Abstract
Key message
Differentially expressed antioxidant enzymes, amino acids and proteins in contrasting rice genotypes, and co-location of their genes in the QTLs mapped using bi-parental population, indicated their role in salt tolerance.
Abstract
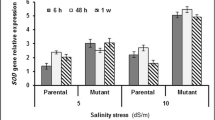
Soil salinity is a major environmental constraint limiting rice productivity. Salt-tolerant ‘CSR27’, salt-sensitive ‘MI48’and their extreme tolerant and sensitive recombinant inbred line (RIL) progenies were used for the elucidation of salt stress tolerance metabolic pathways. Salt stress-mediated biochemical and molecular changes were analyzed in the two parents along with bulked-tolerant (BT) and bulked-sensitive (BS) extreme RILs. The tolerant parent and BT RILs suffered much lower reduction in the chlorophyll as compared to their sensitive counterparts. Activities of antioxidant enzymes superoxide dismutase (SOD) and peroxidase (POD) and non-enzymatic antioxidant ascorbic acid were much higher in salt-stressed CSR27 and BT RILs than MI48 and BS RILs. Further, the tolerant lines showed significant enhancement in the levels of amino acids methionine and proline in response to salt stress in comparison to the sensitive lines. Similarly, the tolerant genotypes showed minimal reduction in cysteine content whereas sensitive genotypes showed a sharp reduction. Real time PCR analysis confirmed the induction of methionine biosynthetic pathway (MBP) enzymes cystathionine-β synthase (CbS), S-adenosyl methionine synthase (SAMS), S-adenosyl methionine decarboxylase (SAMDC) and serine hydroxymethyl transferase (SHMT) genes in tolerant lines, suggesting potential role of the MBP in conferring salt tolerance in rice variety CSR27. Proteome profiling also confirmed higher expression of SOD, POD and plastidic CbS and other proteins in the tolerant lines, whose genes were co-located in the QTL intervals for salt tolerance mapped in the RIL population. The study signifies integrated biochemical-molecular approach for identifying salt tolerance genes for genetic improvement for stress tolerant rice varieties.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACN:
-
Acetonotrile
- PMF:
-
Peptide mass fingerprint
- TFA:
-
Trifluoroacetic acid
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- POD:
-
Peroxidase
- CHAPS:
-
3-[(3-Cholamidopropyl) dimethylammonio]-1-propanesulphonate
- IEF:
-
Isoelectric focusing
- IPG:
-
Immobilized pH gradient
References
Abbasi FM, Komatsu S (2004) A proteomic approach to analyze salt-responsive proteins in rice leaf sheath. Proteomics 4:2072–2081
Aghaei K, Ehsanpour AA, Komatsu S (2008) Proteome analysis of potato under salt stress. J Proteome Res 7:4858–4868
Amirjani MR (2012) Effect of NaCl on rice physiological properties. Arch Phytopathol Plant Prot 45(2):228–243
Ashraf M (2009) Biotechnological approach of improving plant salt tolerance using antioxidants as markers. Biotechnol Adv 27:84–93
Atkinson NJ, Urwin PE (2012) The interaction of plant biotic and abiotic stresses: from genes to the field. J Exp Bot 63:3523–3543
Bartels D, Sunkar R (2005) Drought and salt tolerance in plants. Crit Rev Plant Sci 24:23–58
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare LD (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Benstein RM, Ludewig K, Wulfert S, Wittek S, Gigolashvili T, Frerigmann H, Gierth M, Flügge U, Krueger S (2013) Arabidopsis phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase1 of the phosphoserine pathway is essential for development and required for ammonium assimilation and tryptophan biosynthesis. Plant Cell 25:5011–5029. doi:10.1105/tpc.113.118992
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein–dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chattopadhyay A, Subba P, Pandey A, Bhushan D, Kumar R, Datta A, Chakraborty S, Chakraborty N (2011) Analysis of the grasspea proteome and identification of stress-responsive proteins upon exposure to high salinity, low temperature, and abscisic acid treatment. Phytochemistry 72(10):1293–1307
