Abstract
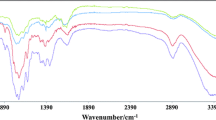
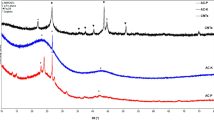
Extracted cellulose fibers from Quinoa wastes were successfully incorporated with multi-walled carbon nanotubes/ZnO (MWCNTs/ZnO). Manganese complex was supported on natural cellulose and reacted with MWCNT/Zn bio-nanocomposite to have MWCNT/ZnO/Mn complex@oxidized cellulose. This novel bio-nanocomposite was characterized by SEM, TEM, FT-IR, TGA, and EDS. The catalytic activity of this composite was considered on the oxidation of alcohols. High conversion and selectivities of desired aldehyde and ketone products were obtained applying H2O2 and under solvent-free conditions. This heterogeneous catalyst was easily recycled and reused eight times without any significant catalytic activities and stabilities.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martin-Luengo MA, Yates M, Ramos M, Saez Rojo E, Martinez Serrano AM, Gonzalez Gil L, Ruiz Hitzky E (2011) Biomaterials from beer manufacture waste for bone growth scaffolds. Green Chem Lett Rev 4:229–233
Al-Barakah F, Radwan S, Abdel-Aziz R (2013) Using biotechnology in recycling agricultural waste for sustainable agriculture and environmental protection. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 2:446–459
Farooq M, Zou T, Riviere G, Sipponen MH, Österberg M (2019) Strong, ductile, and waterproof cellulose nanofibril composite films with colloidal lignin particles. Biomacromol 202:693–704
Udangawa RN, Mikael PE, Mancinelli C, Chapman C, Willard CF, Simmons TJ, Linhardt RJ (2019) Novel cellulose-halloysite hemostatic nanocomposite fibers with a dramatic reduction in human plasma coagulation time. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:15447–15456
Seku K, Reddy Gang B, Pejjai B, Kadimpati KK, Golla N (2018) Microwave-assisted synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their application in catalytic, antibacterial and antioxidant activities. J Nanostruct Chem 8:179–188
Qi H, Liu J, Mäder E (2014) Smart cellulose fibers coated with carbon nanotube networks. Fibers 2:295–307
Chen C, Bu X, Feng Q, Li D (2018) Cellulose nanofiber/carbon nanotube conductive nano-network as a reinforcement template for polydimethylsiloxane. Nanocomposit Polymers 10:1000–1010
Chen J, Liao X, Xiao W, Yang J, Jiang Q, Li G (2019) Facile and green method to structure ultralow-threshold and lightweight polystyrene/mwcnt composites with segregated conductive networks for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 711:9904–9915
Chen X, Zhang H, Ci C, Sun W, Wang Y (2019) Few-layered boronic ester based covalent organic frameworks/carbon nanotube composites for high-performance k-organic batteries. ACS Nano 133:3600–3607
Chakraborty I, Chakrabarty N, Senapati A, Chakraborty AK (2018) CuO@NiO /Polyaniline/MWCNT nanocomposite as high-performance electrode for supercapacitor. J Phys Chem C 122(48):27180–27190
Zhang Y, Huang R, Peng S, Ma Z (2015) MWCNTs/Cellulose hydrogels prepared from NaOH/urea aqueous solution with improved mechanical properties. J Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/413497
Mari KH, Mieno T (2017) Production and properties of carbon nanotube/cellulose composite paper. J Nanomaterials. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6745029
Kafi-Ahmadi L, Shirmohammadzadeh L (2017) Synthesis of Co(II) and Cr(III) salicylidenic Schiff base complexes derived from thiourea as precursors for nano-sized Co3O4 and Cr2O3 and their catalytic, antibacterial properties. J Nanostruct Chem 7:179–190
