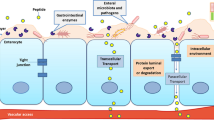
Abstract
Oral bioavailability is the main decisive factor in achieving the desired systemic drug concentration, and it can be increased by developing novel dosage forms that can avoid first-pass metabolism. The current study aimed to employ the quality-by-design (QbD) approach to develop and optimize the therapeutically efficient instant release buccal films (IRBFs) of eletriptan, which should not only be able to avoid the first-pass metabolism, but also circumvent the condition of gastric stasis which is associated with migraine. The solvent casting method was employed to fabricate IRBFs, including hydroxypropyl methylcellulose E-5 (HPMC E5) as a polymer, glycerin as a plasticizer and permeation enhancer, and tween-80 (T80) as a surfactant. The prepared films were subjected to different physicochemical characterizations using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), surface morphology, disintegration time (DT), in vitro, and ex vivo permeation studies. The findings have shown that prepared films were rapidly disintegrating (DT < 30 s), immediately dissolving (TDT < 120 s), and instantly releasing and allowing rapid permeation of the drug. The outcomes of the study have assisted to develop the optimized formulation, followed by its characterization, which showed that the findings were quite similar to those, predicted by the statistical tool for the optimized formulation. The similarity of predicted and obtained results have confirmed the reproducibility of the prepared IRBFs.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steiner TJ, Stovner LJ, Birbeck GL (2013) Migraine: the seventh disabler (Wiley online library). J Headache Pain 14:289–290
Pallavi K, Pallavi T (2017) Formulation and evaluation of fast dissolving films of eletriptan hydrobromide. Int J Curr Pharm Res 9:59
Elella MHA, Goda ES, Gab-Allah MA, Hong SE, Pandit B, Lee S, Yoon KR (2021) Xanthan gum-derived materials for applications in environment and eco-friendly materials: a review. J Environ Chem Eng 9(1):104702
Raju S, Reddy PS, Kumar VA, Deepthi A, Reddy KS, Reddy PM (2011) Flash release oral films of metoclopramide hydrochloride for pediatric use: formulation and in vitro evaluation. J Chem Pharm Res 3:636–646
Kumria R, Nair AB, Goomber G, Gupta S (2016) Buccal films of prednisolone with enhanced bioavailability. Drug Deliv 23:471–478
Preis M, Woertz C, Kleinebudde P, Breitkreutz J (2013) Oromucosal film preparations: classification and characterization methods. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 10:1303–1317
Zaman M, Hanif M, Khan MA (2018) Arabinoxylan-based mucoadhesive oral films of tizanidine HCL designed and optimized using central composite rotatable design. Polym Plast Technol Eng 57:471–483
Spandana B, Shashidher B, Dinesh S, Nagaraj B (2020) Eletriptan hydrobromide Orodispersible tablets: design, development and in vitro characterization. Res J Pharm Technol 13:5339–5344
Prabhu P, Malli R, Koland M, Vijaynarayana K, D’Souza U, Harish N, Shastry C, Charyulu R (2011) Formulation and evaluation of fast dissolving films of levocitirizine di hydrochloride. Int J Pharm Investig 1:99
Goudanavar P, Bagali R, Patil S, Chandashkhara S (2010) Formulation and in vitro evaluation of mucoadhesive buccal films of Glibenclamide. Pharm Lett 2:382–387
O’Connor AE, Willenbacher N (2004) The effect of molecular weight and temperature on tack properties of model polyisobutylenes. Int J Adhes Adhes 24:335–346
Zaman M, Hassan R, Razzaq S, Mahmood A, Amjad MW, Raja MAG, Qaisar AA, Majeed A, Hanif M, Tahir RA (2020) Fabrication of polyvinyl alcohol based fast dissolving oral strips of sumatriptan succinate and metoclopramide HCL. Sci Prog 103:0036850420964302
Chaudhary H, Gauri S, Rathee P, Kumar V (2013) Development and optimization of fast dissolving oro-dispersible films of granisetron HCl using Box-Behnken statistical design. Bull Fac Pharm Cairo Univ 51:193–201
Irfan M, Rabel S, Bukhtar Q, Qadir MI, Jabeen F, Khan A (2016) Orally disintegrating films: a modern expansion in drug delivery system. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal 24:537–546