Cho K, Torres NL, Subbramanyam S, Deepak SA, Sardesai N, Han O, Williams CE, Ishii H, Iwahashi H, Rakwal R (2006) Protein extraction/solubilization protocol for monocot and dicot plant gel-based proteomics. J Plant Biol 49:413–420
Cho K, Agrawal GK, Shibato J, Jung YH, Kim YK, Nahm BH, Jwa NS, Tamogami S, Han O, Kohda K, Iwahashi H, Rakwal R (2007) Survey of differentially expressed proteins and genes in Jasmonic acid treated rice seedling shoot and root at the proteomics and transcriptomics levels. J Proteome Res 6:3581–3603
Choudhary MK, Basu D, Datta A, Chakraborty N, Chakraborty S (2009) Dehydration-responsive nuclear proteome of rice (Oryza sativa L.) illustrates protein network, novel regulators of cellular adaptation and evolutionary perspective. Mol Cell Proteom 8:1579–1598
Cossins EA, Chen L (1997) Folates and one-carbon metabolism in plants and fungi. Phytochem 45:437–452
Demiral T, Turkan I (2005) Comparative lipid peroxidation, antioxidant defense systems and proline content in roots of two rice cultivars differing in salt tolerance. Environ Expt Bot 53:247–257
Do PT, Drechsel O, Heyer AG, Hincha DK, Zuther E (2014) Changes in free polyamine levels, expression of polyamine biosynthesis genes, and performance of rice cultivars under salt stress: a comparison with responses to drought. Front Plant Sci 5:182
Duijn EV, Bakkes PJ, Heeren RMA, Heuvel RH, Heerikhuizen H, Vies SM, Heck AJR (2005) Monitoring macromolecular complexes involved in the chaperonin-assisted protein folding cycle by mass spectrometry. Nat Methods 2:371–376
FAO The state of food insecurity in the world (2014) World food and agriculture in review
FAO The state of food and agriculture (2008) World food and agriculture in review
Foyer CH (1993) Ascorbic acids. In: Antioxidant in higher plants. Alscher RG, Hess JL. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 31–58
Fridovich I (1986) Superoxide dismutases. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol 58:61–97
Giannopolitis CN, Ries SK (1977) Superoxide dismutase occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiol 59:309–314
Giovanelli J, Mudd SH, Datko AH (1985) Quantitative analysis of pathways of methionine metabolism and their regulation in Lemna. Plant Physiol 78:555–560
Gomez JM, Jimenez A, Olmos E, Sevilla F (2004) Location and effects of long-term NaCl stress on superoxide dismutase and ascorbate peroxidase isoenzymes of pea (Pisum sativum cv. Puget) chloroplasts. J Exp Bot 55(394):119–130
Gong B, Li X, VandenLangenberg KM, Wen D, Sun S, Wei M, Li Y, Yang F, Shi Q, Wang X (2014) Over expression of S-adenosyl-l-methionine synthetase increased tomato tolerance to alkali stress through polyamine metabolism. Plant Biotechnol J 12:694–708
Guo Z, Tan J, Zhuo C, Wang C, Xiang B, Wang Z (2014) Abscisic acid, H2O2 and nitric oxide interactions mediated cold-induced S-adenosylmethionine synthetase in Medicago sativa subsp. falcata that confers cold tolerance through up-regulating polyamine oxidation. Plant Biotechnol J 12(5):601–612
Hancock JT, Henson D, Nyirenda M, Desikan R, Harrison J, Lewis M, Hughes J, Neill SJ (2005) Proteomic identification of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase as an inhibitory target of hydrogen peroxide in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Biochem 43:828–835
Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA (2000) Plant cellular and molecular responses to high salinity. Ann Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 51:463–499
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198
Hernandez JA, Alamansa MS (2002) Short-term effects of salt stress on antioxidant systems and leaf water relations of pea leaves. Physiol Plant 115:251–257
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. California Agriculture Experiment Station Circular 347, revised
