Abstract
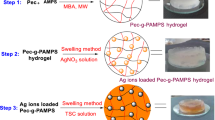
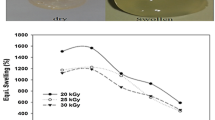
Silver nanoparticles made by green synthesis have been incorporated into pectin-based copolymer gel to make a nanocomposite gel to be used as an adsorbent material for the removal of divalent metal ions and dyes from aqueous solutions. Silver nanoparticles were obtained by mixing silver nitrate with aqueous solution of pectin followed by microwave irradiation. The nanocomposite hydrogel was obtained by the microwave-assisted polymerization of 2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid (AMPS) and acrylamide (AAm) in the presence of N,N’-methylene-bis-acrylamide (MBA) in pectin solution containing silver particles. Characterization of the nanocomposite gel was done by FTIR, TGA, XRD, FESEM and EDS techniques. The system was evaluated for its capacity to adsorb cationic dye, crystal violet (CV) and metal ions [Cu(II) and Pb(II)] from aqueous solutions. The presence of Ag nanoparticles is observed to enhance the adsorption capacity of the gel for the above mentioned adsorbates. The kinetic studies revealed second-order adsorption processes which fit well into Langmuir model. The evaluation of thermodynamic parameters indicated the adsorption process to be exothermic and spontaneous. A maximum of 1950 mg/g CV, 111 mg/g Cu(II) and 130 mg/g Pb(II) could be removed from the aqueous solution which is quite high in comparison with other reported materials. The desorption studies indicated the possible reusability of the nanocomposite.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lakshmipathy R, Sarada NC (2015) A fixed bed column study for the removal of Pb2+ ions by watermelon rind. Environ Sci Water Res Technol 1:244–250. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4EW00027G
Shirsath SR, Patil AP, Bhanvase BA, Sonawane SH (2015) Ultrasonically prepared poly(acrylamide)-kaolin composite hydrogel for removal of crystal violet dye from wastewater. J Environ Chem Eng 3:1152–1162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2015.04.016
Cao J, Cao H, Zhu Y, Wang S, Qian D, Chen G, Sun M, Huang W (2017) Rapid and effective removal of Cu2+ from aqueous solution using novel chitosan and laponite-based nanocomposite as adsorbent. Polymers 9:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9010005
Panic VV, Seslija SI, Nesic AR, Velickovic SJ (2013) Adsorption of azo dyes on polymer materials. Hem Ind 67:881–900
Salehi R, Arami M, Mahmoodi NM, Bahrami H, Khorramfar S (2010) Novel biocompatible composite (chitosan-zinc oxide nanoparticle): preparation, characterization and dye adsorption properties. Colloids Surf B 80:86–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2010.05.039
Shenvi SS, Isloor AM, Ismail AF, Shilton SJ, Ahmed AA (2015) Humic acid based biopolymeric membrane for effective removal of methylene blue and rhodamine B. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:4965–4975. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.5b00761
Mallampati R, Xuanjun L, Adin A, Valiyaveettil S (2015) Fruit peels as efficient renewable adsorbents for removal of dissolved heavy metals and dyes from water. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 3:1117–1124. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.5b00207
Mohammadi AA, Alinejad A, Kamarehie B, Javan S, Ghaderpoury A, Ahmadpour M, Ghaderpoori M (2017) Metal-organic framework Uio-66 for adsorption of methylene blue dye from aqueous solutions. Int J Environ Sci Technol 14:1959–1968. https://doi.org/10.1007/s1376
Pourjavadi A, Hosseini SH, Seidib F, Soleyman R (2013) Magnetic removal of crystal violet from aqueous solutions using polysaccharide-based magnetic nanocomposite hydrogels. Polym Int 62:1038–1044. https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.4389
Wang J, Liu F (2014) Enhanced and selective adsorption of heavy metal ions on ion-imprinted simultaneous interpenetrating network hydrogels. Des Monomers Polym 17:19–254. https://doi.org/10.1080/15685551.2013.771314
Bhattacharyya R, Ray SK (2013) Kinetic and equilibrium modeling for adsorption of textile dyes in aqueous solutions by carboxymethyl cellulose/poly(acrylamide-co-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) semi-interpenetrating network hydrogel. Polym Eng Sci 53:2439–2453. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.23501
Zhang J, Wang A (2014) Polysaccharide-based composite hydrogels for removal of pollutants from water. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Nicolaus B, Moriello VS, Lama L, Poli A, Gambacorta A (2004) Polysaccharides from extremophilic microorganisms. Orig Life Evol Biosph 34:159–169
Kopecek J (2002) Polymer chemistry: swell gels. Nature 417:388–391
Ullah F, Othman MBH, Javed F, Ahmad Z, Akil HM (2015) Classification, processing and application of hydrogels: a review. Mater Sci Eng C 57:414–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.07.053
Chirani N, Yahia L, Gritsch L, Motta FL, Chirani S, Fare S (2016) History and applications of hydrogels. J Biomed Sci 4:1–23. https://doi.org/10.4172/2254-609X.100013
Tu H, Yu Y, Chen J, Shi X, Zhou J, Deng H, Du Y (2017) Highly cost-effective and high-strength hydrogels as dye adsorbents from natural polymers: chitosan and cellulose. Polym Chem 8:2913–2921. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7PY00223H
