Abstract
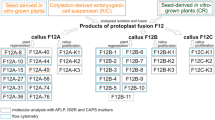
Somatic hybridization is a potential method for gene transfer from wild relatives to cultivated crops that can overcome sexual incompatibilities of two distantly related species. In this study, interspecific asymmetric somatic hybrids of Brassica oleracea var. botrytis (cauliflower) and Brassica nigra (black mustard) were obtained by protoplast fusion and their backcrossed (BC3) and selfed (S3) offspring were analyzed. Cytological analysis showed that the B. nigra chromosomes were successively eliminated in the backcrosses with cauliflower. The fertility of the hybrid progenies was quite different due to the asynchronous and abnormal chromosome behavior of pollen mother cells (PMC) during meiosis. Analysis of sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) showed that all of these hybrids mainly had the DNA banding pattern from the two parents with some alterations. Genetically, the selfed generations were closer to B. nigra, while the backcrossed generations were closer to the cauliflower parent. Analysis of cleaved amplified polymorphic sequences (CAPS) and restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLP) showed that all somatic hybrids in this study contained chloroplast (cp) DNA of the donor parent black mustard, while mitochondrial (mt) DNA showed evidence of recombination and variations in the regions analyzed. Furthermore, three BC3 plants (originated from somatic hybrids 3, 4, 10) with 2–8 B. nigra-derived chromosomes shown by genomic in situ hybridization (GISH) displayed a more cauliflower-like morphology and high resistance to black-rot. These plants were obtained as bridge materials for further analysis and breeding.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bain DC (1955) Resistance of cabbage to black rot. Phytopathology 45:35–37
Cheng YJ, Guo WW, Deng XX (2003) Molecular characterization of cytoplasmic and nuclear genomes in phenotypically abnormal Valencia orange (Citrus sinensis)+Meiwa kumquat (Fortunella crassifolia) intergeneric somatic hybrids. Plant Cell Rep 21:445–451
Cheng AX, Xia GM, Zhi DY, Chen HM (2004) Intermediate fertile Triticum aestivum (+) Agropyron elongatum somatic hybrids are generated by low doses of UV irradiation. Cell Res 14:86–91
Chevre AM, Eber F, This P, Barret P, Tanguy X, Brun H, Delseny M, Renard M (1996) Characterization of Brassica nigra chromosomes and blackleg resistance in B. napus–B. nigra addition lines. Plant Breeding 115:113–118
Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB (1983) A plant DNA minipreparation: version II. Plant Mol Rep 1:19–21
Dickson MD, Hunter JE (1987) Inheritance of resistance in cabbage seedlings to black rot. HortScience 22:108–109
Dolezel J, Binarova P, Lucretti S (1989) Analysis of nuclear DNA content in plant cells by flow cytometry. Biol Plant 31:113–120
Du XZ, Ge XH, Yao XC, Zhao ZG, Li ZY (2009) Production and cytogenetic characterization of intertribal somatic hybrids between Brassica napus and Isatis indigotica and backcross progenies. Plant Cell Rep 28:1105–1113
Ferriol M, Picó B, Nuez F (2003) Genetic diversity of a germplasm collection of Cucurbita pepo using SRAP and AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 107:271–282
Fu CH, Chen CL, Guo WW, Deng XX (2004) GISH, AFLP and PCR-RFLP analysis of an intergeneric somatic hybrid combining Goutou sour orange and Poncirus trifoliata. Plant Cell Rep 23:391–396
Gerdemann MK, Sacristán MD, Braatz C, Schieder O (1994) Utilization of asymmetric somatic hybridization for the transfer of disease resistance from Brassica nigra to Brassica napus. Plant Breeding 113:106–113
Gernand D, Rutten T, Pickering R, Houben A (2006) Elimination of chromosomes in Hordeum vulgare × H. bulbosum crosses at mitosis and interphase involves micronucleus formation and progressive heterochromatinization. Cytogenet Genome Res 114:169–174
Glimelius K (1999) Somatic hybridization. In: Go′mez-Campo C (ed) Biology of Brassica Coenospecies. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 107–148
Glimelius K, Fahlesson J, Landgren M, Sjodin C, Sundberg E (1991) Gene transfer via somatic hybridization in plants. Tibtech 9:24–30
Groat CM (2003) The sodium chloride tolerance of Brassica nigra. Dissertation, University of California
Hansen LN, Earle ED (1994) Novel flowering and fatty acid characters in rapid cycling Brassica napus L. resynthesized by protoplast fusion. Plant Cell Rep 14:151–156
Hansen LN, Earle ED (1995) Transfer of resistance to Xanthomonas campestris pv campestris into Brassica oleracea L. by protoplast fusion. Theor Appl Genet 91:1293–1300
Hansen LN, Earle ED (1997) Somatic hybrids between Brassica oleracea l. and Sinapis alba L. with resistance to Alternaria brassicae (Berk) Sacc. Theor Appl Genet 94:1078–1085
Ignatov A, Kuginuki Y, Hida K (1998) Race-specific reaction of resistance to black rot in Brassica oleracea. Eur J Plant Pathol 104:821–827
Jourdan P, Salazar E (1993) Brassica carinata resythesized by protoplast fusion. Theor Appl Genet 86:567–572
Li SD (1995) Advances in main vegetable crops breeding for diseases resistance in China [M]. Science Press, Beijing, pp 263–266
Li G, Quiros CF (2001) Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP), a new marker system based on a simple PCR reaction: its application to mapping and gene tagging in Brassica. Theor Appl Genet 103:455–461
