Abstract
Key message
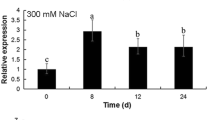
SpAQP1 was strongly induced by salt in an ABA-independent way, promoted seed germination and root growth in transgenic tobaccos and increased salt tolerance by increasing the activities of antioxidative enzymes.
Abstract
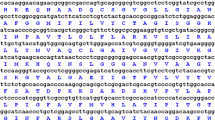
Aquaporin (AQP) plays crucial roles in the responses of plant to abiotic stresses such as drought, salt and cold. Compared to glycophytes, halophytes often have excellent salt and drought tolerances. To uncover the molecular mechanism of halophyte Sesuvium portulacastrum tolerance to salt, in this study, an AQP gene, SpAQP1, from S. portulacastrum was isolated and characterized. The amino acid sequence of SpAQP1 shared high homology with that of plant plasma membrane intrinsic proteins (PIPs) and contained the distinct molecular features of PIPs. In the phylogenic tree, SpAQP1 was evidently classified as the PIP2 subfamily. SpAQP1 is expressed in roots, stems and leaves, and was significantly induced by NaCl treatment and inhibited by abscisic acid (ABA) treatment. When heterologously expressed in yeast and tobacco, SpAQP1 enhanced the salt tolerance of yeast strains and tobacco plants and promoted seed germination and root growth under salt stress in transgenic plants. The activity of antioxidative enzymes including superoxide dismutase, peroxidase and catalase was increased in transgenic plants overexpressing SpAQP1. Taken together, our studies suggested that SpAQP1 functioned in the responses of S. portulacastrum to salt stress and could increase salt tolerance by enhancing the antioxidative activity of plants.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharon R, Shahak Y, Wininger S, Bendov R, Kapulnik Y, Galili G (2003) Overexpression of a plasma membrane aquaporin in transgenic tobacco improves plant vigor under favorable growth conditions but not under drought or salt stress. Plant Cell 15:439–447
Aroca R, Porcel R, Ruiz-Lozano JM (2012) Regulation of root water uptake under abiotic stress conditions. J Exp Bot 63(1):43–57
Bienert GP, Heinen RB, Berny MC, Chaumont F (2014) Maize plasma membrane aquaporin ZmPIP2;5, but not ZmPIP1;2, facilitates transmembrane diffusion of hydrogen peroxide. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Biomembr 1838(1):216–222
Blokhina O, Virolainen E, Fagerstedt KV (2003) Antioxidants, oxidative damage and oxygen deprivation stress: a review. Ann Bot 91:179–194
Boursiac Y, Chen S, Luu DT, Sorieul M, van den Dries N, Maurel C (2005) Early effects of salinity on water transport in Arabidopsis roots molecular and cellular features of aquaporin expression. Plant Physiol 139(2):790–805
Cakmak I, Strbac D, Marschner H (1993) Activities of hydrogen peroxide-scavenging enzymes in germinating wheat seeds. J Exp Bot 44(1):127–132
Chaumont F, Barrieu F, Jung R, Chrispeels MJ (2000) Plasma membrane intrinsic proteins from maize cluster in two sequence subgroups with differential aquaporin activity. Plant Physiol 122:1025–1034
Chaumont F, Barrieu F, Wojcik E, Chrispeels MJ, Jung R (2001) Aquaporins constitute a large and highly divergent protein family in maize. Plant Physiol 125(3):1206–1215
Cui XH, Hao FS, Chen H, Chen J, Wang XC (2008) Expression of the Vicia faba VfPIP1 gene in Arabidopsis thaliana plants improves their drought resistance. J Plant Res 121:207–214
Danielson J, Johanson U (2008) Unexpected complexity of the aquaporin gene family in the moss Physcomitrella patens. BMC Plant Biol 8:45
Dynowski M, Schaaf G, Loque D, Moran O, Ludewig U (2008) Plant plasma membrane water channels conduct the signalling molecule H2O2. Biochem J 414:53–61
Fan W, Zhang Z, Zhang Y (2009) Cloning and molecular characterization of fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate aldolase gene regulated by high-salinity and drought in Sesuvium portulacastrum. Plant Cell Rep 28(6):975–984
Gao Z, He X, Zhao B, Zhou C, Liang Y, Ge R, Shen Y, Huang Z (2010) Overexpressing a putative aquaporin gene from wheat, TaNIP, enhances salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 51(5):767–775
Giannopolitis CN, Ries SK (1977) Superoxide dismutases I. Occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiol 59(2):309–314
Gomes D, Agasse A, Thiébaud P, Delrot S, Gerós H, Chaumont F (2009) Aquaporins are multifunctional water and solute transporters highly divergent in living organisms. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Biomembr 1788:1213–1228