Chatap VK, Karale AM, Wagh P, Deshmukh PK, Patil SD, Bari SB (2013) Fabrication of specially designed novel mold for casting of perindopril erbumine mouth dissolving film. Adv Pharmacol Pharm 1:58–67
Patel RS, Poddar S (2009) Development and characterization of mucoadhesive buccal patches of salbutamol sulphate. Curr Drug Deliv 6:140–144
Maddela S, Nalluri BN (2019) Development of Zolmitriptan mouth dissolving films: formulation variables, mechanical properties, and in vitro drug release studies. Development 12:273–279
El-Setouhy DA, Abd El-Malak NS (2010) Formulation of a novel tianeptine sodium orodispersible film. AAPS PharmSciTech 11:1018–1025
Semalty M, Semalty A, Kumar G (2008) Formulation and characterization of mucoadhesive buccal films of glipizide. Indian J Pharm Sci 70:43
Morales JO, McConville JT (2011) Manufacture and characterization of mucoadhesive buccal films. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 77:187–199
Kunte S, Tandale P (2010) Fast dissolving strips: A novel approach for the delivery of verapamil. J Pharm Bioallied Sci 2:325
Hanif M, Zaman M, Chaurasiya V (2015) Polymers used in buccal film: a review. Des Monomers Polym 18:105–111
Bajdik J, Marciello M, Caramella C, Domján A, Süvegh K, Marek T, Pintye-Hódi K (2009) Evaluation of surface and microstructure of differently plasticized chitosan films. J Pharm Biomed Anal 49:655–659
Bhyan B, Jangra S, Kaur M, Singh H (2011) Orally fast dissolving films: innovations in formulation and technology. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res 9:9–15
Hasnain MS, Guru PR, Rishishwar P, Ali S, Ansari MT, Nayak AK (2020) Atenolol-releasing buccal patches made of Dillenia indica L. fruit gum: preparation and ex vivo evaluations. SN Appl Sci 2(1):1–10
Zaman M, Hanif M, Shaheryar Z (2018) Development of Tizanidine HCl-Meloxicam loaded mucoadhesive buccal films: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. PLoS ONE 13(3):e0194410
Zaman M, Hanif MJ (2018) In vitro and ex vivo assessment of hydrophilic polymer-and plasticizer-based thin buccal films designed by using central composite rotatable design for the delivery of meloxicam. Adv Polym Technol 37(6):1823–1836
Bala R, Pawar P, Khanna S, Arora S (2013) Orally dissolving strips: a new approach to oral drug delivery system. Int J Pharm Investig 3:67
Newton A, Rani S, Sukhjinder K (2016) Fabrication and evaluation of fast disintegrating oral hybrid films of propranolol hydrochloride by using pectin and synthetic polymers. J Dev Drugs 5:157
Raza SN, Kar AH, Wani TU, Khan NA (2019) Formulation and evaluation of mouth dissolving films of losartan potassium using 32 factorial design. Int J Pharm Sci Res 10:1402–1411
Rajeev J, Mukundan S, Raj BK, Dhanaja V, Subburaj T, Kamalasanan K (2018) Formulation of a novel immediate release heterolithic buccal patch of aspirin. J Pharm Sci Res 10:2079–2083
Kianfar F, Chowdhry BZ, Antonijevic MD, Boateng JS (2012) Novel films for drug delivery via the buccal mucosa using model soluble and insoluble drugs. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 38:1207–1220
Talja RA, Helén H, Roos YH, Jouppila K (2007) Effect of various polyols and polyol contents on physical and mechanical properties of potato starch-based films. Carbohyd Polym 67:288–295
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Wilshire Labs (Pvt) Ltd., Lahore, for providing the drug eletriptan. The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for funding this work through research group no. RG-1441-340.
Funding
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for funding this work through research group no. RG-1441–340.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization was carried out by Q.A., M.Z., T.R., and M.J.; methodology by M.Z., Q.A, T.R.; formal analysis and investigation by Q.A., M.Z., and W.S.; writing by Q.A. and W.S.; writing review and editing by M.Z., M.J., and T.R.; funding acquisition and supervision by M.Z.; all authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ain, Q.u., Zaman, M., Jamshaid, M. et al. Optimization and evaluation of instant release buccal films of eletriptan: a quality-by-design approach. Polym. Bull. 80, 10429–10455 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-022-04547-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-022-04547-x