Abstract
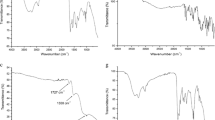
The objective of this study was to develop biodegradable, environmentally friendly, economical and smart gelatin-based hydrogels and ferrogels as controlled drug delivery systems. Cross-linking is an important treatment for controlling the drug release from hydrogels, as well as enhancing the thermal and mechanical stability of hydrogels. In this study, gelatin-based hydrogels and ferrogels were synthesized at different cross-linker concentrations, ranging from 4 to 16 wt% to allow for different mesh and pore sizes in the gelatin matrix. The gels were characterized by thermogravimetric analysis, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. The swelling properties and in-vitro release of tetracycline as a model drug from the hydrogels and ferrogels cross-linked with different ratios by the diffusion mechanism were tested in solutions of pH 6.5 and 7.4 at 37 °C, which mimics environments similar to those of the mouth and intestines. The results showed that the swelling and drug release properties of all the gelatin hydrogels and ferrogels significantly depended on the cross-link level because of the effect of the cross-linking mechanism on reducing the number of free carboxyl and free amino groups of gelatin matrix. In addition, it was observed that the presence of magnetic nanoparticles in the gelatin matrix has an effect of decreasing the swelling and drug release percent of the gelatin-based hydrogels.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fonseca-Santos B, Chorilli M (2017) An overview of carboxymethyl derivatives of chitosan: their use as biomaterials and drug delivery systems. Mater Sci Eng C 77:1349–1362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2017.03.198
Wang R, Shou D, Lv O, Kong Y, Deng L, Shen J (2017) pH-Controlled drug delivery with hybrid aerogel of chitosan, carboxymethyl cellulose and graphene oxide as the carrier. Int J Biol Macromol 103:248–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.05.064
Liu TY, Hu SH, Liu KH, Liu DM, Chen SY (2006) Preparation and characterization of smart magnetic hydrogels and its use for drug release. J Magn Magn Mater 304(1):e397–e399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2006.01.203
García-Astrain C, Guaresti O, González K, Santamaria-Echart A, Eceiza A, Corcuera MA, Gabilondo N (2016) Click gelatin hydrogels: Characterization and drug release behaviour. Mater Lett 182:134–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2016.06.115
Biswal D, Anupriya B, Uvanesh K, Anis A, Banerjee I, Pal K (2016) Effect of mechanical and electrical behavior of gelatin hydrogels on drug release and cell proliferation. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 53:174–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2015.08.017
Varghese JS, Chellappa N, Fathima NN (2014) Gelatin–carrageenan hydrogels: role of pore size distribution on drug delivery process. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 113:346–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.08.049
Treesuppharat W, Rojanapanthu P, Siangsanoh C, Manuspiya H, Ummartyotin S (2017) Synthesis and characterization of bacterial cellulose and gelatin-based hydrogel composites for drug-delivery systems. Biotechnol Rep 15:84–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2017.07.002
Prabha G, Raj V (2017) Sodium alginate–polyvinyl alcohol–bovin serum albumin coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles as anticancer drug delivery vehicle: doxorubicin loading and in vitro release study and cytotoxicity to HepG2 and L02 cells. Mater Sci Eng C 79:410–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2017.04.075
Singh B, Sharma V (2017) Crosslinking of poly (vinylpyrrolidone)/acrylic acid with tragacanth gum for hydrogels formation for use in drug delivery applications. Carbohydr Polym 157:185–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.09.086
Wu J, Xie X, Zheng Z, Li G, Wang X, Wang Y (2017) Effect of pH on polyethylene glycol (PEG)-induced silk microsphere formation for drug delivery. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 80:549–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2017.05.072
Bubpamala T, Viravaidya-Pasuwat K, Pholpabu P (2020) Injectable poly (ethylene glycol) hydrogels cross-linked by metal–phenolic complex and albumin for controlled drug release. ACS Omega 5:19437–19445. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c01393
Dreiss CA (2020) Hydrogel design strategies for drug delivery. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 48:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cocis.2020.02.001
Kwon Y, Song M, Hwang YG, Chang SH, Hong WJ (2008) Effect of materials structure and composition on properties of siloxane-containing hydrogels. Curr Appl Phys 8(3):486–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2007.10.042
