Abstract
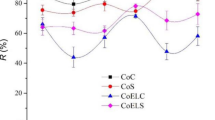
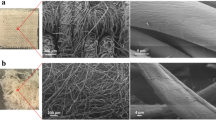
End-of-life textile recycling presents a real economic and environmental challenge. From a circular economy perspective, we attempt to evaluate the chitosan–ZnO nanocomposite efficiency in the recycling of cotton-used fabric, accompanied by the electroanalytic and the optoelectronic investigation of the resulting nanocomposites. For comparison, the precipitation and the sonochemical pathways were used as in situ treatment methods. The effect of chitosan characteristics on the antibacterial sustainability of the treated fabrics and the properties of the resulting nanocomposites were studied. The chemical bonding, crystal structure, morphology, optical and optoelectronic properties, intermolecular interactions and antibacterial properties of the resulting free nanocomposites were investigated. The treated used fabrics were characterized by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy equipped with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy before and after 20 washes. Density functional theory study and atoms in molecules analysis of cellulose–nanocomposite interaction were carried out. The results indicate an effective dose of 2 mg against tested bacteria for all the nanocomposites. The nanocomposites have an orange-red emission with no Zn defects and large oscillator strength (ƒ) values. Medium molecular weight chitosan-based nanocomposites showed more intense orange-red emission and higher ƒ values. Sustainable antibacterial properties of treated fabrics are generated with high molecular weight chitosan-based nanocomposites. More than 83% of the antibacterial activity is retained after 20 washes. The theoretical study confirms the stability of the free nanocomposite (chitosan–ZnO) and its destabilization by contacting the fabric when ZnO is a rod shaped, which generates its growth-promoting.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Suarez-Eiroa B, Fernandez E, Mendez-Martínez G, Soto-Onate D (2019) Operational principles of circular economy for sustainable development: linking theory and practice. J Clean Prod 214:952–961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.12.271
Mallakpour S, Sirous F, Hussain CM (2021) A journey to the world of fascinating ZnO nanocomposites made of chitosan, starch, cellulose, and other biopolymers: progress in recent achievements in eco-friendly food packaging, biomedical, and water remediation technologies. Int J Biol Macromol 170:701–716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.12.163
Pinto RJB, Carlos LD, Marques PAAP, Silvestre AJD, Freire CSR (2014) An overview of luminescent bio-based composites. J Appl Polym Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/APP.41169
Ponnamma D, Sadasivuni KK, AlMaadeed MA (2015) Introduction of biopolymer composites: what to do in electronics? In: Sadasivuni KK, Ponnamma D, Kim J, Cabibihan J-J, AlMaadeed MA (eds) Biopolymer composites in electronics. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-809261-3.00001-2
Koszewska M (2018) circular economy: challenges for the textile and clothing industry. Autex Res J 18:337–347. https://doi.org/10.1515/aut-2018-0023
Mosquera MAF (2017) Circular economy at the micro level: a dynamic view of incumbents’ struggles and challenges in the textile industry. J Clean Prod 168:833–845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.09.056
Jia F, Yin S, Chen L, Chen X (2020) Circular economy in textile and apparel industry: a systematic literature review. J Clean Prod 259:120728–120748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120728
Zins HM (2011) Reusable medical textiles. In: Bartels VT (ed) Handbook of medical textiles. Woodhead Publishing Limited, Cambridge, pp 80–105. https://doi.org/10.1533/9780857093691.1.80
To MH, Uisan K, Ok YS, Pleissner D, Lin CSK (2019) Recent trends in green and sustainable chemistry: rethinking textile waste in a circular economy. Curr Opin Green Sustain Chem 20:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsc.2019.06.002
Morganti P (2016) Circular economy: a new horizon for bio- nanocomposites from waste materials. Int J Biotech Well 5:1–7. https://doi.org/10.6000/1927-3037.2016.05.04.1
