Abstract
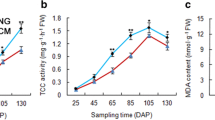
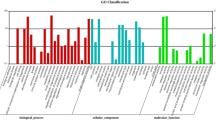
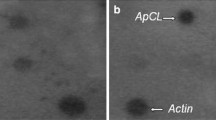
Panax notoginseng is a highly valued Chinese medicinal herb. To understand the molecular mechanism of the much higher pharmacological activities of roots of 3-year-old plants over 1-year-old ones,two cDNA libraries were constructed using the suppression subtractive hybridization (SSH) method. Positive cDNA clones from each of the two libraries were randomly selected for dot-blotting analysis. A total of 110 genes were highly expressed in 3-year-old roots and 80 genes in 1-year-old roots. Of these, 87 cDNA fragments were sequenced, assembled, and compared with sequences in GenBank, and 81 individual cDNAs were identified. These cDNAs were the first expressed sequence tags of P. notoginseng in GenBank. The result of reverse transcription PCR analysis of six genes was consistent with that of the dot-blot analysis. The global gene expression profile showed that there were significant differences between 1- and 3-year-old roots of P. notoginseng plants. Some important structural and regulatory genes which may be involved in isoprenoid biosynthesis were found to be over-expressed in 3-year-old roots, such as genes encoding 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl-4-diphosphat-synthase (IspG-protein), multi-copper oxidase type I family protein, NADH flavin oxidoreductase, lipase and aconitase.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SSH:
-
Suppression subtractive hybridization
- DIG:
-
Digoxygenin
- ESTs:
-
Expressed sequence tags
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcription PCR
- IspG:
-
1-Hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl-4-diphosphat-synthase
References
Belbahri L, Elleuch H, Villarroel R, Inze D, Thomas D(1999) The Isolation of an Arabidopsis thaliana cDNA clone encoding S-adenosyl-l-homocysteine hydrolase. Plant Physiol 121:313
Chen QS (1987) Pharmacological studies on notoginseng saponins isolated from the fibrous root of Panax notoginseng. Zhong Yao Tong Bao 12:45–47
Chomezynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guandinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159
Cui XM, Chen ZJ, Wang CL, Zeng J (2001) Studies on Saponin Accumulative in Regularities Panax notoginseng (Burk) F. H. Chen. China J Chin Mater Med 26:27–28
Gabrielsen M, Rohdich F, Eisenreich W, Gräwert T, Hecht S (2004) Biosynthesis of isoprenoids: A bifunctional IspDF enzyme from Campylobacter jejuni. Eur J Biochem 271:3028–3035
Han J, Zhong JJ (2002) High density cell culture of Panax notoginseng for production of ginseng saponin and polysaccharide in an airlift bioreactor. Biotechnol Lett 24:1927–1930
Haralampidis K, Trojanowska M, Osbourn AE (2001) Biosynthesis of Triterpenoid Saponins in Plants. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 75:31–49
Liang M, Peng D, Yang GX et al (2006) Advances on the Plant Terpenoid Isoprenoid Biosynthetic Pathway and Its Key Enzymes. Biotech Bull 1:22–30
Ma WG, Mizutani M, Malterud KE, Lu SL, Ducrey B, Tahara S (1999) Saponins from the roots of Panax notoginseng. Phytochemistry 52:1133–1139
Nair MS, Anilkumar AT (1996) Versatile chiral intermediates for terpenoid synthesis using lipase catalysed ylation. Tetrahedron:Asymmetry 7:511–514
Riva S, Monti D, luisetti M, Danieli B (1998) Enzymatic modification of natural compounds with pharmacological properties. Ann NY Acad Sci 864:70–80
Robbins AH (1989) Structure of activated aconitase: formation of the [4Fe-4S] cluster in the crystal. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:3639–3643
Rohdich F, Bacher A, Eisenreich W (2004) Perspectives in anti-infective drug design. The late steps in the biosynthesis of the universal terpenoid precursors, isopentenyl diphosphate and dimethylallyl diphosphate. Bioorg Chem 32:292–308
Rohdich F, Hecht S, Bacher A, Eisenreich W (2003) Deoxyxylulose phosphate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis: studies on the mechanisms of the reactions catalyzed by IspG and IspH protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:1586–1591
Tehlivets O, Hasslacher M, Kohlwein SD (2004) S-Adenosyl-l-homocysteine hydrolase in yeast: key enzyme of methylation metabolism and coordinated regulation with phospholipid synthesis. FEBS letters 577:501–506
Vongsangnak W, Guaa J, Chauvatcharin S, Zhong JJ (2004) Towards efficient extraction of notoginseng saponins from cultured cells of Panax notoginseng. J Biochem Eng 18:115–120
Wan JB, Yang FQ, Li SP, Wang YT, Cui XM (2006) Chemical characteristics for different parts of Panax notoginseng using pressurized liquid extraction and HPLC-ELSD. J Pharm Biomed Anal 41:1596–601
Xu DQ, Zhang YB, Xiong YZ, Gui JF, Jiang SW (2003) Construction of forward and reverse subtracted cDNAlibraries between muscle tissue of meishan and landrace pigs. Acta genetica sinica 30:668–672
Yang ZG, Chen AQ, Yu SD (2005) Recent advances in the research of pharmacological activities of Panax notoginseng saponins. Chin J Vet Drug 39:33–37
Zang XP, Qi LL, Li DR (2007) Advances in studies on pharmacological effect of active components of Panax notoginseng. J Med Res 36:96–98
Zhong JJ,Wang DJ (1996) Improvement of cell growth and production of ginseng saponin and polysaccharide in suspension cultures of Panax notoginseng. J Biotechnol 4:669–672
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Feng Hong for excellent technical assistance and helpful discussions and Wenshan Research Institute of Sanqi Science and Technology, Yunnan, China for providing plant materials.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by D. Somers.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, F., Zhu, Y. & Zhang, Y. Identification and characterization of differentially expressed genes involved in pharmacological activities of roots of Panax notoginseng during plant growth. Plant Cell Rep 27, 923–930 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-008-0516-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-008-0516-y