales LO (2021) Effects of UV radiation on transcript and metabolite accumulation are dependent on monochromatic light background in cucumber. Physiol Plant 173(3):750–761. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.13551
Qian H, Liu T, Deng M, Miao H, Cai C, Shen W, Wang Q (2016) Effects of light quality on main health-promoting compounds and antioxidant capacity of Chinese kale sprouts. Food Chem 196:1232–1238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.10.055
Rai N, Morales LO, Aphalo PJ (2021) Perception of solar UV radiation by plants: photoreceptors and mechanisms. Plant Physiol 186(3):1382–1396. https://doi.org/10.1093/plphys/kiab162
Sheerin DJ, Hiltbrunner A (2017) Molecular mechanisms and ecological function of far-red light signalling. Plant, Cell Environ 40(11):2509–2529. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12915
Shi M, Wang Y, Wang X, Deng C, Cao W, Hua Q, Kai G (2020) Simultaneous promotion of tanshinone and phenolic acid biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots by overexpressing Arabidopsis MYC2. Ind Crops Prod 155:112826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112826
Su N, Lu Y, Wu Q, Liu Y, Xia Y, Xia K, Cui J (2016) UV-B-induced anthocyanin accumulation in hypocotyls of radish sprouts continues in the dark after irradiation. J Sci Food Agric 96(3):886–892. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.7161
Tajoddin M, Manohar S, Lalitha J (2014) Effect of soaking and germination on polyphenol content and polyphenol oxidase activity of mung bean (Phaseolus Aureus L.) cultivars differing in seed color. Int J Food Properties 17(4):782–790. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2012.654702
Tantharapornrerk N, Vichitsoonthonkul T, Techavuthiporn C, Photchanachai S (2021) Growth and antioxidant system of Chinese kale microgreens in response to different illumination of light sources. New Zealand J Crop Horticult Sci 1–15. doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/01140671.2021.1958876
Yadav A, Singh D, Lingwan M, Yadukrishnan P, Masakapalli SK, Datta S (2020) Light signaling and UV-B-mediated plant growth regulation. J Integr Plant Biol 62(9):1270–1292. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12932
Yao Y, Yang X, Tian J, Liu C, Cheng X, Ren G (2013) Antioxidant and antidiabetic activities of black mung bean (Vigna radiata L.). J Agric Food Chem 61(34):8104–8109. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf401812z
Yu B, Pan Y, Liu Y, Chen Q, Guo X, Tang Z (2021) A comprehensive analysis of transcriptome and phenolic compound profiles suggests the role of flavonoids in cotyledon greening in Catharanthus roseus seedling. Plant Physiol Biochem 167:185–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.07.028
Zhang D, Jiang C, Huang C, Wen D, Lu J, Chen S, Zhang T, Shi Y, Xue J, Ma W, Xiang L, Sun W, Chen S (2019a) The light-induced transcription factor FtMYB116 promotes accumulation of rutin in Fagopyrum tataricum. Plant, Cell Environ 42(4):1340–1351. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.13470
Zhang X, Bian Z, Li S, Chen X, Lu C (2019b) Comparative analysis of phenolic compound profiles, antioxidant capacities, and expressions of phenolic biosynthesis-related genes in soybean microgreens grown under different light spectra. J Agric Food Chem 67(49):13577–13588. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b05594
Zhang S, Ma J, Zou H, Zhang L, Li S, Wang Y (2020a) The combination of blue and red LED light improves growth and phenolic acid contents in Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. Ind Crops Prod 158:112959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112959
Zhang X, Bian Z, Yuan X, Chen X, Lu C (2020b) A review on the effects of Light-Emitting Diode (LED) light on the nutrients of sprouts and microgreens. Trends Food Sci Technol 99:203–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2020.02.031
Zheng C, Ma J-Q, Ma C-L, Shen S-Y, Liu Y-F, Chen L (2019) Regulation of growth and flavonoid formation of tea plants (Camellia sinensis) by blue and green light. J Agric Food Chem 67(8):2408–2419. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b07050
Zoratti L, Karppinen K, Luengo Escobar A, Häggman H, Jaakola L (2014) Light-controlled flavonoid biosynthesis in fruits. Front Plant Sci 5:534–534. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00534
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA [grant number CARS-08], Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation [grant number 2021A1515012110] and the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program (ASTIP) from Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences.
Funding
This work was supported by the China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA [grant number CARS-08], Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation [grant number 2021A1515012110] and the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program (ASTIP) from Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: [X. G.]; Data curation: [Y. C.], [H. C.]; Formal analysis: [Y. Z.]; Funding acquisition: [L. W.], [X. G.]; Investigation: [X. C.]; Methodology: [H. C.], [X. G.]; Project administration: [X. G.]; Resources: [X. C.]; Software: [Y. C.], [Y. Z.]: Supervision: [X. G.]; Validation: [Y. C.], [L. W.]; Visualization: [Y. C.]; Writing – original draft: [Y. C.]; Writing – review & editing: [X. G.], [L. W.]. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Communicated by Li Tian.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, Y., Chen, H., Zhao, Y. et al. Effect of light quality on polyphenol biosynthesis in three varieties of mung bean sprouts with different color seed coats. Plant Cell Rep 42, 253–268 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-022-02954-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-022-02954-y