Preethi S, Abarna K, Nithyasri M, Kishore P, Deepika K, Ranjithkumar R, Bhuvaneshwari V, Bharathi D (2020) Synthesis and characterization of chitosan/zinc oxide nanocomposite for antibacterial activity onto cotton fabrics and dye degradation applications. Int J Biol Macromol 164:2779–2787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.047
Jatoi AS, Khan FSA, Mazari SA, Mubarak NM, Abro R, Ahmed J, Ahmed M, Baloch H, Sabzoi N (2020) Current applications of smart nanotextiles and future trends. In: Ehrmann A, Nguyen TA, Tri PN (eds) Nanosensors and nanodevices for smart multifunctional textiles. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 343–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-820777-2.00019-4
Massella D, Giraud S, Guan J, Ferri A, Salaün F (2019) Manufacture techniques of chitosan-based microcapsules to enhance functional properties of textiles. In: Crini G, Lichtfouse E (eds) Sustainable agriculture reviews 35. Springer Nature, Switzerland, pp 303–336. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-16538-3_8
Rajendran K, Sivalingam T (2013) Industrial method of cotton fabric finishing with chitosan–ZnO composite for anti-bacterial and thermal stability. Ind Crops Prod 47:160–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.03.007
Wu Y, Yang Y, Zhang Z, Wang Z, Zhao Y, Sun L (2018) Fabrication of cotton fabrics with durable antibacterial activities finishing by Ag nanoparticles. Text Res J 89:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1177/0040517518758002
Attia NF, Elashery SEA, Oh H (2020) Nanomaterials-based antibacterial textiles. In: Ehrman A, Nguyen T, Tri PN (eds) Nanosensors and nanodevices for smart multifunctional textiles. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 135–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-820777-2.00009-1
Román LE, Gomez ED, Solís JL, Gómez MM (2020) Antibacterial cotton fabric functionalized with copper oxide nanoparticles. Molecules 25:1–21. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25245802
Barros FCF, Sousa Neto VO, Carvalho TV, Vieira RS, Silva GMM, Nascimento RF (2015) Recent development of chitosan nanocomposites with multiple potential uses. In: Thakur VK, Thakur MK (eds) Eco-friendly polymer nanocomposites. Springer, New Delhi, pp 497–531. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-2473-0_16
Cheaburu-Yilmaz CN, Yilmaz O, Vasile C (2015) Eco-friendly chitosan-based nanocomposites: chemistry and applications. In: Thakur VK, Thakur MK (eds) Eco-friendly polymer nanocomposites. Springer, New Delhi, pp 341–386. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-2473-0_11
Safeera TA, Anila EI (2017) Wet chemical synthesis of chitosan capped ZnO: Na nanoparticles for luminescence applications. Int J Biol Macromol 104:1833–1836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.02.027
Alamdari S, Ghamsari MS, Lee C, Han W, Park H-H, Tafreshi MJ, Afarideh H, Majles Ara MH (2020) Preparation and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of sambucus ebulus. Appl Sci 10:3620–3639. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103620
Jangir LK, Kumari Y, Kumar A, Kumar M, Awasthi K (2017) Investigation of luminescence and structural properties of ZnO nanoparticles, synthesized with different precursors. Mater Chem Front 1:1413–1421. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7qm00058h
Gupta AK, Hsu C-H, Purwidyantri A, Prabowo BA, Chiu K-P, Chen C-H, Tian Y-C, Lai C-S (2020) ZnO- Nanorod processed PC-SET as the light-harvesting model for plasmontronic fluorescence sensor. Sens Actuators B 307:127597–127608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127597
Dheivamalar S, Bansurabanu K (2018) Enhancing the light harvesting efficiency, open circuit voltage and stability of molybdenum doped ZnO6 nanocluster in dye-sensitized solar cells: (a DFT study). Orient J Chem 34:2292–2304. https://doi.org/10.13005/ojc/340509
Belay A (2010) Measurement of integrated absorption cross-section, oscillator strength and number density of caffeine in coffee beans by integrated absorption coefficient technique. Food Chem 121:585–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.12.052
Prokhorov E, Luna-Bárcenas G, Yáñez Limón JM, Sánchez AG, Kovalenko Y (2020) Chitosan-ZnO nanocomposites assessed by dielectric, mechanical, and piezoelectric properties. Polymers 12:1991–2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12091991