Guo L, Wang ZY, Lin H, Cui WE, Chen J, Liu M, Chen ZL, Qu LJ, Gu H (2006) Expression and functional analysis of the rice plasma-membrane intrinsic protein gene family. Cell Res 16:277–286
Hasewaga PM, Bressan RA, Zhu JK, Bohnert HJ (2000) Plant cellular and molecular response to high salinity. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 51:263–499
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. Calif Agric Exp Stn Circ 347:1–32 (2nd edit)
Hooijmaijers C, Rhee JY, Kwak KJ, Chung GC, Horie T, Katsuhara M, Kang H (2012) Hydrogen peroxide permeability of plasma membrane aquaporins of Arabidopsis thaliana. J Plant Res 125:147–153
Jaleel CA, Riadh K, Gopi R, Manivannan P, Inès J, Al-Juburi HJ, Zhao CX, Shao HB, Panneerselvam R (2009) Antioxidant defense responses: physiological plasticity in higher plants under abiotic constraints. Acta Physiol Plant 31:427–436
Jang JY, Kim DG, Kim YO, Kim JS, Kang H (2004) An expression analysis of a gene family encoding plasma membrane aquaporins in response to abiotic stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 54(5):713–725
Jang JY, Lee SH, Rhee JY, Chung GC, Ahn SJ, Kang H (2007a) Transgenic Arabidopsis and tobacco plants overexpressing an aquaporin respond differently to various abiotic stresses. Plant Mol Biol 64:621–632
Jang JY, Rhee JY, Kim DG, Chung GC, Lee JH, Kang H (2007b) Ectopic expression of a foreign aquaporin disrupts the natural expression patterns of endogenous aquaporin genes and alters plant responses to different stress conditions. Plant Cell Physiol 48:1331–1339
Johanson U, Karlsson M, Johansson I, Gustavsson S, Sjovall S, Fraysse L, Weig AR, Kjellbom P (2001) The complete set of genes encoding major intrinsic proteins in Arabidopsis provides a framework for a new nomenclature for major intrinsic proteins in plants. Plant Physiol 126:1358–1369
Kaldenhoff R, Fischer M (2006) Aquaporins in plants. Acta Physiol 187(1–2):169–176
Katsuhara M (2007) Molecular mechanisms of water uptake and transport in plant roots: research progress with water channel aquaporins. Plant Root 1:22–26
Katsuhara M, Koshio K, Shibasaka M, Hayashi Y, Hayakawa T, Kasamo K (2003) Over-expression of a barley aquaporin increased the shoot/root ratio and raised salt sensitivity in transgenic rice plants. Plant Cell Physiol 44(12):1378–1383
Kirch HH, Vera-Estrella R, Golldack D, Quigley F, Michalowski CB, Barkla BJ, Bohnert HJ (2000) Expression of water channel proteins in Mesembryanthemum crystallinum. Plant Physiol 123:111–124
Li G, Santoni V, Maurel C (2014) Plant aquaporins: roles in plant physiology. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Gen Subj 1840:1574–1582
Li GW, Zhang MH, Cai WM, Sun WN, Su WA (2008) Characterization of OsPIP2; 7, a water channel protein in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 49(12):1851–1858
Lian HL, Yu X, Lane D, Sun WN, Tang ZC, Su W (2006) Upland rice and lowland rice exhibited different PIP expression under water deficit and ABA treatment. Cell Res 16:651–660
Lokhande VH, Srivastava AK, Srivastava S, Nikam TD, Suprasanna P (2011) Regulated alterations in redox and energetic status are the key mediators of salinity tolerance in the halophyte Sesuvium portulacastrum (L.) L. Plant Growth Regul 65(2):287–298
Mahdieh M, Mostajeran A, Horie T, Katsuhara M (2008) Drought stress alters water relations and expression of PIP-type aquaporin genes in Nicotiana tabacum plants. Plant Cell Physiol 49:801–813
Martínez-Ballesta MC, Aparicio F, Pallás V, Martínez V, Carvajal M (2003) Influence of saline stress on root hydraulic conductance and PIP expression in Arabidopsis. J Plant Physiol 160:689–697
Martinez-Ballesta MC, Carvajal M (2014) New challenges in plant aquaporin biotechnology. Plant Sci 217:71–77
Marulanda A, Azcón R, Chaumont F, Ruiz-Lozano JM, Aroca R (2010) Regulation of plasma membrane aquaporins by inoculation with a Bacillus megaterium strain in maize (Zea mays L.) plants under unstressed and salt-stressed conditions. Planta 232:533–543
Maurel C, Verdoucq L, Luu DT, Santoni V (2008) Plant aquaporins: membrane channels with multiple integrated functions. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:595–624
Messedi D, Labidi N, Grignon C, Abdelly C (2004) Limits imposed by salt to the growth of the halophyte Sesuvium portulacastrum. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 167:720–725
Messedi D, Sleimi N, Abdelly C (2001) Salt tolerance in Sesuvium portulacastrum. In: Horst WJ (ed) Plant nutrition-Food security and sustainability of agro-ecosystems. Springer, The Netherlands, pp 406–407
