Abstract
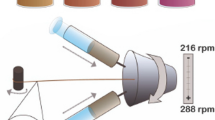
To date, electrospun yarns have been applied in various research fields such as composites, filtrations, and biomedical engineering regarding their unique and fabulous characteristics. Herein, a multilayer polyamide6/poly urethane/polyamide6 (PA6/PU/PA6) nanofibrous yarn was designed and fabricated based on the Bob-Tex spinning technique. Morphology and mechanical properties of the fabricated three-layer structure were evaluated. The obtained results represented tensile strength of 81, 70.5, and 51 MPa for the electrospun PA6, PU, and three-layer yarns, respectively. In addition, the three-layer nanofibrous yarn exhibited higher elastic modulus than the PA6 nanofiber yarn. Moreover, the nanofibrous PA6, PU, and three-layer yarns displayed elongation rate of 59.9, 120.5, and 71.3% and work of rupture of 2631, 4671, and 2902.5 MPa, respectively. Furthermore, evaluation of the raptured ends showed ductile fracture of the PA6 nanofibers and brittle fracture of the PU electrospun fibers.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hajiani F, Jeddi AAA, Gharehaghaji AA (2012) An investigation on the effects of twist on geometry of the electrospinning triangle and polyamide 66 nanofiber yarn strength. Fibers Polym 13:244–252
Fakhrali A, Ebadi SV, Gharehaghaji AA (2014) Production of core-sheath nanofiber yarn using two opposite asymmetric nozzles. Fibers Polym 15:2535–2540
Najafi SJ, Gharehaghaji AA, Etrati SM (2016) Fabrication and characterization of elastic hollow nanofibrous PU yarn. Mater Design 99:328–334
He JX, Zhou YM, Wu YC, Liu RT (2014) Nanofiber coated hybrid yarn fabricated by novel electrospinning-airflow twisting method. Surf Coatings Technol 258:398–404
Javazmi L, Ravandi SAH, Ghareaghaji AA (2014) Fabrication and characterization of PET nanofiber hollow yarn. Fibers Polym 15:954–960
Shahrabi S, Gharehaghaji AA, Latifi M (2016) Fabrication of electrospun polyamide-66 nanofiber layer for high-performance nanofiltration in clean room applications. J Ind Text 45:1100–1114
Hajiani F, Ghareaghaji AA, Jeddi AAA et al (2014) Wicking properties of polyamide 66 twisted nanofiber yarn by tracing the color alteration in yarn structure. Fibers Polym 15:1966–1976
He J, Zhou Y, Qi K et al (2013) Continuous twisted nanofiber yarns fabricated by double conjugate electrospinning. Fibers Polym 14:1857–1863
Fakhrali A, Ebadi SV, Gharehaghaji AA et al (2016) Analysis of twist level and take-up speed impact on the tensile properties of PVA/PA6 hybrid nanofiber yarns. E-Polymers 16:125–135
Shuakat MN, Lin T (2016) Direct electrospinning of nanofibre yarns using a rotating ring collector. J Text Inst 107:791–799. https://doi.org/10.1080/00405000.2015.1061785
Akcoren D, Avci MZ, Gokce ZG et al (2018) Fabrication and characterization of poly(butyl acrylate-co-methyl methacrylate)-polypyrrole nanofibers. Polym Bull 75:1607–1617. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-017-2110-3
Asghari Mooneghi S, Gharehaghaji AA, Hosseini-Toudeshky H, Torkaman G (2015) Failure mechanism of polyamide 66 nanofiber yarns under fatigue and static tensile loading. J Appl Polym Sci 132. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.41925
Yan T, Tian L, Pan Z (2016) Structures and mechanical properties of plied and twisted polyacrylonitrile nanofiber yarns fabricated by a multi-needle electrospinning device. Fibers Polym 17:1627–1633
Dabirian F, Hosseini SA (2009) Novel method for nanofibre yarn production using two differently charged nozzles. Fibres Text East Eur 74:45–47
Li X, Yao C, Sun F et al (2008) Conjugate electrospinning of continuous nanofiber yarn of poly(L-lactide)/nanotricalcium phosphate nanocomposite. J Appl Polym Sci 107:3756–3764
Ghane N, Mazinani S, Gharehaghaji AA (2018) Fabrication and characterization of hollow nanofibrous PA6 yarn reinforced with CNTs. J Polym Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-018-1477-7
Maleki H, Gharehaghaji AA, Moroni L, Dijkstra PJ (2013) Influence of the solvent type on the morphology and mechanical properties of electrospun PLLA yarns. Biofabrication 5. https://doi.org/10.1088/1758-5082/5/3/035014
Maleki H, Gharehaghaji AA, Criscenti G et al (2015) The influence of process parameters on the properties of electrospun PLLA yarns studied by the response surface methodology. J Appl Polym Sci 132. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.41388
Gu X, Li N, Luo J et al (2018) Electrospun polyurethane microporous membranes for waterproof and breathable application: the effects of solvent properties on membrane performance. Polym Bull 75:3539–3553. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-017-2223-8