AATCC Test method 138–2005, AATCC Technical manual (2010)
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB et al (2009) Gaussian 09, revision A.02. Wallingford CT, Gaussian Inc
Environment MSM (2014) Release 8. Accelrys Software Inc., San Diego, Calif, USA
Bader RFW (1991) A quantum theory of molecular structure and its applications. Chem Rev 91:893–928. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr00005a013
Lu T, Chen F (2012) Multiwfn: a multifunctional wavefunction analyzer. J Comput Chem 33:580–592
Wang X, Du Y, Liu H (2004) Preparation, characterization and antimicrobial activity of chitosan–Zn complex. Carbohydr Polym 56:21–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2003.11.007
Xu S, Wang ZL (2011) One-dimensional ZnO nanostructures: solution growth and functional properties. Nano Res 4:1013–1098. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-011-0160-7
AbdElhady MM (2012) Preparation and characterization of chitosan/Zinc oxide nanoparticles for imparting antimicrobial and UV protection to cotton fabric. Int J Carbohydr Chem. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/840591
El-Nahhal IM, Zourab SM, Kodeh FS, Elmanama AA, Selmane M, Genois I, Babonneau F (2013) Nano-structured zinc oxide–cotton fibers: synthesis, characterization and applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 24:3970–3975. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-013-1349-1
Yadav A, Prasad V, Kathe AA, Raj S, Yadav D, Sundaramoorthy C, Vigneshwaran N (2006) Functional finishing in cotton fabrics using zinc oxide nanoparticles. Bull Mater Sci 29:641–645. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-006-0017-y
Mason T, Peters D (2002) Practical sonochemistry uses and applications of ultrasound. Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge
Patil AB, Bhanage BM (2016) Sonochemistry: a greener protocol for nanoparticles synthesis. In: Aliofkhazraei M (ed) Handbook of nanoparticles. Springer, Switzerland, pp 143–166
Shahraki RR, Ebrahim SAS, Masoudpanah SM (2015) Synthesis and characterization of superparamagnetic zinc ferrite–chitosan composite nanoparticles. J Supercond Nov Magn 28:2143–2147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-015-3015-8
Pholnak C, Sirisathitkul C, Harding DJ (2011) Characterizations of octahedral zinc oxide synthesized by sonochemical method. J Phys Chem Solids 72:817–823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2011.04.005
Cayley GR, Hague DN (1971) Correlation between the metal-nitrogen stretching frequency and the coordination number in zinc ammines. Trans Faraday Soc 67:2896–2901. https://doi.org/10.1039/TF9716702896
Zabihi E, Babaei A, Shahrampour D, Arab-Bafrani Z, Mirshahidi KS, Majidi HJ (2019) Facile and rapid in-situ synthesis of chitosan-ZnO nano-hybrids applicable in medical purposes; a novel combination of biomineralization, ultrasound, and bio-safe morphology-conducting agent. Int J Biol Macromol 131:107–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.01.224
Yusof NAA, Zain NM, Pauzi N (2019) Synthesis of chitosan/Zinc oxide nanoparticles stabilized by chitosan via microwave heating. Bull Chem React Eng Catal 14:450–458. https://doi.org/10.9767/bcrec.14.2.3319.450-458
Anandhavelu S, Thambidurai S (2011) Preparation of chitosan–zinc oxide complex during chitin deacetylation. Carbohydr Polym 83:1565–1569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.10.006
Montero-Muñoz M, Ramos-Ibarra JE, Rodríguez-Páez JE, Marques GE, Teodoro MD, Coaquira JAH (2020) Growth and formation mechanism of shape-selective preparation of ZnO structures: correlation of structural, vibrational and optical properties. Phys Chem Chem Phys 22:7329–7339. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9CP06744B
Kahn M, Monge M, Collière V, Senocq F, Maisonnat A, Chaudret B (2005) Size- and shape-control of crystalline zinc oxide nanoparticles: a new organometallic synthetic method. Adv Funct Mater 15:458–468. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.200400113
Abiraman T, Kavitha G, Rengasamy R, Balasubramanian S (2016) Antifouling behavior of chitosan adorned zinc oxide nanorods. RSC Adv. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.200400113
