Abstract
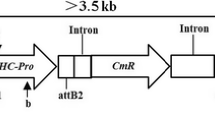
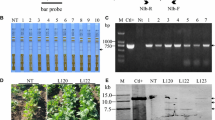
We transformed a construct containing the sense coat protein (CP) gene of Soybean dwarf virus (SbDV) into soybean somatic embryos via microprojectile bombardment to acquire SbDV-resistant soybean plants. Six independent T0 plants were obtained. One of these transgenic lines was subjected to further extensive analysis. Three different insertion patterns of Southern blot hybridization analysis in T1 plants suggested that these insertions introduced in T0 plants were segregated from each other or co-inherited in T1 progenies. These insertions were classified into two types, which overexpressed SbDV-CP mRNA and accumulated SbDV-CP-specific short interfering RNA (siRNA), or repressed accumulation of SbDV-CP mRNA and siRNA by RNA analysis prior to SbDV inoculation. After inoculation of SbDV by the aphids, most T2 plants of this transgenic line remained symptomless, contained little SbDV-specific RNA by RNA dot-blot hybridization analysis and exhibited SbDV-CP-specific siRNA. We discuss here the possible mechanisms of the achieved resistance, including the RNA silencing.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bass BL (2000) Double-stranded RNA as a template for gene silencing. Cell 101:235–238
Bazzini AA, Hopp HE, Beachy RN, Asurmendi S (2006) Posttranscriptional gene silencing does not play a significant role in potato virus X coat protein-mediated resistance. Virology 96:1175–1178
Beachy RN (1999) Coat-protein-mediated resistance to tobacco mosaic virus: discovery mechanisms and exploitation. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 354:659–664
Carmell MA, Hannon GJ (2004) RNaseIII enzymes and the initiation of gene silencing. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11:214–218
Chen YK, Lohuis D, Goldbach R, Prins M (2004) High frequency induction of RNA-mediated resistance against cucumber mosaic virus using inverted repeat constructs. Mol Breed 14:215–226
Cuozzo M, O’Connell KM, Kaniewski W, Fang RX, Chua NH, Tumer NE (1988) Viral protection in transgenic plants expressing the cucumber mosaic virus coat protein or its antisense RNA. Biotechnology 6:549–557
Elbashir SM, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T (2001) RNA interference is mediated by 21-and 22-nucleotide RNAs. Genes Dev 15:188–200
English JJ, Baulcombe DC (1997) The influence of small changes in transgene transcription on homology-dependent virus resistance and gene silencing. Plant J 12:1311–1318
Fu X, Duc LT, Fontana S, Bong BB, Tinjuangjun P, Sudhakar D, Twyman RM, Christou P, Kohli A (2000) Linear transgene constructs lacking vector backbone sequences generate low-copy-number transgenic plants with simple integration patterns. Transgenic Res 9:11–19
Furutani N, Hidaka S (2004) Efficient production of transgenic soybean using a co-transformation method. Breed Sci 54:91–98
Hamilton AJ, Baulcombe DC (1999) A species of small antisense RNA in posttranscriptional gene silencing in plants. Science 286:950–952
Hammond SM, Bernstein E, Beach D, Hannon GJ (2000) An RNA-directed nuclease mediated post-transcriptional gene silencing in Drosophila cells. Nature 404:293–296
Hemenway C, Fang RX, Kaniewski WK, Chua NH, Tumer NE (1988) Analysis of the mechanism of protection in transgenic plants expressing the potato virus X coat protein or its antisense RNA. EMBO J 7:1273–1280
Ingelbrecht IL, Irvine JE, Mirkov TE (1999) Posttranscriptional gene silencing in transgenic sugarcane. Dissection of homology-dependent virus resistance in a monocot that has a complex polyploid genome. Plant Physiol 199:1187–1197
Jan FJ, Pang SZ, Tricoli DM, Gonsalves D (2000) Evidence that resistance in squash mosaic comovirus coat protein-transgenic plants is affected by plant developmental stage and enhanced by combination of transgenes from different lines. J Gen Virol 81: 2299–2306
Kalantidis K, Psaradakis S, Tabler M, Tsagris M (2002) The occurrence of CMV-specific short RNAs in transgenic tobacco expressing virus-derived double-stranded RNA is indicative of resistance to the virus. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 15:826–833
Matzke MA, Mette MF, Matzke AJ (2000) Transgenic silencing by the host genome defence: implications for the evolution of epigenetic control mechanisms in plants and vertebrates. Plant Mol Biol 43:401–415
Missiou A, Kalantidis K, Boutla A, Tzortzakaki S, Tabler M, Tsagris M (2004) Generation of transgenic potato plants highly resistant to potato virus Y (PVY) through RNA silencing. Mol Breed 14:185–197
Mitsuhara I, Ugaki M, Hirochika H, Ohshima M, Murakami T, Gotoh Y, Katayose Y, Nakamura S, Honkura R, Nishimiya S, Ueno K, Mochizuki A, Tanimoto H, Tsugawa H, Otsuki Y, Ohashi Y (1996) Efficient promoter cassettes for enhanced expression of foreign genes in dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous plants. Plant Cell Physiol 37:49–59