Hu L, Li H, Pang H, Fu J (2012) Responses of antioxidant gene, protein and enzymes to salinity stress in two genotypes of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) differing in salt tolerance. J Plant Physiol 169(2):146–156
Kim YO, Kim JS, Kang H (2005) Cold-inducible zinc finger containing glycine-rich RNA-binding protein contributes to the enhancement of freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 42:890–900
Kim JK, Bamba T, Harada K, Fukusaki AKE (2007) Time-course metabolic profiling in Arabidopsis thaliana cell cultures after salt stress treatment. J Exp Botany 58(3):415–442
Kim SH, Kim SH, Palaniyandi SA, Yang SH, Suh JW (2015) Expression of potato S-adenosyl-l-methionine synthase (SbSAMS) gene altered developmental characteristics and stress responses in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 87:84–91
Kunert Kj, Ederer M (1985) Leaf aging and lipid peroxidation: the role of the antioxidants vitamin E and C. Physiol Plant 65:85–88
Lee DH, Kim YS, Lee CB (2001) The inductive responses of the antioxidant enzymes by salt stress in the rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Plant Physiol 158:737–745
Less H, Galili G (2009) Coordinations between gene modules control the operation of plant amino acid metabolic networks. BMC Syst Biol 26:3–14
Lichtenthaler HK, Welburn AR (1983) Determination of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochem Soc Trans 11:591–592
Liepman AH, Olsen LJ (2004) Genomic analysis of aminotransferases in Arabidopsis thaliana. Crit Rev Plant Sci 23:73–89
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Lugan R, Niogret MF, Leport L, Guégan JP, Larher FR, Savoure A, Kopka J, Bouchereau A (2010) Metabolome and water homeostasis analysis of Thellungiella salsuginea suggests that dehydration tolerance is a key response to osmotic stress in this halophyte. Plant Journal 64:215–229
Ma H, Song L, Shu Y, Wang S, Niu J, Wang Z, Yu T, Gu W, Ma H (2012) Comparative proteomic analysis of seedling leaves of different journal of proteomics salt tolerant soybean genotypes. J Proteom 75:1529–1546
Manaa A, Ahmed HB, Valot B, Bouchet JP, Aschi-Smiti S, Causse M, Faurobert M (2011) Salt and genotype impact on plant physiology and root proteome variations in tomato. J Exp Botany 62(8):2797–2813
Meloni DA, Oliva MA, Martinez CA, Cambraia J (2003) Photosynthesis and activity of superoxide dismutase, peroxidase and glutathione reductase in cotton under salt stress. Environ Exp Botany 49:69–76
Mishra V, Srivastava G, Prasad SM, Abraham G (2008) Growth, photosynthetic pigments and photosynthetic activity on seedling stage of Vigna unguiculata in response to UV-B and dimethoate. Pesticide Biochem Physiol 92:30–37
Mishra V, Srivastava G, Prasad SM (2009) Antioxidant response of bitter gourd (Momordica charantia L.) seedlings to interactive effect of dimethoate and UV-B irradiation. Sci Hortic 120:373–378
Mishra V, Mishra P, Srivastava G, Prasad SM (2011) Effect of dimethoate and UV-B irradiation on the response of antioxidant defense systems in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L.) seedlings. Pesticide Biochem Physiol 100:118–123
Misra AN, Sahu SM, Mishra M, Singh P, Meera I, Das N, Kar M, Sahu P (1997) Sodium chloride induced changes in leaf growth and pigment and protein contents in two rice cultivars. Biol Plant 39:257–262
Mizuno H, Kawahara Y, Sakai H, Kanamori H, Wakimoto H, Yamagata H, Oono Y, Wu J, Ikawa Itoh T, Matsumoto T (2010) Massive parallel sequencing of mRNA in identification of unannotated salinity stress-inducible transcripts in rice (Oryza sativa L.). BMC Genom 11:683–696
Moradi F, Ismail A (2007) Responses of photosynthesis, chlorophyll fluorescence and ROS-scavenging systems to salt stress during seedling and reproductive stages in rice. Ann Bot 99:1161–1173