Li J, Tian L, Pan N, Pan ZJ (2014) Mechanical and electrical properties of the PA6/SWNTs nanofiber yarn by electrospinning. Polym Eng Sci 54:1618–1624
Ravandi SAH, Tork RB, Dabirian F et al (2015) Characteristics of yarn and fabric made out of nanofibers. Mater Sci Appl 06:103–110
Maleki H, Gharehaghaji AA, Toliyat T, Dijkstra PJ (2016) Drug release behavior of electrospun twisted yarns as implantable medical devices. Biofabrication 8:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1088/1758-5090/8/3/035019
ElMessiry M, Fadel N (2019) The tensile properties of electrospun Poly vinyl chloride and cellulose acetate (PVC/CA) bi-component polymers nanofibers. Alexandria Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2019.08.003
Cui S, Sun X, Li K et al (2019) Polylactide nanofibers delivering doxycycline for chronic wound treatment. Mater Sci Eng C 104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.109745
Dias AM, da Silva FG, de Monteiro APF et al (2019) Polycaprolactone nanofibers loaded oxytetracycline hydrochloride and zinc oxide for treatment of periodontal disease. Mater Sci Eng C 103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.109798
Valipouri A, Gharehaghaji AA, Ravandi SAH, Dabirian F (2015) Study of capillary rise in biodegradable porous poly (l-lactic acid) electrospun nano/micro fiber yarns. J Ind Text 44:899–911
Ryšánek P, Malý M, Čapková P et al (2017) Antibacterial modification of nylon-6 nanofibers: structure, properties and antibacterial activity. J Polym Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-017-1365-6
Asghari Mooneghi S, Gharehaghaji AA, Hosseini-Toudeshky H, Torkaman G (2019) Effect of fatigue loading on wicking properties of polyamide 66 nanofiber yarns. J Appl Polym Sci 136. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.47206
Yang X, Wang Y, Qing X (2019) A flexible capacitive sensor based on the electrospun PVDF nanofiber membrane with carbon nanotubes. Sens Actuators A Phys 299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2019.111579
Yan T, Wang Z, Wang YQ, Pan ZJ (2018) Carbon/graphene composite nanofiber yarns for highly sensitive strain sensors. Mater Des 143:214–223
Mi HY, Jiang Y, Jing X et al (2019) Fabrication of triple-layered vascular grafts composed of silk fibers, polyacrylamide hydrogel, and polyurethane nanofibers with biomimetic mechanical properties. Mater Sci Eng C 98:241–249
Du L, Zhang Y, Li X et al (2020) High performance anti-smog window screens via electrospun nanofibers. J Appl Polym Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.48657
Levitt AS, Knittel CE, Vallett R et al (2017) Investigation of nanoyarn preparation by modified electrospinning setup. J Appl Polym Sci 134:19
Maleknia L, DIlamian M, Pilehrood M et al (2018) Preparation, process optimization and characterization of core-shell polyurethane/chitosan nanofibers as a potential platform for bioactive scaffolds. Res Pharm Sci 13:273–282. https://doi.org/10.4103/1735-5362.228957
Ali MG, Mousa HM, Blaudez F et al (2020) Dual nanofiber scaffolds composed of polyurethane- gelatin/nylon 6- gelatin for bone tissue engineering. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 597:124817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.124817
Klein W, Textile Institute (1993) New spinning systems. Textile Institute, p 260
Banitaba SN, Amini G, Gharehaghaji AA, Jeddi AAA (2017) Fabrication of hollow nanofibrous structures using a triple layering method for vascular scaffold applications. Fibers Polym 18:2342–2348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-017-1009-9
Banitaba SN, Gharehaghaji AA, Jeddi AAA (2021) Fabrication and characterization of hollow electrospun PLA structure through a modified electrospinning method applicable as vascular graft. Bull Mater Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-021-02463-w
Moghbelnejad Z, Gharehaghaji AA, Yousefzadeh M, Hajiani F (2021) Investigation of wicking phenomenon and tensile properties in three-layer composite nanofibrous PA/PLLA yarn. Polym Eng Sci 61:576–585. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.25601
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sohanaki, P., Ahamadloo, E., Gharehaghaji, A.A. et al. Fabrication and characterization of three-layer nanofibrous yarn (PA6/PU/PA6). Polym. Bull. 79, 7245–7264 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-03835-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-03835-2