Abstract
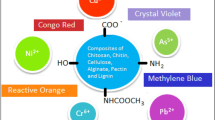
In this work, we designed novel chitosan-g-poly-(IA-co-DADMAC)/Fe3O4 polymer composite hydrogel using in situ ultrasonic wave-assisted polymerization method and applied for the uptake of methylene blue (MB) and congo red (CR) dyes from aqueous solution. The polymer composite hydrogel was characterized via FT-IR, XRD, TGA, FE-SEM, BET and VSM analysis. More interestingly, dyes can be efficiently adsorbed and after adsorption conveniently separated from solution by using external magnet. For dye adsorption studies, congo red (anionic dye) and methylene blue dyes (cationic dye) were taken as the target pollutant. Adsorption isotherm followed Fruendlich model with 862.06 mg/g and 1111.11 mg/g, respectively, adsorption capacity and the adsorption kinetics was most appropriately explained using pseudo-second-order kinetic model. This study will provide a new perspective for the design and fabrication of novel, safe and effective systems for dye removal.
Graphical abstract
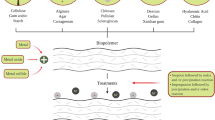
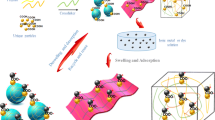
A common approach of using polymer composite hydrogel as an adsorption of dye molecules, magnetic separation, removal and their regeneration.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Patel SR, Patel RH, Patel MP (2020) Eco-friendly bioadsorbent-based polymer composites as a pH-responsive material for selective removal of anionic and azo dyes from aqueous solutions. J Macromol Sci Part A 1–14
Nazir MA, Yasar A Bashir MA, Siyal SH, Najam T, Javed MS, Rehman AU (2020) Quality assessment of the noncarbonated-bottled drinking water: comparison of their treatment techniques. Int J Environ Anal Chem 1–12
Patel SR, Patel MP (2021) Green and facile preparation of ultrasonic wave-assisted chitosan-g-poly-(AA/DAMPB)/Fe3O4 composite hydrogel for sequestration of reactive black 5 dye. Polym Bull 1–25
Abbas A, Murtaza S, Munir M, Zahid T, Abbas N, Mushtaq A (2011) Removal of Congo red from aqueous solutions with Raphanus sativus peels and activated carbon: a comparative study. American-Eurasian J Agric Environ Sci 10(5):802–809
Salleh MAM, Mahmoud DK, Karim WAWA, Idris A (2011) Cationic and anionic dye adsorption by agricultural solid wastes: a comprehensive review. Desalin 280(1–3):1–13
Jiang C, Fu B, Cai H, Cai T (2016) Efficient adsorptive removal of Congo red from aqueous solution by synthesized zeolitic imidazolate framework-8. Chem Spe Bioavail 28(1–4):199–208
Sharma J, Janveja B (2008) A study on removal of congo red dye from the effluents of textile industry using rice husk carbon activated by steam. Rasayan J Chem 1(4):936–942
Ibrahim MM (2019) Cr2O3/Al2O3 as adsorbent: physicochemical properties and adsorption behaviors towards removal of Congo red dye from water. J Environ Chem Eng 7(1):102848
Shah HUR, Ahmad K, Naseem HA, Parveen S, Ashfaq M, Aziz T, Shaheen S (2021) Synthetic routes of azo derivatives: a brief overview. J Mol Str 131181
Ahmad K, Naseem HA, Parveen S, Shah SSA, Shaheen S, Ashfaq A, Ashfaq M (2019) Synthesis and spectroscopic characterization of medicinal azo derivatives and metal complexes of Indandion. J Mol Str 1198:126885
Alam MS, Khanom R, Rahman MA (2015) Removal of congo red dye from industrial wastewater by untreated sawdust. American J Environ Protec 4(5):207–213
Yang G, Wu L, Xian Q, Shen F, Wu J, Zhang Y (2016) Removal of congo red and methylene blue from aqueous solutions by vermicompost-derived biochars. PLoS ONE 11(5):0154562
Han R, Ding D, Xu Y, Zou W, Wang Y, Li Y, Zou L (2008) Use of rice husk for the adsorption of congo red from aqueous solution in column mode. Bioresource Tech 99(8):2938–2946