Attallah OA, Al-Ghobashy MA, Nebsen M, Salem MY (2016) Removal of cationic and anionic dyes from aqueous solution with magnetite/pectin and magnetite/silica/pectin hybrid nanocomposites: kinetic, isotherm and mechanism analysis. RSC Adv 6:11461–11480. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA23452B
Pandey N, Shukla SK, Singh NB (2017) Water purification by polymer nanocomposites: an overview. Nanocomposites 3:47–66. https://doi.org/10.1080/20550324.2017.1329983
Kono H (2015) Preparation and characterization of amphoteric cellulose hydrogels as adsorbents for the anionic dyes in aqueous solutions. Gels 1:94–116. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels1010094
Karthika JS, Vishalakshi B (2015) Novel stimuli responsive gellan gum-graft-poly(DMAEMA) hydrogel as adsorbent for anionic dye. Int J Biol Macromol 81:648–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.08.064
Peng N, Hu D, Zeng J, Li Y, Liang L, Chang C (2016) Superabsorbent cellulose-clay nanocomposite hydrogels for highly efficient removal of dye in water. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4:7217–7224. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b02178
Ghorai S, Sarkar A, Raoufi M, Panda AB, Hchonherr H (2014) Enhanced removal of methylene blue and methyl violet dyes from aqueous solution using a nanocomposite of hydrolyzed polyacrylamide grafted xanthan gum and incorporated nanosilica. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:4766–4777. https://doi.org/10.1021/am4055657
Krishna KA, Vishalakshi B (2017) Gellan gum based novel composite hydrogel: evaluation as adsorbent for cationic dyes. J Appl Polym Sci 134:45527–45535. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.45527
Kurita O, Fujiwara T, Yamazaki E (2008) Characterization of the pectin extracted from citrus peel in the presence of citric acid. Carbohydr Polym 74:725–730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2008.04.033
Singha NR, Mahapatra M, Karmakar M, Mondal H, Dutta A, Deb M, Mitra M, Roy C, Chattopadhyay PK, Maiti DK (2018) In situ allocation of a monomer in pectin-g-terpolymer hydrogels and effect of comonomer compositions on superadsorption of metal ions/dyes. ACS Omega 3:4163–4180. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b00446
Jung J, Arnold RD, Wicker L (2013) Pectin and charge modified pectin hydrogel beads as a colon-targeted drug delivery carrier. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 104:116–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.11.042
Munarin F, Guerreiro SG, Grellier MA, Tanzi MC, Barbosa MA, Petrini P, Granja PL (2011) Pectin-based injectable biomaterials for bone tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules 12:568–577. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm101110x
Thakur BR, Singh RK, Handa AK, Rao MA (1997) Chemistry and uses of pectin—a review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 37:47–73. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408399709527767
Mishra RK, Datt M, Banthia AK (2008) Synthesis and characterization of pectin/PVP hydrogel membranes for drug delivery system. AAPS Pharmscitech 9:395–403. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-008-9048-6
Amin MT, Alazba AA, Manzoor U (2014) A review of removal of pollutants from water/wastewater using different types of nanomaterials. Adv Mater Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/825910
Basu S, Samanta HS, Ganguly J (2018) Green synthesis and swelling behavior of Ag-nanocomposite semi-IPN hydrogels and their drug delivery using dolichos biflorus Lin. Soft Matter 16:7–19. https://doi.org/10.1080/1539445X.2017.1368559
Navarro MAG, Rosales JAA, Vazquez EEL, Cortez IEM, Castro AT, Gonzalez VG (2013) Totally ecofriendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles from aqueous dissolution of polysaccharides. Int J Polym Sci. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/436021
Krishna KA, Vishalakshi B (2017) Pectin based ZnO nanocomposite hydrogel: evaluation as adsorbent for divalent metal ions from aqueous solutions. Elixir Nanotechnol 107:47326–47331
Moharana B, Preetha SP, Selvasubramanian S, Malathi S, Balasubramanian S (2014) Synthesis and characterization of pectin capped silver nanoparticles and exploration of its anticancer potentials in experimental carcinogenesis in vitro. Indo Am J Pharm Res 4:5576–5583. https://doi.org/10.1044/1980-iajpr.141165
Sundarajan S, Sameem SM, Sankaranarayanan S, Ramaraj S (2013) Synthesis, characterization and application of zero-valent silver nano adsorbents. IJIRSET 2:8023–8037
Babu VR, Kim C, Kim S, Ahn C, Lee YI (2010) Development of semi-interpenetrating carbohydrate polymeric hydrogels embedded silver nanoparticles and its facile studies on E. coli. Carbohydr Polym 81:196–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.02.050
Kabiri K, Mehr MJZ, Mirzadeh H, Kheirabadi M (2010) Solvent-, ion- and pH-specific swelling of poly(2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid) superabsorbing gels. J Polym Res 17:203–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-009-9306-7