Zhang S, Zhang F, Pan Y, Jin L, Liu B, Mao Y, Huang J (2018) Multiwall-carbon-nanotube/cellulose composite fibers with enhanced mechanical and electrical properties by cellulose grafting. RSC Adv 8:5678–5684
Naeimi A, Abbasspour S, Torabizadeh SA (2020) The first and low cost copper Schiff base/ manganese oxide bio nanocomposite from unwanted plants as a robust industrial catalyst. Artificial Cells, Nanomed, Biotechnol 48:560–571
Naeimi A, Honarmand M, Sedri A (2019) Ultrasonic assisted fabrication of first MoO3/copper complex bio-nanocomposite based on Sesbania sesban plant for green oxidation of alcohols. Ultrason Sonochem 50:331–338
Naeimi A, Payandeh M, Ghara AR, Ghadi FE (2020) In vivo evaluation of the wound healing properties of bio-nanofiber chitosan/ polyvinyl alcohol incorporating honey and Nepeta dschuparensis. Carbohydr Polym 240:116315
Sedri A, Naeimi A, Mohammadi SZ (2018) An innovative synthesis of MoO3/Ag nanocomposite and catalytic application of immobilized molybdenum complex on cellulose extracting from Carthamus tinctorius. Carbohydr Polym 199:236–243
Stevanic JS, Salmén L (2008) Characterizing wood polymers in the primary cell wall of Norway spruce (Picea abies (L.) Karst.) using dynamic FT-IR spectroscopy. Cellulose 15:285
Rong L, Zeng M, Liu H, Wang B, Mao Z, Xu H, Zhang L, Zhong Y, Yuan J, Sui X (2019) Biginelli reaction on cellulose acetoacetate: a new approach for versatile cellulose derivatives. Carbohydr Polym 209:223–229
Mendoza D, Browne C, Raghuwanshi V, Simon G, Garnier G (2019) One-shot TEMPO-Periodate oxidation of native cellulose. Carbohydr Polym. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115292
Spinella S, Maiorana A, Qian Q, Dawson NJ, Hepworth V, McCallum SA, Ganesh M, Singer KD, Gross RA (2016) Concurrent cellulose hydrolysis and esterification to prepare a surface-modified cellulose nanocrystal decorated with carboxylic acid moieties. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4:1538–1550
Chen Y, Chen S, Wang B, Yao J, Wang H (2017) TEMPO-oxidized bacterial cellulose nanofibers-supported gold nanoparticles with superior catalytic properties. Carbohydr Poly 160:34–42
Liu C, Jin RN, Ouyang X, Wang YG (2017) Adsorption behavior of carboxylated cellulose nanocrystal-polyethyleneimine composite for removal of Cr(VI) ions. Appl Surf Sci 408:77–87
Ali MS, Lohedan AA, Abdullah MMS, Afsan Z, Tabassum S (2019) Catalytic induced morpholical transformation of porous ZnO to ZnO nanorods by Sn(IV) and their effect on photocatalytic reduction of methylene blue and DFT calculations. Spectrochimica Acta Part A Mole Biomol Spectro 220:117101
Jiang Z, Chen D, Yu Y, Miao J, Liu Y, Zhang L (2017) Composite fibers prepared from multi-walled carbon nanotubes/cellulose dispersed/dissolved in ammonium/dimethyl sulfoxide mixed solvent. RSC Adv 7:2186–2192
Kshitij J, Mukesh KM, Krishna MP (2020) Fabrication and characterization of bioblocks from agricultural waste using fungal mycelium for renewable and sustainable applications. ACS Appl Bio Mater 3:4
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the South Kerman research center for Agriculture and natural Resources, Kerman University of Medical Science, and University of Jiroft for the support of this work under number contract:10.60.2234 (3.10.1399).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naeimi, A., Khoshkam, S. & Eslaminejad, T. Natural cellulose fibers from Quinoa wastes reinforced carbon nanotube/ZnO bio-nanocomposite as a novel recyclable catalyst for oxidation reaction. Polym. Bull. 79, 7795–7808 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-03876-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-03876-7