Chai Q, Jiao Y, Yu X (2017) Hydrogels for biomedical applications: their characteristics and the mechanisms behind them. Gels 3(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels3010006
Jahanban-Esfahlan R, Derakhshankhah H, Haghshenas B, Massoumi B, Abbasian M, Jaymand M (2020) A bio-inspired magnetic natural hydrogel containing gelatin and alginate as a drug delivery system for cancer chemotherapy. Int J Biol Macromol 156:438–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.04.074
Lu AH, Salabas EL, Schüth F (2007) Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew Chem Int Ed 46(8):1222–1244. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200602866
Liao J, Huang H (2020) Review on magnetic natural polymer constructed hydrogels as vehicles for drug delivery. Biomacromol 21(7):2574–2594. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.0c00566
Kim C, Kim H, Park H, Lee KY (2019) Controlling the porous structure of alginate ferrogel for anticancer drug delivery under magnetic stimulation. Carbohydr Polym 223:115045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115045
Lakkakula JR, Gujarathi P, Pansare P, Tripathi S (2021) A comprehensive review on alginate-based delivery systems for the delivery of chemotherapeutic agent: doxorubicin. Carbohydr Polym 259:117696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.117696
Supramaniam J, Adnan R, Kaus NHM, Bushra R (2018) Magnetic nanocellulose alginate hydrogel beads as potential drug delivery system. Int J Biol Macromol 118:640–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.06.043
Ko ES, Kim C, Choi Y, Lee KY (2020) 3D printing of self-healing ferrogel prepared from glycol chitosan, oxidized hyaluronate, and iron oxide nanoparticles. Carbohydr Polym 245:116496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116496
Jafari H, Atlasi Z, Mahdavinia GR, Hadifar S, Sabzi M (2021) Magnetic κ-carrageenan/chitosan/montmorillonite nanocomposite hydrogels with controlled sunitinib release. Mater Sci Eng C 124:112042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2021.112042
Gambin B, Melnikova P, Kruglenko E, Strzałkowski R, Krajewski M (2022) Impact of the agarose ferrogel fine structure on magnetic heating efficiency. J Magn Magn Mater 550:169000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2021.169000
Omer AM, Sadik WAA, El-Demerdash AGM, Hassan HS (2021) Formulation of pH-sensitive aminated chitosan–gelatin crosslinked hydrogel for oral drug delivery. J Saudi Chem Soc 25(12):101384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2021.101384
Samal SK, Goranov V, Dash M, Russo A, Shelyakova T, Graziosi P, Lungaro L, Riminucci A, Uhlarz M, Banobre-Lopez M, Rivas J, Herrmannsdörfer T, Rajadas J, De Smedt S, Braeckmans K, Kaplan DL, Dediu VA (2015) Multilayered magnetic gelatin membrane scaffolds. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(41):23098–23109. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b06813
Siangsanoh C, Ummartyotin S, Sathirakul K, Rojanapanthu P, Treesuppharat W (2018) Fabrication and characterization of triple-responsive composite hydrogel for targeted and controlled drug delivery system. J Mol Liq 256:90–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.02.026
Eyadeh MM, Rabaeh KA, Hailat TF, Aldweri FM (2018) Evaluation of ferrous Methylthymol blue gelatin gel dosimeters using nuclear magnetic resonance and optical techniques. Radiat Meas 108:26–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radmeas.2017.11.004
Saber-Samandari S, Saber-Samandari S, Joneidi-Yekta H, Mohseni M (2017) Adsorption of anionic and cationic dyes from aqueous solution using gelatin-based magnetic nanocomposite beads comprising carboxylic acid functionalized carbon nanotube. Chem Eng J 308:1133–1144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.10.017
Derakhshankhah H, Jahanban-Esfahlan R, Vandghanooni S, Akbari-Nakhjavani S, Massoumi B, Haghshenas B, Rezaei A, Farnudiyan-Habibi A, Samadian H, Jaymand M (2021) A bio-inspired gelatin-based pH-and thermal-sensitive magnetic hydrogel for in vitro chemo/hyperthermia treatment of breast cancer cells. J Appl Polym Sci 138(24):50578. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.50578
Thakur S, Govender PP, Mamo MA, Tamulevicius S, Thakur VK (2017) Recent progress in gelatin hydrogel nanocomposites for water purification and beyond. Vacuum 146:396–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2017.05.032
Dash R, Foston M, Ragauskas AJ (2013) Improving the mechanical and thermal properties of gelatin hydrogels cross-linked by cellulose nanowhiskers. Carbohydr Polym 91(2):638–645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.08.080