Munns R, James RA, Läuchli A (2006) Approaches to increasing the salt tolerance of wheat and other cereals. J Exp Bot 57:1025–1043
Nair P, Kandasamy S, Zhang J, Ji X, Kirby C, Benkel B, Hodges MD, Critchley AT, Hiltz D, Prithiviraj B (2012) Transcriptional and metabolomic analysis of Ascophyllum nodosum mediated freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Genom 13:643
Noctor G, De Paepe R, Foyer CH (2007) Mitochondrial redox biology and homeostasis in plants. Trends Plant Sci 12:125–134
Nohzadeh MS, Habibi RM, Heidari M, Salekdeh GH (2007) Proteomics reveals new salt responsive proteins associated with rice plasma membrane. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71:2144–2145
Ortega-Galisteo AP, Rodriguez-Serrano M, Pazmin DM, Gupta DK, Sandalio LM, Romero-Puertas MC (2012) S-Nitrosylated proteins in pea (Pisum sativum L.) leaf peroxisomes: changes under abiotic stress. J Exp Bot 63(5):2089–2103
Oser BL (1979) Hawks physiological chemistry. McGraw Hill, New York, pp 702–705
Pandit A, Rai V, Bal S, Sinha S, Kumar V, Chauhan M, Gautam RK, Singh R, Sharma PC, Singh AK, Gaikwad K, Sharma TR, Mohapatra T, Singh NK (2010) Combining QTL mapping and transcriptome profiling of bulked RILs for identification of functional polymorphism for salt tolerance genes in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Genet Genom 284:121–136
Pandit A, Rai V, Sharma TR, Sharma PC, Singh NK (2011) Differentially expressed genes in sensitive and tolerant rice varieties in response to salt-stress. J Plant Biochem Biotech 20:149–154
Parker R, Flowers TJ, Moore AL, Harpham NV (2006) An accurate and reproducible method for proteome profiling of the effects of salt stress in the rice leaf lamina. J Exp Bot 57:1109–1118
Petricka JJ, Schauer MA, Megraw M, Breakfield NW, Thompson JW, Georgiev S, Soderblom EJ, Ohler U, Moseley MA, Grossniklaus U, Benfey PN (2012) The protein expression landscape of the Arabidopsis root. PNAS 109(18):6811–6818
Ralph S, Park JY, Bohlmann J, Mansfield S (2006) Dirigent proteins in conifer defense: gene discovery, phylogeny, and differential wound- and insect induced expression of a family of DIR and DIR-like genes in spruce (Picea spp.). Plant Mole Biol 60:21–40
Reddy MP, Vora AB (1986) Changes in pigment composition. Hill reaction activity and saccharides metabolism in bajra (Penisetum typhoides S & H) leaves under NaCl salinity. Photosynthetica 20:50–55
Rey P, Cuine S, Eymery F, Garin J, Court M, Jacquot JP, Rouhier N, Broin M (2005) Analysis of the proteins targeted by CDSP32, a plastidic thioredoxin participating in oxidative stress responses. Plant J 41:31–42
Ruiz JM, Blumwald E (2002) Salinity-induced glutathione synthesis in Brassica napus. Planta 214:965–969
Sarhadi E, Bazargani MM, Sajise AG, Abdolahi S, Vispo NA, Arceta M, Nejad GM, Singh RK, Salekdeh GH (2012) Proteomic analysis of rice anthers under salt stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 58:280–287
Scandalios JG (1993) Oxygen stress and superoxide dismutase. Plant Physiol 101:712–726
Sedigheh HG, Mortazavian M, Norouzian D, Atyabi M, Akbarzadeh A, Hasanpoor K, Ghorbani M (2011) Oxidative stress and leaf senescence. BMC Res. Notes 4:477
Sengupta S, Majumder AL (2009) Insight into the salt tolerance factors of a wild halophytic rice, Porteresiacoarctata: a physiological and proteomic approach. Planta 229:911–929
Singh RK, Mishra B (2004) Role of Central Soil Salinity Research Institute in Genetic improvement of rice varieties in India. In: Sharma SD, Rao UP (eds) Genetic improvement of rice varieties in India. pp 189–242
Singh R, Singh Y, Xalaxo S, Verulkar S, Yadav N, Singh S, Singh N, Prasad KSN, Kondayya K, Ramana Rao PV, Rani MG, Anuradha T, Suraynarayana Y, Sharma PC, Krishnamurthy SL, Sharma SK, Dwivedi JL, Singh AK, Singh PK, Nilanjay Singh NK, Kumar R, Chetia SK, Ahmad T, Rai M, Perraju P, Pande A, Singh DN, Mandal NP, Reddy JN, Singh ON, Kataral JL, Marandi B, Swain P, Sarkar RK, Singh DP, Mohapatra T, Padmawathi G, Ram T, Kathiresan RM, Paramsivam K, Nadarajan S, Thirumeni S, Nagarajan M, Singh AK, Vikram P, Kumar A, Septiningshih E, Singh US, Ismail AM, Mackill D, Singh NK (2016) From QTL to variety-harnessing the benefits of QTLs for drought, flood and salt tolerance in mega rice varieties of India through a multi-institutional network. Plant Sci 242:278–287
