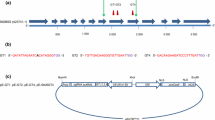
Abstract
Key Message
The StGBSSI gene was successfully and precisely edited in the tetraploid potato using gene and base-editing strategies, leading to plants with impaired amylose biosynthesis.
Abstract
Genome editing has recently become a method of choice for basic research and functional genomics, and holds great potential for molecular plant-breeding applications. The powerful CRISPR-Cas9 system that typically produces double-strand DNA breaks is mainly used to generate knockout mutants. Recently, the development of base editors has broadened the scope of genome editing, allowing precise and efficient nucleotide substitutions. In this study, we produced mutants in two cultivated elite cultivars of the tetraploid potato (Solanum tuberosum) using stable or transient expression of the CRISPR-Cas9 components to knock out the amylose-producing StGBSSI gene. We set up a rapid, highly sensitive and cost-effective screening strategy based on high-resolution melting analysis followed by direct Sanger sequencing and trace chromatogram analysis. Most mutations consisted of small indels, but unwanted insertions of plasmid DNA were also observed. We successfully created tetra-allelic mutants with impaired amylose biosynthesis, confirming the loss of function of the StGBSSI protein. The second main objective of this work was to demonstrate the proof of concept of CRISPR-Cas9 base editing in the tetraploid potato by targeting two loci encoding catalytic motifs of the StGBSSI enzyme. Using a cytidine base editor (CBE), we efficiently and precisely induced DNA substitutions in the KTGGL-encoding locus, leading to discrete variation in the amino acid sequence and generating a loss-of-function allele. The successful application of base editing in the tetraploid potato opens up new avenues for genome engineering in this species.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anders C, Niewoehner O, Duerst A, Jinek M (2014) Structural basis of PAM-dependent target DNA recognition by the Cas9 endonuclease. Nature 513:569–573. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13579
Andersson M, Trifonova A, Andersson AB, Johansson M, Bulow L, Hofvander P (2003) A novel selection system for potato transformation using a mutated AHAS gene. Plant Cell Rep 22:261–267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-003-0684-8
Andersson M, Turesson H, Nicolia A, Falt AS, Samuelsson M, Hofvander P (2017) Efficient targeted multiallelic mutagenesis in tetraploid potato (Solanum tuberosum) by transient CRISPR-Cas9 expression in protoplasts. Plant Cell Rep 36:117–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-016-2062-3
Andersson M et al (2018) Genome editing in potato via CRISPR-Cas9 ribonucleoprotein delivery. Physiol Plant. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12731
Ball SG, van de Wal MHBJ, Visser RGF (1998) Progress in understanding the biosynthesis of amylose. Trends Plant Sci 3:462–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1360-1385(98)01342-9
Bastet A, Zafirov D, Giovinazzo N, Guyon-Debast A, Nogué F, Robaglia C, Gallois J-L (2019) Mimicking natural polymorphism in eIF4E by CRISPR-Cas9 base editing is associated with resistance to potyviruses. Plant Biotechnol J 1:2. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13096
Bortesi L, Fischer R (2015) The CRISPR/Cas9 system for plant genome editing and beyond. Biotechnol Adv 33:41–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2014.12.006
Bull SE et al (2018) Accelerated ex situ breeding of GBSS- and PTST1-edited cassava for modified starch. Sci Adv 4:eaat6086. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aat6086
Butler NM, Atkins PA, Voytas DF, Douches DS (2015) Generation and inheritance of targeted mutations in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) using the CRISPR/Cas system. PLoS ONE 10:e0144591. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0144591
Butler NM, Baltes NJ, Voytas DF, Douches DS (2016) Geminivirus-mediated genome editing in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) using sequence-specific nucleases. Front Plant Sci 7:1045. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01045
Chen L et al (2018) A method for the production and expedient screening of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated non-transgenic mutant plants. Hortic Res 5:13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41438-018-0023-4
Cheng J et al (2012) Diversification of genes encoding granule-bound starch synthase in monocots and dicots is marked by multiple genome-wide duplication events. PLoS One 7:e30088. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0030088
Clasen BM et al (2016) Improving cold storage and processing traits in potato through targeted gene knockout. Plant Biotechnol J 14:169–176. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12370
Delvalle D et al (2005) Soluble starch synthase I: a major determinant for the synthesis of amylopectin in Arabidopsis thaliana leaves. Plant J 43:398–412. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02462.x
