Abstract
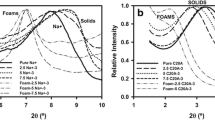
The present work studies the water absorption kinetics of polypropylene foams modified with palygorskite nanoclay. The polypropylene/palygorskite composites were prepared with a modular twin-screw extruder and then foamed in a conical twin-screw extruder. The mechanisms of water absorption kinetics of the polypropylene/palygorskite foams were analyzed using a multi-stage model to understand the influence of the clay concentration, nanoclay dispersion and foam cell morphology on the water absorption behaviour of the foams. The solid nanocomposites were characterized by transmission electron microscopy to measure the clay dispersion in the matrix. The nano-reinforced foams were characterized by optical microscopy to measure the cell size and by scanning electron microscopy to measure the size of the foam micropores. Water absorption, foam density and cell morphology were also measured. The nanoclay modifies the foam cellular structure, generating non-homogeneous and non-uniform open cells; these cells encompass micropores which facilitate water diffusion consequently the water absorption properties of the foams are modified. The different screw configurations used during the extrusion process of the composites yield polypropylene foams with different clay dispersion and consequently different foam cellular structure.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang S, Wang K, Pang Y, Li Y, Wu F, Wang S, Sheng W (2016) Open-cell polypropylene/polyolefin elastomer blend foams fabricated for reusable oil-sorption materials. J Appl Polym Sci 133:1–10
Keshavarz A, Zilouei H, Abdolmaleki A, Asadinezhad A, Nikkhah A (2016) Impregnation of polyurethane foam with activated carbon for enhancing oil removal from water. Int J Environ Sci Technol 13:699–710
Shao L, Ji Z, Ma J, Xue C, Deng F (2017) Morphology and interaction of nanocomposite foams formed with organo-palygorskite and ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymers. Polym Bull 74:413–429
Hwang S, Hsu PP (2013) Effects of silica particle size on the structure and properties of polypropylene/silica composites foams. J Ind Eng Chem 19:1377–1383
Seraji SM, Razavi MK, Davari M, Salami M, Khelgati SH (2011) Effect of clay dispersion on the cell structure of LDPE/clay nanocomposite foams. Polym Compos 32:1095–1105
Guo MC, Heuzey MC, Carreau PJ (2007) Cell structure and dynamic properties of injection molded polypropylene foams. Polym Eng Sci 47:1070–1081
Ladhari A, Daly HB, Belhadjsalah H, Cole KC, Denault J (2010) Investigation of water absorption in clay-reinforced polypropylene nanocomposites. Polym Degrad Stab 95:429–439
Perez RR (2013) Estudio de la estructura celular y de las propiedades de absorción de agua en espumas de Polipropileno reforzado con Paligorskita. Unidad de materiales Centro de Investigación Científica de Yucatán A.C., México
Duncan B, Urquhart J, Roberts S (2005) Review of measurement and modelling of permeation and diffusion in polymers. National Physical Laboratory Middlesex, London
Pilli SP, Smith LV, Vaithiyalingam S (2014) Measuring time-dependent diffusion in polymer matrix composites. Mech Time-Depend Mater 18:633–641
Cai LW, Weitsman Y (1994) Non-Fickian moisture diffusion in polymeric composites. J Compos Mater 28:130–154
Gautam R, Bassi A, Yanful E (2007) A review of biodegradation of synthetic plastic and foams. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 141:85–108
Chow W, Bakar AA, Ishak ZM (2005) Water absorption and hygrothermal aging study on organomontmorillonite reinforced polyamide 6/polypropylene nanocomposites. J Appl Polym Sci 98(2):780–790
Tajvidi M, Najafi SK, Moteei N (2006) Long-term water uptake behavior of natural fiber/polypropylene composites. J Appl Polym Sci 99:2199–2203
Earl J, Shenoi R (2004) Determination of the moisture uptake mechanism in closed cell polymeric structural foam during hygrothermal exposure. J Compos Mater 38:1345–1365
Perez RR, Peña-Quintal A, Gonzalez PI (2019) Cellular structure of PP/PPma/Palygorskite and its capacity to absorb water. Mater Res Express 6:105357
Pinto J, Athanassiou A, Fragouli D (2016) Effect of the porous structure of polymer foams on the remediation of oil spills. J Phys D Appl Phys 49:145601
Tagliavia G, Porfiri M, Gupta N (2012) Influence of moisture absorption on flexural properties of syntactic foams. Compos B Eng 43:115–123
Siriruk A, Weitsman YJ, Penumadu D (2009) Polymeric foams and sandwich composites: material properties, environmental effects, and shear-lag modeling. Compos Sci Technol 69:814–820
Han X (2003) Continuous production of microcellular foams. The Ohio State University, Columbus