Magesh G, Bhoopathi G, Nithya N, Arun AP, Ranjith Kumar E (2018) Tuning effect of polysaccharide Chitosan on structural, morphological, optical and photoluminescence properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Superlattices Microstruct 117:36–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2018.03.003
Barreto MSR, Andrade CT, Azero EG, Paschoalin VMF, Del Aguila EM (2017) Production of chitosan/zinc oxide complex by ultrasonic treatment with antibacterial activity. J Bacteriol Parasitol 8:330–337. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9597.1000330
Nithya A, Jothivenkatachalam K (2015) Chitosan assisted synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles: an efficient solar light driven photocatalyst and evaluation of antibacterial activity. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 26:10207–10216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-3710-z
Chauhan R, Kumar A, Chaudhary RP (2012) Photocatalytic studies of silver doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by chemical precipitation method. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 63:546–553. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-012-2818-3
Morkoç H, Özgur Ü (2009) Zinc oxide: fundamentals materials and device technology. WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co KGaA, Weinheim
Dhillon GS, Kaur S, Brar SK (2014) Facile fabrication and characterization of chitosan-based zinc oxide nanoparticles and evaluation of their antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity. Int Nano Lett 4:107–118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40089-014-0107-6
Cintas P, Cravotto G, Barge A, Martina K (2015) Interplay between mechanochemistry and sonochemistry. Top Curr Chem 369:239–284. https://doi.org/10.1007/128_2014_623
Kumar S, Krishnakumar B, Sobral AJFN, Koh J (2018) Bio-based (Chitosan/PVA/ZnO) nanocomposites film: thermally stable and photoluminescence material for removal of organic dye. Carbohydr Polym 205:559–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.10.108
Mi F-L (2005) Synthesis and characterization of a novel chitosan-gelatin bioconjugate with fluorescence emission. Biomacromol 6:975–987. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm049335p
Huang H, Liu F, Chen S, Zhao Q, Liao B, Long Y, Zeng Y, Xia X (2013) Enhanced fluorescence of chitosan based on size change of micelles and application to directly selective detecting Fe3+ in human serum. Biosens Bioelectron 42:539–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2012.10.098
Packirisamy RG, Govindasamy C, Sanmugam A, Venkatesan S, Kim H-S, Vikraman D (2019) Synthesis of novel Sn1−x ZnxO-chitosan nanocomposites: structural, morphological and luminescence properties and investigation of antibacterial properties. Int J Biol Macromol 138:546–555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.07.120
Sanmugam A, Vikraman D, Venkatesan S, Park HJ (2017) Optical and structural properties of solvent free synthesized starch/chitosan-ZnO nanocomposites. J Nanomater. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7536364
Vossmeyer T, Katsikas L, Giersig M, Popovic IG, Diesner K, Chemseddine A, Eychmuler A, Weller H (1994) CdS nanoclusters: synthesis, characterization, size dependent oscillator strength, temperature shift of the excitonic transition energy, and reversible absorbance shift. J Phys Chem 98:7665–7673. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100082a044
Rabea EI, Badawy MET, Stevens CV, Smagghe G, Steurbaut W (2003) Chitosan as antimicrobial agent: applications and mode of action. Biomacromol 4:1457–1465. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm034130m
Bui VKH, Park D, Lee YC (2017) Chitosan combined with ZnO, TiO2 and Ag nanoparticles for antimicrobialwound healing applications: a mini review of the research trends. Polymers 9:21–45. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9010021
Negi H, Agarwal T, Zaidi MGH, Goel R (2012) Comparative antibacterial efficacy of metal oxide nanoparticles against gram negative bacteria. Ann Microbiol 62:765–772. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-011-0317-3
Sathiya SM, Okram GS, Dhivya SM, Manivannan G, Rajan MAJ (2016) Interaction of chitosan/zinc oxide nanocomposites and their antibacterial activities with Escherichia coli. Mater Today Proc 3:3855–3860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2016.11.040