Teramura AH, Sullivan JH (1994) Effects of UV-B radiation on photosynthesis and growth of terrestrial plants. Photosynth Res 39:463–473
Toubiana D, Batushansky A, Tzfadia O, Scossa F, Khan A, Barak S, Zamir D, Fernie AR, Nikoloski Z, Fait A (2015) Combined correlation-based network and mQTL analyses efficiently identified loci for branched-chain amino acid, serine to threonine, and proline metabolism in tomato seeds. Plant J 81:121–133
Tripathi BN, Gaur JP (2004) Relationship between Cu- and Zn-induced oxidative stress and proline accumulation Scenedesmus sp. Planta 219:97–404
Waditee R, Bhuiyan Md NH, Rai V, Aoki K, Tanaka Y, Hibino T, Suzuki S, Takano J, Jagendorf AT, Takabe T (2005) Genes for direct methylation of glycine provide high levels of glycine betaine and abiotic-stress tolerance in Synechococcus and Arabidopsis. PNAS 102(5):1318–1323
Walden R, Cordeiro A, Tiburcio AF (1997) Polya-mines: small molecules triggering pathways in plant growth and development. Plant Physiol 113:1009–1013
Walia H, Wilson C, Zeng L, Ismail AM, Condamine P, Close TJ (2007) Genome-wide transcriptional analysis of salinity-stressed japonica and indica rice genotypes during panicle initiation stage. Plant Molecular Biology (63):609–623
Wan XY, Liu JY (2008) Comparative proteomics analysis reveals an intimate protein network provoked by hydrogen peroxide stress in rice seedling leaves. Mol Cell Proteom 7:1469–1488
Widodo Patterson JH, Newbigin E, Tester M, Bacic A, Roessner U (2009) Metabolic responses to salt stress of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) cultivars, Sahara and Clipper, which differ in salinity tolerance. J Exp Bot 60:4089–4103
Wirtz M, Birke H, Heeg C, Muller C, Hosp F, Throm C, Konig S, Feldman-Salit A, Rippe K, Petersen G, Wade RC, Rybin V, Scheffzek K, Hell R (2010) Structure and function of the hetero-oligomeric cysteine synthase complex in plants. J Biol Chem 285:32810–32817
Yan S, Tang Z, Su W, Sun W (2005) Proteomic analysis of salt stress-responsive proteins in rice root. Proteomics 5:235–244
Yeo AR, Flowers TJ (1983) Varietal differences of sodium ions in rice leaves. Physiol Plant 59:189–195
Zarembinski TI, Theologis A (1994) Ethylene biosynthesis and action: a case of conservation. Plant Mol Biol 26(5):1579–1597
Zhang XZ (1992) The measurement and mechanism of lipid peroxidation and SOD, POD, and CAT activities in biological system. Agriculture Press, Beijing
Zhang L, Tian LH, Zhao JF, Song Y, Zhang CJ, Guo Y (2009) Identification of an apoplastic protein involved in the initial phase of salt stress response in rice root by two-dimensional electrophoresis. Plant Physiol 149:916–928
Zhao Q, Zhang H, Wang T, Chen S, Dai S (2013) Proteomics-based investigation of salt-responsive mechanisms in plant roots. J Proteom 26:230–253
Acknowledgments
We thankfully acknowledge the financial support of Indian Council of Agricultural Research under the NPTC project (NPTC/2049-3021), VR and TT are thankful to funding support by Department of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of India (DST/INT/JSPS/PROJ/10).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by M. Prasad.
P. Mishra and V. Mishra contributed equally.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, P., Mishra, V., Takabe, T. et al. Elucidation of salt-tolerance metabolic pathways in contrasting rice genotypes and their segregating progenies. Plant Cell Rep 35, 1273–1286 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-016-1959-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-016-1959-1