Abstract
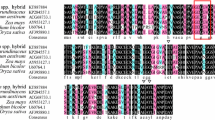
A collection of 29 pathogenesis-related 10 (PR10) genes of Medicago sativa and Medicago truncatula showed that they were almost all obtained from cDNA libraries of tissues undergoing abiotic or biotic stresses. The predicted proteins could be divided into two subclasses, PR10.1 and PR10.2, but in silico predicted models of their three-dimensional structures revealed that they could be further divided based on size of the hydrophobic internal cavity and number of β-bulges. A comparison of the expression of two highly similar M. sativa subclass PR10.1 genes, MsPR10.1A and MsPR10.1B, predicted to have similar sized hydrophobic internal cavities, but a different number of β-bulges revealed differences in their expression patterns. MsPR10.1A was induced faster than MsPR10.1B by ABA, ethylene, and X. campestris pv. alfalfae, but slower than MsPR10.1B by harvesting and wounding. Unlike MsPR10.1A, MsPR10.1B expression was induced in non-harvested tissues following harvesting, but was not induced by heat treatment. Histochemical observations of Nicotiana benthamiana transformed with 657 bp of the MsPR10.1A promoter fused to the β-glucuronidase (GUS) gene showed that GUS expression was wound-inducible in leaves, which was consistent with MsPR10.1A expression in alfalfa leaves. GUS expression in stems and leaves was mostly in vascular tissue. The MsPR10.1A promoter may be valuable in controlling the expression in vascular tissues and disease resistance.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal GK, Rakwal R, Tamogami S, Yonekura M, Kubo A, Saji H (2002) Chitosan activates defense/stress response(s) in the leaves of Oryza sativa seedlings. Plant Physiol Biochem 40:1061–1069
Allison LA, Kiss GB, Bauer P, Poiret M, Pierre M, Savoure A, Kondorosi E, Kondorosi A (1993) Identification of two alfalfa early nodulin genes with homology to members of the pea Enod12 gene family. Plant Mol Biol 21:1573–5028
Bais HP, Vepachedu R, Lawrence CB, Stermitz FR, Vivanco JM (2003) Molecular and biochemical characterization of an enzyme responsible for the formation of hypericin in St John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum L.). J Biol Chem 278:32413–32422
Borsics T, Lados M (2002) Dodder infection induces the expression of a pathogenesis-related gene of the family PR-10 in alfalfa. J Exp Bot 53:1831–1832
Breda C, Sallaud C, El-Turk J, Buffard D, De Kozak I, Esnault R, Kondorosi A (1996) Defense reaction in Medicago sativa, A gene encoding a class 10 PR protein is expressed in vascular bundles. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 9:713–719
Chen GYJ, Jin S, Goodwin PH (2000) An improved method for the isolation of total RNA from Malva pusilla tissues infected with Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. J Phytopathol 148:57–60
Chenna R, Sugawara H, Koike T, Lopez R, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG, Thompson JD (2003) Multiple sequence alignment with the Clustal series of programs. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3497–3500
Chinchilla D, Merchan F, Megias M, Kondorosi A, Sousa C, Crespi M (2003) Ankyrin protein kinases, a novel type of plant kinase gene whose expression is induced by osmotic stress in alfalfa. Plant Mol Biol 51:555–566
Constabel CP, Brisson N (1995) Stigma- and vascular-specific expression of the PR10a gene of potato, a novel pattern of expression of a pathogenesis-related gene. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 8:104–113
Datla RS, Hammerlindl JK, Panchuk B, Pelcher LE, Keller W (1992) Modified binary plant transformation vectors with the wild-type gene encoding NPTII. Gene 122:383–384
Datta SK, Muthukrishnan S (1999) Pathogenesis-related proteins in plants. CRC Press, Washington, DC
Davies KM, King GA (1993) Isolation and characterization of a cDNA clone for a harvest-induced asparagine synthetase from Asparagus officinalis L. Plant Physiol 102:1337–1340
Dean JD, Goodwin PH, Hsiang T (2002) Comparison of relative RT-PCR and northern blot analyses to measure expression of β-1, 3-glucanase in Nicotiana benthamiana infected with Colletotrichum destructivum. Plant Mol Biol Rep 20:347–356
Do HM, Lee SC, Jung HW, Sohn KH, Hwang BK (2004) Differential expression and in situ localization of a pepper defensin (CADEF1) gene in response to pathogen infection, abiotic elicitors and environmental stresses in Capsicum annuum. Plant Sci 166:1297–1305
Edwards K, Johnstone C, Thompson C (1991) A simple and rapid method for the preparation of plant genomic DNA for PCR analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 19:1349
Eisenberg D, Schwarz E, Komarony M, Wall R (1984) Amino acid scale, normalized consensus hydrophobicity scale. J Mol Biol 179:125–142