Zhong R, Zhong Q, Huo M, Yang B, Li H (2020) Preparation of biocompatible nano-ZnO/Chitosan microspheres with multi-functions of antibacterial, UV-shielding and dye photodegradation. Int J Biol Macromol 146:939–945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.09.217
Kresken M, Körber-Irrgang B, Korte-Berwanger M et al (2020) Dissemination of carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates and their susceptibilities to ceftolozane-tazobactam in Germany. Int J Antimicrob Agents 55:10595–10605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105959
Abdeen ZI, El Farargy AF, Negm NA (2018) Nanocomposite framework of chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol/ZnO: preparation, characterization, swelling and antimicrobial evaluation. J Mol Liq 250:335–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.12.032
Rivero PJ, Urrutia A, Goicoechea J, Arregui FJ (2015) Evaluation nanomaterials for functional textiles and fibers. Nanoscale Res Lett 10:501–523. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-015-1195-6
Yusof NAA, Zain NM, Pauzi N (2019) Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles with chitosan as stabilizing agent and their antibacterial properties against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Int J Biol Macromol 124:1132–1136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.228
Hosseinnejad M, Jafari SM (2016) Evaluation of different factors affecting antimicrobial properties of chitosan. Int J Biol Macromol 85:467–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.01.022
Bharathi D, Ranjithkumar R, Chandarshekar B, Bhuvaneshwari V (2019) Preparation of chitosan coated zinc oxide nanocomposite for enhanced antibacterial and photocatalytic activity: as a bionanocomposite. Int J Biol Macromol 129:989–996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.02.061
Muraleedaran MRPK, Abdul Mujeeb VM (2015) Applications of chitosan powder with in situ synthesized nano ZnO particles as an antimicrobial agent. Int J Biol Macromol 77:266–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.03.058
Cloud RM, Cao W, Song G (2013) Functional finishes to improve the comfort and protection of apparel. In: Gulrajani ML (ed) Advances in the dyeing and finishing of technical textiles. Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge, pp 258–279
Ammayappan L, Moses JJ (2009) Study of antimicrobial activity of aloevera, chitosan, and curcumin on cotton, wool, and rabbit hair. Fiber Polym 10:161–166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-009-0161-2
Lim SH, Hudson SM (2004) Application of a fiber-reactive chitosan derivative to cotton fabric as an antimicrobial textile finish. Carbohydr Polym 56:227–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2004.02.005
Zivanovic S, Davis RH, Golden DA (2015) Chitosan as an antimicrobial in food products. In: Taylor TM (ed) Handbook of natural antimicrobials for food safety and quality. Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge, pp 153–181
Kumar PSV, Raghavendra V, Subramanian V (2016) Bader’s theory of atoms in molecules (AIM) and its applications to chemical bonding. J Chem Sci 128:1527–1536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-016-1172-3
Boys SF, Bernardi F (1970) The calculation of small molecular interactions by the differences of separate total energies. some procedures with reduced errors. Mol Phys 19:553–566. https://doi.org/10.1080/00268977000101561
Chang J, Waclawik ER (2012) Experimental and theoretical investigation of ligand effects on the synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 14:1012–1026. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-1012-4
Paukku Y, Michalkova A, Leszczynski J (2009) Quantum-chemical comprehensive study of the organophosphorus compounds adsorption on zinc oxide surfaces. J Phys Chem C 113:1474–1485. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp807744a
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mekahlia, S., Douadi, T. Chitosan–ZnO nanocomposite from a circular economy perspective: in situ cotton-used fabric recycling and the nanocomposite recovering. Polym. Bull. 79, 7491–7529 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-03859-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-03859-8