Avilés F, Aguilar-Montero M (2010) Moisture absorption in foam-cored composite sandwich structures. Polym Compos 31:714–722
Yu YJ, Hearon K, Wilson TS, Maitland DJ (2011) The effect of moisture absorption on the physical properties of polyurethane shape memory polymer foams. Smart Mater Struct 20:1–6
Vlasveld D, Groenewold J, Bersee H, Picken SJ (2005) Moisture absorption in polyamide-6 silicate nanocomposites and its influence on the mechanical properties. Polymer 46:12567–12576
Baschek G, Hartwig G, Zahradnik F (1999) Effect of water absorption in polymers at low and high temperatures. Polymer 40:3433–3441
Ma J, Wang T (2018) Preparation and characterization of water-absorbing polyurethane foam composites with microsized sodium polyacrylate particles. J Appl Polym Sci 135:46702
Lee LJ, Zeng C, Cao X, Han X, Shen J, Xu G (2005) Polymer nanocomposite foams. Compos Sci Technol 65:2344–2363
Chi J, Pérez RR, Gamboa CJ, González PI (2020) Transitory rheological test as a tool to monitor nano-clay dispersion and distribution in polypropylene–palygorskite composites. Polym Bull 77:3537–3562
ASTM D (2013) 5630–standard test method for ash content in plastics. Annual book of ASTM standards
Anderson TW, Darling DA (1952) Asymptotic theory of certain “goodness of fit” criteria based on stochastic processes. Ann Math Statist 23:193–212
Mohebbi A, Mighri F, Ajji A, Rodrigue D (2015) Current issues and challenges in polypropylene foaming: a review. Cell Polym 34:299–338
ASTM D (2003) Standard test method for apparent density of rigid cellular plastics. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, pp 1620–1623
Yasunaga K, Neff RA, Xhang XD, Macosko CW (1996) Study of cell opening in flexible polyurethane foam. J Cell Plast 32:427–448
ASTM A (1990) D570 standard test method for water absorption of plastics. astm d792 standard test methods for density and specific gravity (relative density) of plastics by displacement. ASTM D. 2240
Shen CH, Springer GS (1976) Moisture absorption and desorption of composite materials. J Compos Mater 10:2–20
Kishimoto A (1972) Diffusion of vapours in organic coatings. Prog Org Coat 1:91–112
Van der Wel GK, Adan OCG (1999) Moisture in organic coatings—a review. Prog Org Coat 37:1–14
Berens A, Hopfenberg H (1978) Diffusion and relaxation in glassy polymer powders: 2. Separation of diffusion and relaxation parameters. Polymer 19:489–496
Sun YM (1996) Sorption/desorption properties of water vapour in poly (2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate): 2. Two-stage sorption models. Polymer 37:3921–3928
Roy S, Xu WX, Park SJ, Liechti KM (1999) Anomalous moisture diffusion in viscoelastic polymers: modeling and testing. J Appl Mech 67:391–396
Crank J (1979) The mathematics of diffusion. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Hyndman RJ, Koehler AB (2006) Another look at measures of forecast accuracy. Int J Forecast 22:679–688
García-Romero E, Suárez M (2013) Sepiolite–palygorskite: textural study and genetic considerations. Appl Clay Sci 86:129–144
Huang HX, Wang JK, Sun XH (2008) Improving of cell structure of microcellular foams based on polypropylene/high-density polyethylene blends. J Cell Plast 44:69–85
Antunes M, Realinho V, Velasco JI (2010) Foaming behaviour, structure, and properties of polypropylene nanocomposites foams. J Nanomater 2010:1–11
Gupta N, Woldesenbet E (2003) Hygrothermal studies on syntactic foams and compressive strength determination. Compos Struct 61:311–320
Kord B (2014) Investigation on the long-term water absorption behavior and cell morphology of foamed wood–plastic nanocomposites. J Thermoplast Compos Mater 27:379–394
Soberanis GA (2015) Propiedades reológicas en fundido de materiales compuestos termoplásticos reforzados con nanoarcilla de paligorskita. In: Unidad de Materiales. Centro de Investigación Científica de Yucatán, A.C., México
Soberanis GA, Gonzalez PI, Gordillo JL (2015) Influence of chemically treated palygorskite over the rheological behavior of polypropylene nanocomposites. Ingeniería, Investigación y Tecnología 16(4):491–501
Acknowledgements
Authors appreciate the contribution of Santiago Duarte Aranda for scanning electron microscopy. RRPM acknowledges CONACYT (Mexico) for the scholarship granted during the postdoctoral stay for the development of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Perez-Matu, R.R., Avilés, F. & Gonzalez-Chi, P.I. Water absorption kinetics of palygorskite nanoclay/polypropylene composite foams. Polym. Bull. 81, 4149–4174 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-023-04822-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-023-04822-5