Lawrence MB, Joseph J, Usapkar T, Azavedo F (2021) Swelling and DC conductivity behaviour of gelatin-based ferrogels. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 31(1):129–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01682-8
Schwabe K, Ewe A, Kohn C, Loth T, Aigner A, Hacker MC, Schulz-Siegmund M (2017) Sustained delivery of siRNA poly-and lipopolyplexes from porous macromer-crosslinked gelatin gels. Int J Pharm 526(1–2):178–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.04.065
Bhattacharyya SK, Dule M, Paul R, Dash J, Anas M, Mandal TK, Das P, Das NC, Banerjee S (2020) Carbon dot cross-linked gelatin nanocomposite hydrogel for pH-Sensing and pH-responsive drug delivery. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 6(10):5662–5674. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.0c00982
Zhang H, Tian Y, Zhu Z, Xu H, Li X, Zheng D, Sun W (2016) Efficient antitumor effect of co-drug-loaded nanoparticles with gelatin hydrogel by local implantation. Sci Rep 6(1):26546. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep26546
Nazeri MT, Javanbakht S, Shaabani A, Ghorbani M (2020) 5-aminopyrazole-conjugated gelatin hydrogel: A controlled 5-fluorouracil delivery system for rectal administration. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 57:101669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2020.101669
Zhang K, Yang J, Sun Y, Wang Y, Liang J, Luo J, Cui W, Deng L, Xu X, Wang B, Zhang H (2022) Gelatin-based composite hydrogels with biomimetic lubrication and sustained drug release. Friction 10:232–246. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40544-020-0437-5
Coimbra P, Gil MH, Figueiredo M (2014) Tailoring the properties of gelatin films for drug delivery applications: influence of the chemical cross-linking method. Int J Biol Macromol 70:10–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.06.021
Hussain K, Aslam Z, Ullah S, Shah MR (2021) Synthesis of pH responsive, photocrosslinked gelatin-based hydrogel system for control release of ceftriaxone. Chem Phys Lipids 238:105101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2021.105101
Özkahraman B, Tamahkar E, İdil N, Kılıç Suloglu A, Perçin I (2021) Evaluation of hyaluronic acid nanoparticle embedded chitosan–gelatin hydrogels for antibiotic release. Drug Dev Res 82(2):241–250. https://doi.org/10.1002/ddr.21747
Manish V, Arockiarajan A, Tamadapu G (2021) Influence of water content on the mechanical behavior of gelatin based hydrogels: Synthesis, characterzation, and modeling. Int J Solids Struct 233:111219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2021.111219
Ullah K, Khan SA, Murtaza G, Sohail M, Manan A, Afzal A (2019) Gelatin-based hydrogels as potential biomaterials for colonic delivery of oxaliplatin. Int J Pharm 556:236–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.12.020
Gaihre B, Khil MS, Lee DR, Kim HY (2009) Gelatin-coated magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as carrier system: drug loading and in vitro drug release study. Int J Pharm 365(1–2):180–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2008.08.020
Yakar A, Tansık G, Keskin T, Gündüz U (2013) Tailoring the magnetic behavior of polymeric particles for bioapplications. J Polym Eng 33(3):265–274. https://doi.org/10.1515/polyeng-2012-0034
Akin Sahbaz D, Yakar A, Gündüz U (2019) Magnetic Fe3O4-chitosan micro-and nanoparticles for wastewater treatment. Part Sci Technol 37:732–740. https://doi.org/10.1080/02726351.2018.1438544
Manish V, Siva KV, Arockiarajan A, Tamadapu G (2022) Synthesis and characterization of hard magnetic soft hydrogels. Mater Lett 320:132323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2022.132323
Huang Y, Yu H, Xiao C (2007) pH-sensitive cationic guar gum/poly (acrylic acid) polyelectrolyte hydrogels: swelling and in vitro drug release. Carbohydr Polym 69(4):774–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2007.02.016
Kim SW, Bae YH, Okano T (1992) Hydrogels: swelling, drug loading, and release. Pharm Res 9:283–290. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015887213431
Nath J, Ahmed A, Saikia P, Chowdhury A, Dolui SK (2020) Acrylic acid grafted gelatin/LDH based biocompatible hydrogel with pH-controllable release of vitamin B12. Appl Clay Sci 190:105569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2020.105569
Chen X, Fan M, Tan H, Ren B, Yuan G, Jia Y, Li J, Xiong D, Xing X, Niu X, Hu X (2019) Magnetic and self-healing chitosan-alginate hydrogel encapsulated gelatin microspheres via covalent cross-linking for drug delivery. Mater Sci Eng C 101:619–629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.04.012
Zeng N, He L, Jiang L, Shan S, Su H (2022) Synthesis of magnetic/pH dual responsive dextran hydrogels as stimuli-sensitive drug carriers. Carbohydr Res 520:108632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2022.108632
