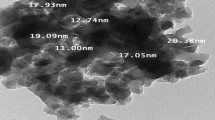
Abstract
Enhancing voltage of polyvinyl chloride (PVC)-insulated cable has been paid a great attention from researchers. Metal oxide nanoparticles such as: SiO2, ZnO, Al2O3 have shown good promise to achieve this goal. However, the great challenge for nanocomposites preparation is the dispersibility and interfacial interaction between filler(s) and PVC matrix to obtain high mechanical and electrical performances of nanocomposites. In this study, two kinds of silane substances, (3-(trimethoxysilyl) propyl methacrylate (MPTS) and (3-aminopropyl) triethoxysilane (APTES)), were used as surface modification agents for γ-Al2O3 nanoparticles (NPs). The silanes grafting on the surface of γ-Al2O3 NPs was confirmed by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). By field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) observation, the interfacial interaction index and dynamic mechanical thermal analysis (DMTA) proved that the presence of silane remarkably improved the dispersibility, interfacial interaction and adhesion of Al2O3 NPs with PVC matrix. Thanks to these improvements, the obtained PVC/Al2O3 nanocomposites had much enhanced mechanical and electrical properties. At 0.75 wt% of loading content, MPTS-modified Al2O3 nanoparticles incorporating into PVC matrix showed the high properties with 60.51 MPa of yield strength, 90.48 MPa of flexural strength and the maximum value of electrical breakdown strength (EEB) could reach up to 98.56 kV/mm. The nanocomposite based on PVC matrix reinforcing with γ-Al2O3 NPs is a promising material for high-quality electric cable manufacturing field.
Graphical abstract















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jeroense M, Saltzer M, Ghorbani H (2013) Technical challenges linked to HVDC cable development. In: Proceedings of the Jicable-HVDC’13. France, p 1.1
Gustafsson A, Saltzer M, Farkas A, Ghorbani G, Quist T, Jeroense M (2014) ABB grid system, Technical Paper, August
Habashy MM, Abd-Elhady AM, Elsad RA, Izzularab MA (2019) Performance of PVC/SiO2 nanocomposites under thermal ageing. Appl Nanosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-018-00941-y
Shwehdi MH, Morsy MA, Abugurain A (2003) Thermal ageing tests on XLPE and PVC cable insulation materials of Saudi Arabia. In: 2003 annual report conference on electrical insulation and dielectric phenomena, Albuquerque, NM, USA
Hajibeygi M, Maleki M, Shabanian M, Ducos F, Vahabi H (2018) New polyvinyl chloride (PVC) nanocomposite consisting of aromatic polyamide and chitosan modified ZnO NPs with enhanced thermal stability, low heat release rate and improved mechanical properties. Appl Surf Sci 439:1163–1179
Mansour SA, Elsad RA, Izzularab MA (2016) Dielectric properties enhancement of PVC nanodielectrics based on synthesized ZnO NPs. J Polym Res 23:1–8
Sugumaran CP (2015) [IEEE 2015 IEEE conference on electrical insulation and dielectric phenomena - (CEIDP) - Ann Arbor, MI, USA (2015.10.18–2015.10.21)]. In: 2015 IEEE conference on electrical insulation and dielectric phenomena (CEIDP) - experimental study on dielectric and mechanical properties of PVC cable insulation with SiO2/CaCO3 nanofillers, pp 503–506. https://doi.org/10.1109/CEIDP.2015.7352072
Shuisheng S, Chunzhong L, Ling Z, Du HL, Burnell-Gray JS (2006) Effects of surface modification of fumed silica on interfacial structures and mechanical properties of poly(vinyl chloride) composites. Eur Polym J 42(7):1643–1652
Gubanski SM (2016) [IEEE 2016 IEEE international conference on high voltage engineering and application (ICHVE) - Chengdu, China (2016.9.19–2016.9.22)]. In: 2016 IEEE international conference on high voltage engineering and application (ICHVE) - insulating materials for next generations of HVAC and HVDC cables. pp 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICHVE.2016.7800823
Liu D, Pourrahimi AM, Olsson RT, Hedenqvist MS, Gedde UW (2015) Influence of nanoparticle surface treatment on particle dispersion and interfacial adhesion in low-density polyethylene/aluminium oxide nanocomposites. Eur Polymer J 66:67–77
Tanaka T (2005) Dielectric nanocomposites with insulating properties. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 12:914–928