Miller G, Suzuki N, Ciftci-Yilmaz S, Mittler R (2010) Reactive oxygen species homeostasis and signalling during drought and salinity stresses. Plant Cell Environ 33:453–467
Moshelion M, Becker D, Biela A, Uehlein N, Hedrich R, Otto B, Levi H, Moran N, Kaldenhoff R (2002) Plasma membrane aquaporins in the motor cells of Samanea saman: diurnal and circadian regulation. Plant Cell 14:727–739
Munns R (2002) Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. Plant Cell Environ 25:239–250
Pasternak D, Nerd A (1995) Research and utilization of halophytes in Israel. In: Choukr-Allah R, Malcolm CV, Hamdy A (eds) Halophyte and biosaline agriculture. Marcell Decker, New York, pp 325–348
Qian ZJ, Song JJ, Chaumont F, Ye Q (2014) Differential responses of plasma membrane aquaporins in mediating water transport of cucumber seedlings under osmotic and salt stresses. Plant Cell Environ 38(3):461–473
Ramani B, Papenbrock J, Schmidt A (2004) Connecting sulfur metabolism and salt tolerance mechanisms in the halophytes Aster tripolium and Sesuvium portulacastrum. J Trop Ecol 45:173–182
Ramani B, Reeck T, Debez A, Stelzer R, Huchzermeyer B, Schmidt A, Papenbrock J (2006) Aster tripolium L. and Sesuvium portulacastrum L.: two halophytes, two strategies to survive in saline habitats. Plant Physiol Biochem 44:395–408
Sade N, Gebretsadik M, Seligmann R, Schwartz A, Wallach R, Moshelion M (2010) The role of tobacco Aquaporin1 in improving water use efficiency, hydraulic conductivity, and yield production under salt stress. Plant Physiol 152:245–254
Sade N, Vinocur BJ, Diber A, Shatil A, Ronen G, Nissan H, Wallach R, Karchi H, Moshelion M (2009) Improving plant stress tolerance and yield production: is the tonoplast aquaporin SlTIP2;2 a key to isohydric to anisohydric conversion? New Phytol 181:651–661
Sakurai J, Ishikawa F, Yamaguchi T, Uemura M, Maeshima M (2005) Identification of 33 rice aquaporin genes and analysis of their expression and function. Plant Cell Physiol 46:1568–1577
Schäffner AR (1998) Aquaporin function, structure, and expression: are there more surprises to surface in water relations? Planta 204(2):131–139
Suga S, Komatsu S, Maeshima M (2002) Aquaporin isoforms responsive to salt and water stresses and phytohormones in radish seedlings. Plant Cell Physiol 43:1229–1237
Sundararaj R, Nagaraj S, Rengasamy R (2014) Assessment of NaCl accumulation and tolerance potential of Sesuvium portulacastrum L. J Acad Ind Res 2(10):578
Sutka M, Li G, Boudet J, Boursiac Y, Doumas P, Maurel C (2011) Natural variation of root hydraulics in Arabidopsis grown in normal and salt-stressed conditions. Plant Physiol 155(3):1264–1276
Venkatesalu V, Chellappan KP (1993) Photochemical characteristics of Sesuvium portulacastrum L. under sodium chloride stress. Photosynthetica 29:139–141
Venkatesalu V, Raj Kumar R, Chellappan KP (1994) Sodium chloride stress on organic constituents of Sesuvium portulacastrum L., a salt marsh halophyte. J Plant Nutr 17:1635–1645
Wan X, Steudle E, Hartung W (2004) Gating of water channels (aquaporins) in cortical cells of young corn roots by mechanical stimuli (pressure pulses): effects of ABA and of HgCl2. J Exp Bot 55:411–422
Wang LL, Chen AP, Zhong NQ, Liu N, Wu XM, Wang F, Xia GX (2014) The Thellungiella salsuginea tonoplast aquaporin TsTIP1;2 functions in protection against multiple abiotic stresses. Plant Cell Physiol 55(1):148–161
Yamada S, Katsuhara M, Kelly WB, Michalowski CB, Bohnert HJ (1995) A family of transcripts encoding water channel proteins: tissue-specific expression in the common ice plant. Plant Cell 7:1129–1142
Zheng X, Van Huystee RB (1992) Peroxidase-regulated elongation of segments from peanut hypocotyls. Plant Sci 81(1):47–56
Zhou S, Hu W, Deng X, Ma Z, Chen L, Huang C, Wang C, Wang J, He YZ, Yang GX, He GY (2012) Overexpression of the wheat aquaporin gene, TaAQP7, enhances drought tolerance in transgenic tobacco. PLoS One 7(12):e52439
Zhu C, Schraut D, Hartung W, Schäffner AR (2005) Differential responses of maize MIP genes to salt stress and ABA. J Exp Bot 56(421):2971–2981
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Major Technology Project of Hainan, China—Germplasm and Gene Resources Research (ZDZX2013023-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by C.-H. Dong.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, W., Liu, X., Zhu, J. et al. An aquaporin gene from halophyte Sesuvium portulacastrum, SpAQP1, increases salt tolerance in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell Rep 35, 385–395 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-015-1891-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-015-1891-9