Esnault R, Buffard D, Breda C, Sallaud C, el Turk J, Kondorosi A (1993) Pathological and molecular characterizations of alfalfa interactions with compatible and incompatible bacteria, Xanthomonas campestris pv. alfalfae and Pseudomonas syringae pv. pisi. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 6:655–664
Fernandes H, Pasternak O, Bujacz G, Bujacz A, Sikorski M, Jaskolski M (2008) Lupinus luteus pathogenesis-related protein as a reservoir for cytokinin. J Mol Biol 378:1040–1051
Fernandes H, Bujacz A, Bujacz G, Jelen F, Jasinski M, Kachlicki P, Otlewski J, Sikorski MM, Jaskolski M (2009) Cytokinin-induced structural adaptability of a Lupinus luteus PR-10 protein. FEBS J 276:1596–1609
Ferullo J, Verzina L, Castonguay Y, Allard G, Madeau P, Willemot C, Laberge S (1996) Post-harvest alteration of in vitro translatable mRNA population in alfalfa (Medicago Sativa L.). Crop Sci 36:1011–1016
Finkelstein RR, Gampala SSL, Rock CD (2002) Abscisic acid signaling in seeds and seedlings. Plant Cell 14:S15–S45
Flores T, Alape-Giron A, Flores-Diaz M, Flores HE (2002) Ocatin, a novel tuber storage protein from the andean tuber crop oca with antibacterial and antifungal activities. Plant Physiol 128:1291–1302
Fujimoto Y, Nagata R, Fukasawa H, Yano K, Azuma M, Iida A, Sugimoto S, Shudo K, Hashimoto Y (1998) Purification and cDNA cloning of cytokinin-specific binding protein from mung bean (Vigna radiata). Eur J Biochem 258:794–802
Horsch RB, Fry JE, Hoffman NL, Eichholtz D, Rogers SG, Fraley RT (1985) A simple and general-method for transferring genes into plants. Science 227:1229–1231
Iuchi S, Kobayashi M, Taji T, Naramoto M, Seki M, Kato T, Tabata S, Kakubari Y, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2001) Regulation of drought tolerance by gene manipulation of 9-cisepoxycarotenoid dioxygenase, a key enzyme in abscisic acid biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 27:325–333
Jefferson RA (1987) Assaying chimeric genes in plants, the GUS gene fusion system. Plant Mol Biol Rep 5:387–405
Jwa NS, Agrawal GK, Tamogami S, Yonekura M, Han O, Iwahashi H, Rakwal R (2006) Role of defense/stress-related marker genes, proteins and secondary metabolites in defining rice self-defense mechanisms. Plant Physiol Biochem 44:261–273
Kumar S, Tamura K, Jakobsen IB, Nei M (2001) MEGA 2, molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software. Bioinformatics 17:1244–1245
Lee SC, Hwang BK (2003) Identification of the pepper SAR82 gene as a molecular marker for pathogen infection, abiotic elicitors and environmental stresses in Capsicum annuum. Planta 216:387–396
Liu JJ, Ekramoddoullah AKM (2006) The family 10 of plant pathogenesis-related proteins, their structure, regulation, and function in response to biotic and abiotic stresses. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 68:3–13
Liu JJ, Ekramoddoullah AKM, Yu X (2003) Differential expression of multiple PR10 proteins in western white pine following wounding, fungal infection and cold-hardening. Physiol Plant 119:544–553
Liu JJ, Ekramoddoullah AK, Piggott N, Zamani A (2005) Molecular cloning of a pathogen/wound-inducible PR10 promoter from Pinus monticola and characterization in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Planta 221:159–169
Lo SCC, Hipskind JD, Nicholson RL (1999) cDNA cloning of a sorghum pathogenesis-related protein PR-10 and differential expression of defense-related genes following inoculation with Cochliobolus heterostrophus or Colletotrichum sublineolum. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 12:479–489
Markovic-Housley Z, Degano M, Lamba D, von Roepenack-Lahaye E, Clemens S, Susani M, Ferreira F, Scheiner O, Breiteneder H (2003) Crystal structure of a hypoallergenic isoform of the major birch pollen allergen Bet v 1 and its likely biological function as a plant steroid carrier. J Mol Biol 325:123–133
Matton DP, Brisson N (1989) Cloning, expression and sequence conservation of pathogenesis-related gene transcripts of potato. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 2:325–331
McGee JD, Hamer JE, Hodges TK (2001) Characterization of a PR-10 pathogenesis-related gene family induced in rice during infection with Magnaporthe grisea. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 14:877–886
Michalska K, Fernandes H, Sikorski M, Jaskolski M (2010) Crystal structure of Hyp-1, a St. John’s wort protein implicated in the biosynthesis of hypericin. J Struct Biol 169:161–171
Mogensen JE, Wimmer R, Larsen JN, Spangfort MD, Otzen DE (2002) The major birch allergen, Bet v 1, shows affinity for a broad spectrum of physiological ligands. J Biol Chem 277:23684–23692
Park CJ, Kim KJ, Shin R, Park JM, Shin YC, Paek KH (2004) Pathogenesis-related protein 10 isolated from hot pepper functions as a ribonuclease in an antiviral pathway. Plant J 37:186–198
Pasternak O, Biesiadka J, Dolot R, Handschuh L, Bujacz G, Sikorski MM, Jaskolski M (2005) Structure of a yellow lupin pathogenesis-related PR-10 protein belonging to novel subclass. Acta Crystallogr Sect D Biol Crystallogr 16:99–107