Demirer GS et al (2019) High aspect ratio nanomaterials enable delivery of functional genetic material without DNA integration in mature plants. Nat Nanotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-019-0382-5
Endo M et al (2018) Genome editing in plants by engineered CRISPR-Cas9 recognizing NG PAM. Nat Plants. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41477-018-0321-8
Fauser F, Schiml S, Puchta H (2014) Both CRISPR/Cas-based nucleases and nickases can be used efficiently for genome engineering in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 79:348–359. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12554
Fossi M, Amundson KR, Kuppu S, Britt AB, Comai L (2019) Regeneration of Solanum tuberosum plants from protoplasts induces widespread genome instability. Plant Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.18.00906
Gaudelli NM, Komor AC, Rees HA, Packer MS, Badran AH, Bryson DI, Liu DR (2017) Programmable base editing of A*T to G*C in genomic DNA without DNA cleavage. Nature 551:464–471. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature24644
Guerineau F, Waugh RJPMB (1993) The U6 small nuclear RNA gene family of potato. Plant Mol Biol 22:807–818. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00027367
Haeussler M et al (2016) Evaluation of off-target and on-target scoring algorithms and integration into the guide RNA selection tool CRISPOR. Genome Biol 17:148. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-016-1012-2
Hameed A, Zaidi SS, Shakir S, Mansoor S (2018) Applications of new breeding technologies for potato improvement front. Plant Sci 9:925. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00925
Helle S et al (2018) Proteome analysis of potato starch reveals the presence of new starch metabolic proteins as well as multiple protease inhibitors. Front Plant Sci 9:746. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00746
Hovenkamp-Hermelink JHM et al (1987) Isolation of an amylose-free starch mutant of the potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Theor Appl Genet 75:217–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00249167
Hsiau T, Maures T, Waite K, Yang J, Kelso R, Holden K, Stoner R (2018) Inference of CRISPR Edits from Sanger trace data. BioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/251082
Hu JH et al (2018) Evolved Cas9 variants with broad PAM compatibility and high DNA specificity. Nature 556:57–63. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature26155
Hua K, Tao X, Yuan F, Wang D, Zhu JK (2018a) Precise A.T to G.C Base editing in the rice genome. Mol Plant 11:627–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2018.02.007
Hua K, Tao X, Zhu JK (2018b) Expanding the base editing scope in rice by using Cas9 variants. Plant Biotechnol J 1:2. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12993
Jin S et al (2019) Cytosine, but not adenine, base editors induce genome-wide off-target mutations in rice. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaw7166
Jinek M, Chylinski K, Fonfara I, Hauer M, Doudna JA, Charpentier E (2012) A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science 337:816–821. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1225829
John B (2003) Comparative protein structure modeling by iterative alignment, model building and model assessment. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3982–3992. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkg460
Kang BC et al (2018) Precision genome engineering through adenine base editing in plants. Nat Plants 4:427–431. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41477-018-0178-x
Kim H, Kim ST, Ryu J, Kang BC, Kim JS, Kim SG (2017) CRISPR/Cpf1-mediated DNA-free plant genome editing. Nat Commun 8:14406. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14406
Krieger E et al (2009) Improving physical realism, stereochemistry, and side-chain accuracy in homology modeling: four approaches that performed well in CASP8. Proteins 77(Suppl 9):114–122. https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.22570
Krishna H, Alizadeh M, Singh D, Singh U, Chauhan N, Eftekhari M, Sadh RK (2016) Somaclonal variations and their applications in horticultural crops improvement. 3 Biotech 6:54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-016-0389-7
Kuipers A, Jacobsen E, Visser R (1994) Formation and deposition of amylose in the potato tuber starch granule are affected by the reduction of granule-bound starch synthase. Gene Expr 6:43–52. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.6.1.43
Lemoine R et al (2013) Source-to-sink transport of sugar and regulation by environmental factors. Front Plant Sci 4:272. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2013.00272
Li C et al (2018) Expanded base editing in rice and wheat using a Cas9-adenosine deaminase fusion. Genome Biol 19:59. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-018-1443-z
Liang Z et al (2017) Efficient DNA-free genome editing of bread wheat using CRISPR/Cas9 ribonucleoprotein complexes. Nat Commun 8:14261. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14261