Liu M, Li ZY (2007) Genome doubling and chromosome elimination with fragment recombination leading to the formation of Brassica rapa-type plants with genomic alterations in crosses with Orychophragmus violaceus. Genome 50:985–993
Liu JH, Xu XY, Deng XX (2005) Intergeneric somatic hybridization and its application to crop genetic improvement. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 82:19–44
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassay with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–479
Narasimhulu SB, Kirti PB, Shyam P, Chopra VL (1992) Resynthesis of Brassica carinata by protoplast fusion and recovery of a novel cytoplasmic hybrid. Plant Cell Rep 11:428–432
Navra′tilova′ B (2004) Protoplast cultures and protoplast fusion focused on Brassicaceae—a review. Hort Sci (Prague) 31:140–157
Pühler A, Arlat M, Becker A, Göttfert M, Morrissey JP, O’Gara F (2004) What can bacterial genome research teach us about bacteria–plant interactions? Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:137–147
Ryschka U, Schumann G, Klocke E, Scholze P, Neumann M (1996) Somatic hybridization in Brassicaceae. Acta Hort 407:201–208
Saal B, Struss D (2005) RGA- and RAPD-derived SCAR markers for a Brassica B-genome introgression conferring resistance to blackleg in oilseed rape. Theor Appl Genet 111:281–290
Scholze P, Kramer R, Ryschka U, Klocke E, Schumann G (2010) Somatic hybrids of vegetable brassicas as source for new resistances to fungal and virus diseases. Euphytica 176:1–14
Shelton AM, Hunter JE (1985) Evaluation of the potential of the flea bettle Phyllotreta cruciferae to transmit Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris, casual agent of black rot of crucifers. Can J Plant Pathol 7:308–310
Sheng XG, Liu F, Zhu YL, Zhao H, Zhang L, Chen B (2008) Production and analysis of intergeneric somatic hybrids between Brassica oleracea and Matthiola incana. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 92:55–62
Sneath PHA, Sokal RR (1973) Numerical taxonomy. WH Freeman and Co, San Francisco
Taylor JD, Conway J, Roberts SJ, Astley D, Vicente JG (2002) Sources and origin of resistance to Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris in Brassica genomes. Phytopathology 92:105–111
Tonguç M, Earle ED, Griffiths PD (2003) Segregation distortion of Brassica carinata derived black rot resistance in Brassica oleracea. Euphytica 134:269–276
Tu YQ, Sun J, Liu Y, Ge XH, Zhao ZG, Yao XC, Li ZY (2008) Production and characterization of intertribal somatic hybrids of Raphanus sativus and Brassica rapa with dye and medicinal plant Isatis indigotica. Plant Cell Rep 27:873–883
Vicente JG, Taylor JD, Sharpe AG, Parkin AP, Lydiate DJ, King GJ (2002) Inheritance of race-specific resistance to Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris in Brassica genomes. Phytopathology 92:1134–1141
Wang YP, Sonntag K, Rudloff E (2003) Development of rapeseed with high erucic acid content by asymmetric somatic hybridization between Brassica napus and Crambe abyssinica. Theor Appl Genet 106:1147–1155
Wang T, Xu SS, Harris MO, Hu J, Liu LW, Cai XW (2006) Genetic characterization and molecular mapping of Hessian fly resistance genes derived from Aegilops tauschii in synthetic wheat. Theor Appl Genet 113:611–618
Wang G, He Q, Liu F, Cheng Z, Talbert PB, Jin W (2011) Characterization of CENH3 proteins and centromere-associated DNA sequences in diploid and allotetraploid Brassica species. Chromosoma Mar 11. [Epub ahead of print]
Wei W, Li Y, Wang L, Liu S, Yan X, Mei D, Li Y, Xu Y, Peng P, Hu Q (2010) Development of a novel Sinapis arvensis disomic addition line in Brassica napus containing the restorer gene for Nsa CMS and improved resistance to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and pod shattering. Theor Appl Genet 120:1089–1097
Westman AL, Dickson MH (2000) Disease reaction to Alternaria brassicicola and Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris in Brassica nigra and other weedy crucifers. Cruciferae Newslett 22:87–88
Zhao ZG, Hu TT, Ge XH, Du XZ, Ding L, Li ZY (2008) Production and characterization of intergeneric somatic hybrids between Brassica napus and Orychophragmus violaceus and their backcrossing progenies. Plant Cell Rep 27:1611–1621
Zhong XB, Hans de Jong J, Zabel P (1996) Preparation of tomato meiotic pachytene and mitotic metaphase chromosomes suitable for fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Chromosome Res 4:24–28
Zhou A, Xia G, Zhang X, Chen H, Hu H (2001) Analysis of chromosomal and organellar DNA of somatic hybrids between Triticum aestiuvm and Haynaldia villosa Schur. Mol Genet Genomics 265:387–393
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from Natural Science Foundation of China (30771206), (31000538) and project of technology innovation ability from Beijing Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences (KJCX201101010-19). Our researches on somatic hybridization benefited from the ‘Sino-Germany Cooperation on Agricultural Science and Technology’.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A.-C. Schmit.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Gx., Tang, Y., Yan, H. et al. Production and characterization of interspecific somatic hybrids between Brassica oleracea var. botrytis and B. nigra and their progenies for the selection of advanced pre-breeding materials. Plant Cell Rep 30, 1811–1821 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-011-1088-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-011-1088-9