Pay A, Heberle Bors E, Hirt H (1992) An alfalfa cDNA encodes a protein with homology to translationally controlled human tumor protein. Plant Mol Biol 19:501–503
Poupard P, Strull D-G, Simoneau P (1998) Two members of the Bet v 1 gene family encoding birch pathogenesis-related proteins display different patterns of root expression and wound-inducibility. Aust J Plant Physiol 25:459–464
Poupard P, Parisi L, Campion C, Ziadi S, Simoneau P (2003) A wound- and ethephon-inducible PR-10 gene subclass from apple is differentially expressed during infection with a compatible and an incompatible race of Venturia inaequalis. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 62:3–12
Rakwal R, Agrawal GK, Yonekura M (1999) Separation of proteins from stressed rice Oryza sativa L. leaf tissues by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, induction of pathogenesis-related and cellular protectant proteins by jasmonic acid, UV irradiation and copper chloride. Electrophoresis 20:3472–3478
Reynolds PHS (1999) Inducible gene expression in plants. CAB, Wallingford
Robert N, Ferran J, Breda C, Coutos-Thevenot P, Boulay M, Buffard D, Esnault R (2001) Molecular characterization of the incompatible interaction of Vitis vinifera leaves with Pseudomonas syringae pv pisi, expression of genes coding for stilbene synthase and class 10 PR protein. Eur J Plant Pathol 107:249–261
Rodriguez-Llorente I, Perez-Hormaeche J, El Mounadi K, Dary M, Caviedes MA, Cosson V, Kondorosi A, Ratet P, Palomares AJ (2004) From pollen tubes to infection threads, recruitment of Medicago floral pectic genes for symbiosis. Plant J 39:587–598
Sikorski MM, Biesiadka J, Kasperska AE, Kopcinska J, Lotocka B, Golinowski W, Legocki AB (1999) Expression of genes encoding PR10 class pathogenesis-related proteins is inhibited in yellow lupine root nodules. Plant Sci 149:125–137
Sneath PHA, Sokal RR (1973) Numerical taxonomy: the principles and practice of numerical taxonomy. W H Freeman & Co, San Francisco, CA
Sohn KH, Lee SC, Jung HW, Hong JK, Hwang BK (2006) Expression and functional roles of the pepper pathogen-induced transcription factor RAV1 in bacterial disease resistance, and drought and salt stress tolerance. Plant Mol Biol 61:897–915
Somssich IE, Schmelzer E, Bollmann JJ, Hahlbrock K (1986) Rapid activation by fungal elicitor of genes encoding “pathogenesis-related” protein in cultured parsley cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:2427–2430
Tewari S, Brown SM, Kenyon P, Balcerzak M, Fristensky B (2003) Plant defense multigene families. II. Evolution of coding sequence and differential expression of PR10 genes in Pisum. http://arXivorg/q-bioPE/0310038
Thaler JS, Owen B, Higgins VJ (2004) The role of the jasmonate response in plant susceptibility to diverse pathogens with a range of lifestyles. Plant Physiol 135:530–538
Van Loon LC, Van Strien EA (1999) The families of pathogenesis-related proteins, their activities, and comparative analysis of PR-1 type proteins. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 55:85–97
Walter MH, Liu JW, Wünn J, Hess D (1996) Bean ribonulease-like pathogenesis-related protein genes Ypr10 display complex patterns of developmental, dark-induced and exogenous-stimulus-dependent expression. Eur J Biochem 239:281–293
Wang CS, Huang JC, Hu JH (1999) Characterization of two subclasses of PR-10 transcripts in lily anthers and induction of their genes through separate signal transduction pathways. Plant Mol Biol 40:807–814
Warner SA, Scott R, Draper J (1993) Isolation of an asparagus intracellular PR gene (AoPR1) wound-responsive promoter by the inverse polymerase chain reaction and its characterization in transgenic tobacco. Plant J 3:191–201
Yasnetskaya EG, Bulgakov VP, Gorbach VI, Shevchenko NM, Fedoreyeva LI, Zhuravlev YuN, Kiselev KV (2003) Ethephon- and jasmonate-elicited pathogenesis-related ribonucleases in cultured ginseng cells. Russ J Plant Physiol 50:492–497
Zhang J (2004) Harvesting inducible gene and promoters in alfalfa. PhD thesis, University of Guelph
Acknowledgments
Funding for this study was provided by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada. Xanthomonas campestris pv. alfalfae strain X61 was kindly provided by Dr. Diane Cuppels, Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada, London, ON, Canada. The authors wish to thank Moez Valliani for his technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by D. Zaitlin.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bahramnejad, B., Goodwin, P.H., Zhang, J. et al. A comparison of two class 10 pathogenesis-related genes from alfalfa and their activation by multiple stresses and stress-related signaling molecules. Plant Cell Rep 29, 1235–1250 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-010-0909-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-010-0909-6