Bajpai SK (2001) Swelling-deswelling behavior of poly(acrylamide-co-maleic acid) hydrogels. J Appl Polym Sci 80:2782–2789. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.1394
Gueu S, Yao B, Adouby K, Ado G (2007) Kinetics and thermodynamics study of lead adsorption on to activated carbons from coconut and seed hull of the palm tree. Int J Environ Sci Technol 4:11–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03325956
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J Am Chem Soc 40:1361–1403. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja02242a004
Dada AO, Olalekan AP, Olatunya AM, Dada O (2012) Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin-Radushkevich isotherm studies of equilibrium sorption of Zn2+ unto phosphoric acid modified rice husk. IOSR-JAC 3:38–45. https://doi.org/10.9790/5736-0313845
Ho YS, McKay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption process. Process Biochem 34:451–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(98)00112-5
Liu H, Liu H (2017) Selective dye adsorption and metal ion detection using multifunctional silsesquioxane-based tetraphenylethene-linked nanoporous polymers. J Mater Chem A 5:9156–9162. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TA01255A
Pour ZS, Ghaemy M (2015) Removal of dyes and heavy metal ions from water by magnetic hydrogel beads based on poly(vinyl alcohol)/carboxymetyl starch-g-poly(vinyl imidazole). RSC Adv 5:64106–64118. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA08025H
Saad M, Tahir H, Khan J, Hameed U, Saud A (2017) Synthesis of polyaniline nanoparticles and their application for the removal of Crystal Violet dye by ultrasonicated adsorption process based on response surface methodology. Ultrason Sonochem 34:600–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2016.06.022
Yan H, Li H, Yang H, Li A, Cheng R (2013) Removal of various cationic dyes from aqueous solutions using a kind of fully biodegradable magnetic composite microsphere. Chem Eng J 223:402–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.02.113
Mahdavinia GR, Hasanpour J, Rahmani Z, Karami S, Etemadi H (2013) Nanocomposite hydrogel from grafting of acrylamide onto HPMC using sodium montmorillonite nanoclay and removal of crystal violet dye. Cellulose 20:2591–2604. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0004-6
Sun P, Hui C, Khan RA, Du J, Zhang Q, Zhao YH (2015) Efficient removal of crystal violet using Fe3O4-coated biochar: the role of the Fe3O4 nanoparticles and modeling study their adsorption behavior. Sci Rep 5:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep12638
Medina RP, Nadres ET Jr, Florencio CB, Rodriguesa DF (2016) Incorporation of graphene oxide into chitosan-poly(acrylic acid) porous polymer nanocomposite for enhanced lead adsorption. Environ Sci Nano 3:638–646. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EN00021E
Liu C, Zhang D, Zhao L, Lu X, Zhang P, He S, Hu G, Tang X (2016) Synthesis of a thiacalix[4]arenetetrasulfonatefunctionalized reduced graphene oxide adsorbent for the removal of lead(II) and cadmium(II) from aqueous solutions. RSC Adv 6:113352–113365. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA24353C
Yu Y, Hu Z, Chen Z, Yang J, Gao H, Chen Z (2016) Organically-modified magnesium silicate nanocomposites for high-performance heavy metal removal. RSC Adv 6:97523–97531. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA20181D
Reddy NS, Rao KM, Vania TJS, Rao KSVK, Lee YI (2015) Pectin/poly(acrylamide-co-acrylamidoglycolic acid) pH sensitive semi-IPN hydrogels: selective removal of Cu2+ and Ni2+, modeling, and kinetic studies. Desalin Water Treat 57:6503–6514. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1008053
Onundi YB, Mamun AA, Al Khatib MF, Ahmed YM (2010) Adsorption of copper, nickel and lead ions from synthetic semiconductor industrial wastewater by palm shell activated carbon. Int J Environ Sci Technol 7:751–758. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326184
Kundu D, Hazra C, Chatterjee A, Chaudhari A, Mishra S (2014) Sonochemical synthesis of poly(methyl methacrylate) core-surfactin shell nanoparticles for recyclable removal of heavy metal ions and its cytotoxicity. RSC Adv 4:24991–25004. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA03008G
Radi S, Tighadouini S, Bacquet M, Degoutin S, Janus L, Mabkhot YN (2016) Fabrication and covalent modification of highly chelate hybrid material based on silica-bipyridine framework for efficient adsorption of heavy metals: isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics studies. RSC Adv 6:82505–82514. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA14349K
Tan WX, Lin ZT, Bu HT, Tian Y, Jiang GB (2012) Nano-micelles based on a rosin derivative as potent sorbents and sinking agents with high absorption capabilities for the removal of metal ions. RSC Adv 2:7279–7289. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2RA20767B
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kodoth, A.K., Badalamoole, V. Silver nanoparticle-embedded pectin-based hydrogel for adsorptive removal of dyes and metal ions. Polym. Bull. 77, 541–564 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-02757-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-02757-4