Nelson JK, Fothergill JC (2004) Internal charge behaviour of nanocomposites. Nanotechnology 15:586–595
Tanaka T, Kozako M, Fuse N, Ohki Y (2005) Proposal of a multi-core model for polymer nanocomposite dielectrics. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 12:669–681
Fleming RJ, Ammala A, Casey PS, Lang SB (2008) Conductivity and space charge in LDPE containing nano and micro-sized ZnO particles. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 15(1):118–126
Yin Y, Dong X, Chen J, Li Z, Dang Z (2006) High field electrical conduction in the nanocomposite of low-density polyethylene and nanoSiOx. IEEJ Trans Fundam Mater 126:1064–1071
Pourrahimi AM, Pallon LKH, Liu D, Hoang TA, Gubanski SM, Hedenqvist MS, Olsson RT, Gedde UW (2016) Polyethylene nanocomposites for the next generation of ultralow-transmission-loss HVDC cables: Insulation containing moisture-resistant MgO Nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(23):14824–14835
Osman MA, Rupp JE, Suter UW (2005) Effect of non-ionic surfactants on the exfoliation and properties of polyethylene-layered silicate nanocomposites. Polymer 46(19):8202–8209
Jiang H, Moon KS, Li Y, Wong CP (2006) Surface functionalized silver nanoparticles for ultrahigh conductive polymer composites. Chem Mater 18(13):2969–2973
Lee HJ, Choi HW, Kim KJ, Lee SC (2006) Modification of hydroxyapatite nanosurfaces for enhanced colloidal stability and improved interfacial adhesion in nanocomposites. Chem Mater 18(21):5111–5118
Zhu J, He Q, Luo Z, Khasanov A, Li Y, Sun L et al (2012) Property manipulated polypropylene–iron nanocomposites with maleic anhydride polypropylene. J Mater Chem 22:15928–15838
Wu D, Wang X, Song Y, Jin R (2004) Nanocomposites of poly(vinyl chloride) and nanometric calcium carbonate particles: effects of chlorinated polyethylene on mechanical properties, morphology, and rheology. J Appl Polym Sci 92:2714–2723
Pukanszky B (1990) Influence of interface interaction on the ultimate tensile properties of polymer composites. Composites 21(3):255–262
Kurimoto M, Okubo H, Kato K, Hanai M, Hoshina Y, Takei M, Hayakawa N (2010) Dielectric properties of epoxy/alumina nanocomposite influenced by control of micrometric agglomerates. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 17:662–670
Zhao H, Li RK (2008) Effect of water absorption on the mechanical and dielectric properties of nano-alumina filled epoxy nanocomposites. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 39(4):602–611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2007.07.006
Haizhong Z, Jian Z, Shiqiang L, Gaochao W, Zhifeng X (2006) Effect of core–shell composite particles on the sintering behavior and properties of nano-Al2O3/polystyrene composite prepared by SLS. Mater Lett 60(9–10):1219–1223
Zefang Z, Hong L (2008) Preparation of α-alumina/polymethacrylic acid composite abrasive and its CMP performance on glass substrate. Microelectron Eng 85(4):714–720
Pravin NN, Vineeta DD (2018) Dielectric behavior of plasticized PVC/alumina nanocomposites. Mater Today Proc 5(1–2):2254–2262
Banerjee S, Dubey S, Gautam RK, Chattopadhyaya MC, Sharma YC (2019) Adsorption characteristics of alumina nanoparticles for the removal of hazardous dye, Orange G from aqueous solutions. Arab J Chem 12(8):5339–5354
Rabu RA, Jewena N, Das SK, Khandaker JI, Ahmed F (2020) Synthesis of metal-oxide (Al2O3) nanoparticles by using autoclave for the efficient absorption of heavy metal ions. J Nanomater Mol Nanotechnol 9(6):1–6
Alamouti AF, Nadafan M, Dehghani Z, Majles-Ara MH, Noghreiyan AV (2021) Structural and optical coefficients investigation of γ-Al2O3 nanoparticles using Kramers-Kronig relations and Z–scan technique. J Asian Ceram Soc 9(1):366–373
Kundie F, Azhari CH, Ahmad ZA (2018) Effect of nano-and micro-alumina fillers on some properties of poly (methyl methacrylate) denture base composites. J Serb Chem Soc 83(1):75–91
Tang B, Ge J, Zhuo L, Wang G, Niu J et al (2005) A facile and controllable synthesis of alumina nanostructure without a surfactant. Eur J Inorg Chem 2005(21):4366–4369
Siengchin S, Karger-Kociss J, Thomann R (2007) Alumina-filled polystyrene micro- and nanocomposites prepared by melt mixing with and without latex precompounding: structure and properties. J Appl Polym Sci 105(5):2963–2972
