Abstract
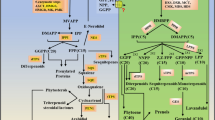
Salidroside, the 8-O-β-d-glucoside of tyrosol, is the main bioactive component of Rhodiola species and is found mainly in the plant roots. It is well known that glucosylation of tyrosol is the final step in the biosynthesis of salidroside; however, the biosynthetic pathway of tyrosol and its regulation are less well understood. A summary of the results of related studies revealed that the precursor of tyrosol might be tyramine, which is synthesized from tyrosine. In this study, a cDNA clone encoding tyrosine decarboxylase (TyrDC) was isolated from Rhodiola sachalinensis A. Bor using rapid amplification of cDNA ends. The resulting cDNA was designated RsTyrDC. RNA gel–blot analysis revealed that the predominant sites of expression in plants are the roots and high levels of transcripts are also found in callus tissue culture. Functional analysis revealed that tyrosine was best substrate of recombinant RsTyrDC. The over-expression of the sense-RsTyrDC resulted in a marked increase of tyrosol and salidroside content, but the levels of tyrosol and salidroside were 274 and 412%, respectively, lower in the antisense-RsTyrDC transformed lines than those in the controls. The data presented here provide in vitro and in vivo evidence that the RsTyrDC can regulate the tyrosol and salidroside biosynthesis, and the RsTyrDC is most likely to have an important function in the initial reaction of the salidroside biosynthesis pathway in R. sachalinensis.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HPLC:
-
High-pressure liquid chromatography
- IPTG:
-
Isopropyl thio-β-d-galactopyranoside
- LC-ESIMS:
-
Liquid chromatography electron spray ionization mass spectrometry
- PLP:
-
Pyridoxal 1-phosphate
- TyrDC:
-
Tyrosine decarboxylase
References
Bartley GE, Breksa AP 3rd, Ishida BK (2010) PCR amplification and cloning of tyrosine decarboxylase involved in synephrine biosynthesis in Citrus. N Biotechnol 27:308–316
Ellis BE (1983) Production of hydroxyphenylethanol glycosides in suspension cultures of Syringa vulgaris. Phytochemistry 22:1941–1943
Facchini PJ, De Luca V (1994) Differential and tissue-specific expression of a gene family for tyrosine/dopa decarboxylase in opium poppy. J Biol Chem 269:26684–26690
Facchini PJ, Huber-Allanach KL, Tari LW (2000) Plant aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylases: evolution, biochemistry, regulation, and metabolic engineering applications. Phytochemistry 54:121–138
Fu KJ, Ohba H, Gilbert MG (2009) Rhodiola. Flora of China 8:251
Gyorgy Z, Jaakola L, Neubauer P, Hohtola A (2009) Isolation and genotype-dependent, organ-specific expression analysis of a Rhodiola rosea cDNA encoding tyrosine decarboxylase. J Plant Physiol 166:1581–1586
Kawalleck P, Keller H, Hahlbrock K, Scheel D, Somssich IE (1993) A pathogen-responsive gene of parsley encodes tyrosine decarboxylase. J Biol Chem 268:2189–2194
Landtag J, Baumert A, Degenkolb T, Schmidt J, Wray V, Scheel D, Strack D, Rosahl S (2002) Accumulation of tyrosol glucoside in transgenic potato plants expressing a parsley tyrosine decarboxylase. Phytochemistry 60:683–689
Li W, Du GS, Huang QN (2005) Salidroside contents and related enzymatic activities in Rhodiola kirilowii callus (Chinese). Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica 25:1645–1648
Ma LQ, Liu BY, Gao DY, Pang XB, Lu SY, Yu HS, Wang H, Yan F, Li ZQ, Li YF, Ye HC (2007) Molecular cloning and overexpression of a novel UDP-glucosyltransferase elevating salidroside levels in Rhodiola sachalinensis. Plant Cell Rep 26:989–999
Ma LQ, Gao DY, Wang YN, Wang HH, Zhang JX, Pang XB, Hu TS, Lu SY, Li GF, Ye HC, Li YF, Wang H (2008) Effects of overexpression of endogenous phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PALrs1) on accumulation of salidroside in Rhodiola sachalinensis. Plant Biol (Stuttg) 10:323–333
Ma LQ, Guo YW, Gao DY, Ma DM, Wang YN, Li GF, Liu BY, Wang H, Ye HC (2009a) Identification of a Polygonum cuspidatum three-intron gene encoding a type III polyketide synthase producing both naringenin and p-hydroxybenzalacetone. Planta 229:1077–1086
Ma LQ, Pang XB, Shen HY, Pu GB, Wang HH, Lei CY, Wang H, Li GF, Liu BY, Ye HC (2009b) A novel type III polyketide synthase encoded by a three-intron gene from Polygonum cuspidatum. Planta 229:457–469
Mao GX, Deng HB, Yuan LG, Li DD, Li YY, Wang Z (2010) Protective role of salidroside against aging in a mouse model induced by d-galactose. Biomed Environ Sci 23:161–166
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassay with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Ouyang JF, Lou J, Yan C, Ren ZH, Qiao HX, Hong DS (2010) In vitro promoted differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells towards hepatocytes induced by salidroside. J Pharm Pharmacol 62:530–538
Samanani N, Park SU, Facchini PJ (2005) Cell type-specific localization of transcripts encoding nine consecutive enzymes involved in protoberberine alkaloid biosynthesis. Plant Cell 17:915–926
Sambrooke J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York
Tolonen A, Hohtola A, Jalonen J (2003) Comparison of electrospray ionization and atmospheric pressure chemical ionization techniques in the analysis of the main constituents from Rhodiola rosea extracts by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom 38:845–853
Xu JF, Su ZG (1997) Regulation of metabolism for improved salidroside production in cell suspension culture of Rhodiola sachalinensis A. Bor: the effect of precursors (Chinese). Nat Prod Res Dev 10:8–14
Xu JF, Su ZG, Feng PS (1998) Activity of tyrosol glucosyltransferase and improved salidroside production through biotransformation of tyrosol in Rhodiola sachalinensis cell cultures. J Biotechnol 69–73
Yousef GG, Grace MH, Cheng DM, Belolipov IV, Raskin I, Lila MA (2006) Comparative phytochemical characterization of three Rhodiola species. Phytochemistry 67:2380–2391
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 30872029 and 30900112) and Key Natural Science Foundation of Beijing Municipality (Nos. 5111001, 6071001 and 6092007), and Funding Project for Academic Human Resources Development in Institutions of Higher Learning Under the Jurisdiction of Beijing Municipality (Nos. PHR20090516 and PHR201108279), and Foundation of Beijing Municipal Education Committee (No. KM201110020001), and Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia (No. 2010BS0502).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by L. Jouanin.
Ji-Xing Zhang, Lan-Qing Ma contributed equally to this work.
Gene: RsTyrDC (GenBank accession no. DQ471943).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, JX., Ma, LQ., Yu, HS. et al. A tyrosine decarboxylase catalyzes the initial reaction of the salidroside biosynthesis pathway in Rhodiola sachalinensis . Plant Cell Rep 30, 1443–1453 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-011-1053-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-011-1053-7