Ponnusami V, Madhuram R, Krithika V, Srivastava SN (2008) Effects of process variables on kinetics of methylene blue sorption onto untreated guava (Psidium guajava) leaf powder: statistical analysis. Chem Eng J 140(1–3):609–613
Rafatullah M, Sulaiman O, Hashim R, Ahmad A (2010) Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: a review. J Hazard Mater 177(1–3):70–80
Harris JT, McNeil AJ (2020) Localized hydrogels based on cellulose nanofibers and wood pulp for rapid removal of methylene blue. J Polym Sci
Dadhaniya PV, Patel MP, Patel RG (2006) Swelling and dye adsorption study of novel superswelling [Acrylamide/N-vinylpyrrolidone/3 (2-hydroxyethyl carbamoyl) acrylic acid] hydrogels. Polym Bull 57(1):21–31
Salzano de Luna M, Altobelli R, Gioiella L, Castaldo R, Scherillo G, Filippone G (2017) Role of polymer network and gelation kinetics on the mechanical properties and adsorption capacity of chitosan hydrogels for dye removal. J Polym Sci Part B: Polym Phy 55(24):1843–1849
Hui M, Shengyan P, Yaqi H, Rongxin Z, Anatoly Z, Wei C (2018) A highly efficient magnetic chitosan “fluid” adsorbent with a high capacity and fast adsorption kinetics for dyeing wastewater purification. Chem Eng J 345:556–565
Li Y, Gao H, Wang C, Zhang X, Zhou H (2018) One-step fabrication of chitosan-Fe (OH)3 beads for efficient adsorption of anionic dyes. Inter J Biolog Macromol 117:30–41
You L, Huang C, Lu F, Wang A, Liu X, Zhang Q (2018) Facile synthesis of high performance porous magnetic chitosan-polyethylenimine polymer composite for Congo red removal. Inter J Biolog Macromol 107:1620–1628
Liu L, Wang R, Yu J, Hu L, Wang Z, Fan Y (2018) Adsorption of Reactive Blue 19 from aqueous solution by chitin nanofiber-/nanowhisker-based hydrogels. RSC adv 8(28):15804–15812
Mai TTT, Ha PT, Pham HN, Le TTH, Pham HL, Phan TBH, Nguyen XP (2012) Chitosan and O-carboxymethyl chitosan modified Fe3O4 for hyperthermic treatment. Adv Nat Sci Nanosci Nanotechnol. 3(1):015006
Safee NHA, Abdullah MP, Othman MR (2010) Carboxymethyl chitosan− Fe3O4 nanoparticles: synthesis and characterization. Malays J Anal Sci 14:63–68
Guo J, Ye X, Liu W, Wu Q, Shen H, Shu K (2009) Preparation and characterization of poly (acrylonitrile-co-acrylic acid) nanofibrous composites with Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. Mater Lett 63(15):1326–1328
Veličković SJ, Džunuzović ES, Griffiths PC, Lacik I, Filipović J, Popović IG (2008) Polymerization of itaconic acid initiated by a potassium persulfate/N, N-dimethylethanolamine system. J Appl Polym Sci 110(5):3275–3282
Willke T, Vorlop KD (2001) Biotechnological production of itaconic acid. Appl Microbio Biotech 56(3–4):289–295
Yu Y, Li Y, Liu L, Zhu C, Xu Y (2011) Synthesis and characterization of pH-and thermoresponsive poly (N-isopropylacrylamide-co-itaconic acid) hydrogels crosslinked with N-maleyl chitosan. J Polym Resear 18(2):283–291
Ahmad K, Ashfaq M, Shah SSA, Hussain E, Naseem HA, Parveen S, Ayub A (2021) Effect of metal atom in zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIF-8 & 67) for removal of Pb2+ & Hg2+ from water. Food Chem Toxic 149:112008
Ayub A, Irfan A, Raza ZA, Abbas M, Muhammad A, Ahmad K, Munwar A (2021) Development of poly (1-vinylimidazole)-chitosan composite sorbent under microwave irradiation for enhanced uptake of Cd (II) ions from aqueous media. Polym Bull 1–21
Shah HUR, Ahmad K, Naseem HA, Parveen S, Ashfaq M, Rauf A, Aziz T (2021) Water stable graphene oxide metal-organic frameworks composite (ZIF-67@ GO) for efficient removal of Malachite Green from water. Food and Chem Toxic 112312