Isabela MFL, Abersfelder K, Oliveira PW, Mousavi SH, Junqueira RMR (2018) Flower-like silicon dioxide/polymer composite particles synthesized by dispersion polymerization route. J Mater Sci 53:11367–11377
Liugang C, Guotian Y, Kunpeng L, Qingfeng W, Dayan X, Guo M (2014) Al–O–Si bond formation in Boehmite-fumed silica mixtures during mechanochemical activation. Interceram Int Ceram Rev 63(7–8):372–375
Temuujin J, Okada K, MacKenzie KJD (1998) Characterization of aluminosilicate (mullite) precursors prepared by a mechanochemical process. J Mater Res 13(8):2184–2189
Martin W, Fritjof N, Emma L, Wen-Chung T, Henrik H, Anna C, Gedde UW, Eva M (2014) Polymer-grafted Al2O3-nanoparticles for controlled dispersion in poly(ethylene-co-butyl acrylate) nanocomposites. Polymer 55(9):2125–2138
Mueller R, Kammler HK, Wegner K, Pratsinis SE (2002) OH surface density of SiO2 and TiO2 by thermogravimetric analysis. Langmuir 19:160–165
Nordell P, Nawaz S, Azhdar B, Hillborg H, Gedde UW (2012) Preparation and characterization of aluminum oxide–poly(ethylene-co-butyl acrylate) nanocomposites. J Appl Polym Sci 125(2):975–983
Gulsen AA, Ismail A (2011) A study on fusion and rheological behaviors of PVC/SiO2 microcomposites and nanocomposites: the effects of SiO2 particle size. Polym Eng Sci 51(8):1574–1579
Saad ALG, Aziz HA, Dimitry OIH (2004) Studies of electrical and mechanical properties of poly(vinyl chloride) mixed with electrically conductive additives. J Appl Polym Sci 91:1590–1598
Jancar J, Kucera J (1990) Yield behavior of polypropylene filled with CaCO3 and Mg(OH)2. I: ‘“zero”’ interfacial adhesion. Polym Eng Sci 30:707–713
Jancar J, Kucera J (1990) Yield behavior of PP/CaCO3 and PP/Mg(OH)2 composites. II: enhanced interfacial adhesion. Polym Eng Sci 30:714–720
Chen J, Nie XA, Jiang JC, Zhou YH (2017) Thermal degradation and plasticizing mechanism of poly(vinyl chloride) plasticized with a novel cardanol derived plasticizer. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 292:012008
Selulosa-Polivinilklorida SR, Sheltami RM, Kargarzadeh HA, Abdullah IB (2015) Effects of silane surface treatment of cellulose nanocrystals on the tensile properties of cellulose-polyvinyl chloride nanocomposite. Sains Malays 44:801–810
Fuquiang TF, Lei Q, Wang X, Wang Y (2012) Investigation of electrical properties of LDPE/ZnO nanocomposite dielectrics. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 19:763–769
Theodosiou K, Vitellas I, Gialas I, Agoris DP (2004) Polymer films degradation and breakdown in high voltage AC fields. J Electr Eng 55:225–231
Danikas MG, Tanaka T (2009) Nanocomposites—a review of electrical treeing and breakdown. IEEE Electr Insul Mag 25:19–25
Yeetsorn R (2010) Development of electrically conductive thermoplastic composites for bipolar plate application in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell, a thesis, Doctor of Philosophy in Chemical Engineering, Waterloo, Ontario, Canada (2010)
Tanaka T, Matsunawa A, Ohki Y, Kozako M, Kohtoh M, Okabe S (2006) Treeing phenomenon inepoxy/alumina nanocomposite and interpretation by a multi-core model. IEEJ Trans Fundam Mater 126:1128–1135
Jonscher AK, Lacoste R (1984) On a cumulative model of dielectric breakdown in solids. IEEE Trans Electr Insul 19:567–577
Mansour SA, Yahia IS, Yakuphanoglu F (2010) The electrical conductivity and dielectric properties of C.I. Basic Violet 10. Dyes Pigments 87:144–148
Mansour SA, Yahia IS, Sakr GB (2010) Electrical conductivity and dielectric relaxation behavior of fluorescein sodium salt (FSS). Solid State Commun 150:1386–1391
Abdullah ET, Naje AN (2011) AC electrical and dielectric properties of PVC-MWCNT nanocomposites. Indian J Sci Technol 4(7):731–735
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the Vietnam Ministry of International Trade and Industry (code number of 031.2021.ĐT.BO/HĐKHCN).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huynh, M.D., Trung, T.H., Tuan, V.M. et al. The influence of silane-grafted aluminum oxide nanoparticles on the interfacial interaction phase and electric performance of polyvinyl chloride-based nanocomposite. Polym. Bull. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-024-05232-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-024-05232-x