Ma X, Zhu Q, Chen Y, Liu YG (2016) CRISPR/Cas9 platforms for genome editing in plants: developments and applications. Mol Plant 9:961–974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2016.04.009
Masson J, Lecerf M, Rousselle P, Perennec P, Pelletier G (1987) Plant regeneration from protoplasts of diploid potato derived from crosses of Solanum tuberosum with wild solanum species. Plant Sci 53:167–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-9452(87)90127-0
Melo F, Sánchez R, Sali A (2002) Statistical potentials for fold assessment protein. Science 11:430–448. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.110430
Muth J, Hartje S, Twyman RM, Hofferbert HR, Tacke E, Prufer D (2008) Precision breeding for novel starch variants in potato. Plant Biotechnol J 6:576–584. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7652.2008.00340.x
Nazarian-Firouzabadi F, Visser RGF (2017) Potato starch synthases: functions and relationships. Biochem Biophys Rep 10:7–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrep.2017.02.004
Nekrasov V, Wang C, Win J, Lanz C, Weigel D, Kamoun S (2017) Rapid generation of a transgene-free powdery mildew resistant tomato by genome deletion. Sci Rep 7:482. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-00578-x
Nishida K et al (2016) Targeted nucleotide editing using hybrid prokaryotic and vertebrate adaptive immune systems. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaf8729
Nishimasu H et al (2018) Engineered CRISPR-Cas9 nuclease with expanded targeting space. Science 361:1259. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aas9129
Pan C et al (2016) CRISPR/Cas9-mediated efficient and heritable targeted mutagenesis in tomato plants in the first and later generations. Sci Rep 6:24765. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep24765
Park I-M, Ibáñez AM, Zhong F, Shoemaker CF (2007) Gelatinization and pasting properties of waxy and non-waxy rice starches. Starch Stärke 59:388–396. https://doi.org/10.1002/star.200600570
Pauwels L et al (2018) A dual sgRNA approach for functional genomics in Arabidopsis thaliana. G3 (Bethesda) 8:2603–2615. https://doi.org/10.1534/g3.118.200046
Peng A et al (2017) Engineering canker-resistant plants through CRISPR/Cas9-targeted editing of the susceptibility gene CsLOB1 promoter in citrus. Plant Biotechnol J 15:1509–1519. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12733
Popp MW, Maquat LE (2016) Leveraging rules of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay for genome engineering and personalized medicine. Cell 165:1319–1322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.053
Puchta H (2005) The repair of double-strand breaks in plants: mechanisms and consequences for genome evolution. J Exp Bot 56:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eri025
Ricroch A, Clairand P, Harwood W (2017) Use of CRISPR systems in plant genome editing: toward new opportunities in agriculture. Emerg Top Life Sci 1:169–182. https://doi.org/10.1042/etls20170085
Roldan I et al (2007) The phenotype of soluble starch synthase IV defective mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana suggests a novel function of elongation enzymes in the control of starch granule formation. Plant J 49:492–504. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02968.x
Rongine De Fekete MA, Leloir LF, Cardini CE (1960) Mechanism of starch biosynthesis. Nature 187:918. https://doi.org/10.1038/187918a0
Salomon S, Puchta H (1998) Capture of genomic and T-DNA sequences during double-strand break repair in somatic plant cells. EMBO J 17:6086–6095. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/17.20.6086
Schindele P, Wolter F, Puchta H (2018) Transforming plant biology and breeding with CRISPR/Cas9, Cas12 and Cas13. FEBS Lett 592:1954–1967. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.13073
Shen MY, Sali A (2006) Statistical potential for assessment and prediction of protein structures. Protein Sci 15:2507–2524. https://doi.org/10.1110/ps.062416606
Shimatani Z et al (2017) Targeted base editing in rice and tomato using a CRISPR-Cas9 cytidine deaminase fusion. Nat Biotechnol 35:441–443. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3833
Sonnewald U, Kossmann J (2013) Starches—from current models to genetic engineering. Plant Biotechnol J 11:223–232. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12029
Soyars CL, Peterson BA, Burr CA, Nimchuk ZL (2018) Cutting edge genetics: CRISPR/Cas9 editing of plant genomes. Plant Cell Physiol 59:1608–1620. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcy079
Steinert J, Schiml S, Fauser F, Puchta H (2015) Highly efficient heritable plant genome engineering using Cas9 orthologues from Streptococcus thermophilus and Staphylococcus aureus. Plant J 84:1295–1305. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13078
Sternberg SH, Richter H, Charpentier E, Qimron U (2016) Adaptation in CRISPR-Cas systems. Mol Cell 61:797–808. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2016.01.030
Tang X et al (2018) A large-scale whole-genome sequencing analysis reveals highly specific genome editing by both Cas9 and Cpf1 (Cas12a) nucleases in rice. Genome Biol 19:84. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-018-1458-5