Kilic M, Apaydin-Varol E, Putun AE (2011) Adsorptive removal of phenol from aqueous solutions on activated carbon prepared from tobacco residues: equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics. J Hazard Mater 189(1–2):397–403
Sirajudheen P, Karthikeyan P, Vigneshwaran S, Meenakshi S (2020) Synthesis and characterization of La(III) supported carboxymethylcellulose-clay composite for toxic dyes removal: evaluation of adsorption kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamics. Int J Biol Macromol 161:1117–1126
Ahmad K, Shah HUR, Nasim HA, Ayub A, Ashfaq M, Rauf A, Hussain E (2021) Synthesis and characterization of water stable polymeric metallo organic composite (PMOC) for the removal of arsenic and lead from brackish water. Toxin Rev 1–11
Khan NA, Najam T, Shah SSA, Hussain E, Ali H, Hussain S, Ashfaq M (2020) Development of Mn-PBA on GO sheets for adsorptive removal of ciprofloxacin from water: kinetics, isothermal, thermodynamic and mechanistic studies. Mater Chem Phys 245:122737
Doan VD, Tran TKN, Nguyen AT, Tran VA, Nguyen TD (2021) Comparative study on adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes by nanomagnetite supported on biochar derived from Eichhornia crassipes and Phragmites australis stems. Environ Nanotech Monit Manag 100569
Chen C, Mi S, Lao D, Shi P, Tong Z, Li Z, Hu H (2019) Single-step synthesis of eucalyptus sawdust magnetic activated carbon and its adsorption behavior for methylene blue. RSC Adv 9(39):22248–22262
Ahmad K, Parveen S, Aziz T, Naseem HA, Ashfaq M, Rauf A (2021) Metal Organic Framework (KIUB-MOF-1) as efficient adsorbent for cationic and anionic dyes from brackish water. J Mol Str 130898
Ghaedi M, Hajjati S, Mahmudi Z, Tyagi I, Agarwal S, Maity A, Gupta VK (2015) Modeling of competitive ultrasonic assisted removal of the dyes–Methylene blue and Safranin-O using Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Chem Eng J 268:28–37
Ai L, Zhang C, Chen Z (2011) Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by a solvothermal-synthesized graphene/magnetite composite. J hazard Mater 192(3):1515–1524
Roosta M, Ghaedi M, Daneshfar A, Sahraei R, Asghari A (2014) Optimization of the ultrasonic assisted removal of methylene blue by gold nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon using experimental design methodology. Ultrasonics sonochem 21(1):242–252
Salem IA, El-Maazawi MS (2000) Kinetics and mechanism of color removal of methylene blue with hydrogen peroxide catalyzed by some supported alumina surfaces. Chemosphere 41(8):1173–1180
Khoshsang H, Ghaffarinejad A, Kazemi H, Wang Y, Arandiyan H (2018) One-pot synthesis of S-doped Fe2O3/C magnetic nanocomposite as an adsorbent for anionic dye removal: equilibrium and kinetic studies. J Nanostr Chem 8(1):23–32
Kamal S, Khan F, Kausar H, Khan MS, Ahmad A, Ishraque Ahmad S, Nami SA (2020) Synthesis, characterization, morphology, and adsorption studies of ternary nanocomposite comprising graphene oxide, chitosan, and polypyrrole. Polym Compos 41(9):3758–3767
Prajapati AK, Mondal MK (2021) Development of CTAB modified ternary phase α-Fe2O3-Mn2O3-Mn3O4 nanocomposite as innovative super-adsorbent for Congo red dye adsorption. J Environ Chem Eng 9(1):104827
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by UGC CPEPA-II (C/CPEPA/chem/2018-19/2442(2) as SRF. We also greatly thankful to the head of the department of chemistry at Sardar Patel University for providing the research facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, S.R., Patel, M.P. Selective capture of anionic and cationic dyes via chitosan-g-poly-(IA-co-DADMAC)/Fe3O4 polymer composite hydrogel. Polym. Bull. 79, 11079–11101 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-04017-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-04017-w