Li P, Zhou M, Liu H, Lei H, Jian B, Liu R, Li X, Wang Y, Zhou B (2022) Preparation of green magnetic hydrogel from soybean residue cellulose for effective and rapid removal of copper ions from wastewater. J Environ Chem Eng 10(5):108213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.108213
Alinejad-Mir A, Amooey AA, Ghasemi S (2018) Adsorption of direct yellow 12 from aqueous solutions by an iron oxide-gelatin nanoadsorbent; kinetic, isotherm and mechanism analysis. J Clean Prod 170:570–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.09.101
Ji Y, Yang X, Ji Z, Zhu L, Ma N, Chen D, Jia X, Tang J, Cao Y (2020) DFT-calculated IR spectrum amide I, II, and III band contributions of N-methylacetamide fine components. ACS Omega 5(15):8572–8578. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b04421
Pereira VDA, Ribeiro IS, Paula HC, de Paula RC, Sommer RL, Rodriguez RJS, Abreu FO (2020) Chitosan-based hydrogel for magnetic particle coating. React Funct Polym 146:104431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2019.104431
Skopinska-Wisniewska J, Tuszynska M, Olewnik-Kruszkowska E (2021) Comparative study of gelatin hydrogels modified by various cross-linking agents. Materials 14(2):396. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14020396
Tanwar A, Date P, Ottoor D (2021) ZnO NPs incorporated gelatin grafted polyacrylamide hydrogel nanocomposite for controlled release of ciprofloxacin. Colloids Interface Sci Commun 42:100413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colcom.2021.100413
Yin OS, Ahmad I, Amin MCIM (2015) Effect of cellulose nanocrystals content and pH on swelling behaviour of gelatin based hydrogel. Sains Malays 44(6):793–799
Yeamsuksawat T, Zhao H, Liang J (2021) Characterization and antimicrobial performance of magnetic Fe3O4@Chitosan@Ag nanoparticles synthesized via suspension technique. Mater Today Commun 28:102481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2021.102481
Rodríguez-Rodríguez R, Espinosa-Andrews H, Velasquillo-Martínez C, García-Carvajal ZY (2020) Composite hydrogels based on gelatin, chitosan and polyvinyl alcohol to biomedical applications: a review. Int J Polym Mater Polym Biomater 69(1):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/00914037.2019.1581780
Işıklan N, Hussien NA, Türk M (2021) Synthesis and drug delivery performance of gelatin-decorated magnetic graphene oxide nanoplatform. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 616:126256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126256
Dwivedi R, Singh AK, Dhillon A (2017) pH-responsive drug release from dependal-M loaded polyacrylamide hydrogels. J Sci Adv Mater Dev 2(1):45–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsamd.2017.02.003
Favatela F, Horst MF, Bracone M, Gonzalez J, Alvarez V, Lassalle V (2021) Gelatin/Cellulose nanowhiskers hydrogels intended for the administration of drugs in dental treatments: Study of lidocaine as model case. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 61:101886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2020.101886
Arafa EG, Sabaa MW, Mohamed RR, Elzanaty AM, Abdel-Gawad OF (2022) Preparation of biodegradable sodium alginate/carboxymethylchitosan hydrogels for the slow-release of urea fertilizer and their antimicrobial activity. React Funct Polym 174:105243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2022.105243
Suhail M, Wu PC, Minhas MU (2021) Development and characterization of pH-sensitive chondroitin sulfate-co-poly (acrylic acid) hydrogels for controlled release of diclofenac sodium. J Saudi Chem Soc 25(4):101212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2021.101212
Dangi D, Mattoo M, Kumar V, Sharma P (2022) Synthesis and characterization of galactomannan polymer hydrogel and sustained drug delivery. Carbohydr Polym Technol Appl 4:100230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carpta.2022.100230
Shariatinia Z, Ziba M (2022) Smart pH-responsive drug release systems based on functionalized chitosan nanocomposite hydrogels. Surf Interfaces 29:101739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2022.101739
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares there is no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper. The paper has not been published elsewhere and that it has not been submitted simultaneously for publication elsewhere.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Akın Şahbaz, D. Gelatin-based hydrogels and ferrogels as smart drug delivery systems: synthesis, characterization and drug release kinetics. Polym. Bull. 81, 5215–5235 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-023-04963-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-023-04963-7