Tian S et al (2018) Engineering herbicide-resistant watermelon variety through CRISPR/Cas9-mediated base-editing. Plant Cell Rep 37:1353–1356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-018-2299-0
Untergasser A, Cutcutache I, Koressaar T, Ye J, Faircloth BC, Remm M, Rozen SG (2012) Primer3—new capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res 40:e115. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks596
Veillet F, Gaillard C, Coutos-Thevenot P, La Camera S (2016) Targeting the AtCWIN1 gene to explore the role of invertases in sucrose transport in roots and during botrytis cinerea infection. Front Plant Sci 7:1899. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01899
Veillet F et al (2019) Transgene-free genome editing in tomato and potato plants using agrobacterium-mediated delivery of a CRISPR/Cas9 cytidine base editor. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020402
Visser RGF, Somhorst I, Kuipers GJ, Ruys NJ, Feenstra WJ, Jacobsen EJM (1991) Inhibition of the expression of the gene for granule-bound starch synthase in potato by antisense constructs. MGG GG 225:289–296. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00269861
Wang S, Zhang S, Wang W, Xiong X, Meng F, Cui X (2015) Efficient targeted mutagenesis in potato by the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Plant Cell Rep 34:1473–1476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-015-1816-7
Wang J, Meng X, Hu X, Sun T, Li J, Wang K, Yu H (2018) xCas9 expands the scope of genome editing with reduced efficiency in rice. Plant Biotechnol J 1:2. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13053
Webb B, Sali A (2016) comparative protein structure modeling using MODELLER. Curr Protoc Bioinform 54:561–563. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpbi.3
Woo JW et al (2015) DNA-free genome editing in plants with preassembled CRISPR-Cas9 ribonucleoproteins. Nat Biotechnol 33:1162–1164. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3389
Yan F et al (2018) Highly efficient A.T to G.C base editing by Cas9n-guided tRNA adenosine deaminase in rice. Mol Plant 11:631–634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2018.02.008
Yoo SD, Cho YH, Sheen J (2007) Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplasts: a versatile cell system for transient gene expression analysis. Nat Protoc 2:1565–1572. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.199
Zeeman SC, Kossmann J, Smith AM (2010) Starch: its metabolism, evolution, and biotechnological modification in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:209–234. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-042809-112301
Zong Y et al (2017) Precise base editing in rice, wheat and maize with a Cas9-cytidine deaminase fusion. Nat Biotechnol 35:438–440. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3811
Zong Y et al (2018) Efficient C-to-T base editing in plants using a fusion of nCas9 and human APOBEC3A. Nat Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.4261
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Puchta and his team (Botanical Institute II, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Karlsruhe, Germany) for providing the pDeCas9 plasmid via Marianne Mazier (INRA-UR1052, Montfavet, France) and Keiji Nishida for providing the pDicAID_nCas9-PmCDA_NptII_Della plasmid. We thank Fabien Nogué and Peter Rogowsky for their efficient management of the GENIUS project and their constructive discussions. We are grateful to Gabriel Guihard for his contribution in the sequencing of Desiree alleles. We thank the BrACySol BRC (INRA Ploudaniel, France) that provided us with the plants that were used in this study and Gisèle Joly and Catherine Chatot from Florimond Desprez/Germicopa (France) for helpful discussions and choice of the starch elite cultivar Furia. We are grateful to Jean-Louis Rolot from CRAW (Belgium) for providing us with the procedure to obtain in vitro microtubers as well as to Marie-Ange Dantec and all the INRA Ploudaniel greenhouse staff for acclimation and cultivation of the regenerated plantlets. Finally, we are thankful to Carolyn Engel-Gautier and Marina Perez Benitez for their help in correcting the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the INRA UMR IGEPP and the Investissement d’Avenir program of the French National Agency of Research for the project GENIUS (ANR-11-BTBR-0001_GENIUS). ZT is funded by a CIFRE PhD grant from SYNGENTA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FV, LC and JEC designed the experiments. FV, LC, MPK, ZT, FS, MM and NS performed the experiments. FV and JLG wrote the article. FV, LC, FS, NS, PD, JLG and JEC discussed the data and revised the article. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Laurence Tomlinson.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Veillet, F., Chauvin, L., Kermarrec, MP. et al. The Solanum tuberosum GBSSI gene: a target for assessing gene and base editing in tetraploid potato. Plant Cell Rep 38, 1065–1080 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-019-02426-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-019-02426-w