Mourrain P, van Blokland R, Kooter JM, Vaucheret H (2007) A single transgene locus triggers both transcriptional and post-transcriptional silencing through double-stranded RNA production. Planta 225:365–379
Pang SZ, Jan FJ, Tricoli DM, Russell PF, Carney KJ, Hu JS, Fuchs M, Quemada HD, Gonsalves D (2000) Resistance to squash mosaic comovirus in transgenic squash plants expressing its coat protein genes. Mol Breed 6:87–93
Pang SZ, Jan FJ, Carney K, Stout J, Tricoli DM, Quemada HD, Gonsalves D (1996) Post-transcriptional transgene silencing and consequent tospovirus resistance in transgenic lettuce are affected by transgene dosage and plant development. Plant J 9:899–909
Park YD, Papp I, Moscone EA, Iglesias VA, Vaucheret H, Matzke AJM, Matzke MA (1996) Gene silencing mediated by promoter homology occurs at the level of transcription and results in meiotically heritable alterations in methylation and gene activity. Plant J 9:183–194
Paz MM, Martinez JC, Kalvig AB, Fonger TM, Wang K (2006) Improved cotyledonary node method using an alternative explant derived from mature seed for efficient Agrobacterium-mediated soybean transformation. Plant Cell Rep 25:206–213
Powell-Abel P, Nelson RS, De B, Hoffman N, Rogers SG, Fraley RT, Beachy RN (1986) Delay of disease development in transgenic plants that express the tobacco mosaic virus coat protein gene. Science 232:738–743
Reddy MSS, Dinkins RD, Collins GB (2003) Gene silencing in transgenic soybean plants transformed via particle bombardment. Plant Cell Rep 21:676–683
Sijen T, Wellink J, Hiriart J-B, van Kammen A (1996) RNA mediated virus resistance: role of repeated transgene and delineation of targeted regions. Plant Cell 8:2277–2294
Smith HA, Swaney SL, Parks TD, Wernsman EA, Dougherty WG (1994) Transgenic plant virus resistance mediated by untranslatable sense RNAs: expression, regulation, and fate of nonessential RNAs. Plant Cell 9:1441–1453
Smith NA, Singh SP, Wang MB, Stoutjesdijk PA, Green AG, Waterhouse PM (2000) Total silencing by intron-spliced hairpin RNAs. Nature 407:319–320
Tamada T (1975) Studies on the soybean dwarf disease. Rep Hokkaido Pref Agric Exp Stn 25:1–144 (In Japanese with English abstract)
Terauchi H, Kanematsu S, Honda K, Mikoshiba Y, Ishiguro K, Hidaka S (2001) Comparison of complete nucleotide sequences of genomic RNAs of four Soybean dwarf virus strains that differ in their vector specificity and symptom production. Arch Virol 146:1885–1898
Tougou M, Furutani N, Yamagishi N, Shizukawa Y, Takahata Y, Hidaka S (2006) Development of resistant transgenic soybeans with inverted repeat-coat protein genes of soybean dwarf virus. Plant Cell Rep 25:1213–1218
Vaucheret H, Fagard M (2001) Transcriptional gene silencing in plants: targets, inducers and regulators. Trends Genet 17:29–35
Voinnet O, Pinto YM, Baulcombe DC (1999) Suppression of gene silencing: a general strategy used by diverse DNA and RNA viruses of plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:14147–14152
Wang MB, Metzlaff M (2005) RNA silencing and antiviral defense in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8:216–222
Wang MB, Abbott DC, Waterhouse PM (2000) A single copy of a virus-derived transgene encoding hairpin RNA gives immunity to barley yellow dwarf virus. Mol Plant Pathol 1:347–356
Waterhouse PM, Graham MW, Wang MB (1998) Virus resistance and gene silencing in plants can be induced by simultaneous expression of sense and antisense RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:13959–13964
Yamagishi N, Terauchi H, Kanematsu S, Hidaka S (2003) Characterization of the small subgenomic RNA of soybean dwarf virus. Arch Virol 148:1827–1834
Yamagishi N, Terauchi H, Honda K, Kanematsu S, Hidaka S (2006) Discrimination of four soybean dwarf virus strains by dot-blot hybridization with specific probes. J Virol Methods 133:219–222
Zamore PD, Tuschl T, Sharp PA, Bartel DP (2000) RNAi: double-stranded RNA directs the ATP-dependent cleavage of mRNA at 21 to 23 nucleotide intervals. Cell 101:25–33
Zeng P, Vadnais DV, Zhang Z, Polacco JC (2004) Refined glufosinate selection in Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merrill]. Plant Cell Rep 22:478–482
Acknowledgments
We thank Motoko Kobayashi for technical assistance. We are grateful to Hidetaka Terauchi, Jun-ichi Sakai and Seiji Kanematsu for supporting basic research of SbDV. This work was funded by the Project for the Development of Innovative Transgenic Plants of the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J.R. Liu.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tougou, M., Yamagishi, N., Furutani, N. et al. Soybean dwarf virus-resistant transgenic soybeans with the sense coat protein gene. Plant Cell Rep 26, 1967–1975 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-007-0404-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-007-0404-x