Abstract
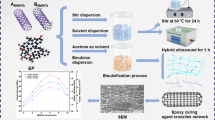
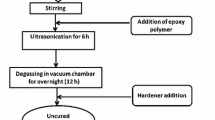
In this study, MWCNT/epoxy composites were fabricated via combination of ultrasonication with two post-processing techniques namely, casting and hot-pressing, respectively. The effect of these two post processing techniques and MWCNT loading ranging from 0 to 1.0 vol% on the mechanical, electrical and thermal properties of MWCNT/epoxy composites were investigated. The addition of MWCNT in epoxy reduced the tensile strength and tensile modulus of the MWCNT/epoxy composites compared to unfilled epoxy. However, the MWCNT/epoxy composites prepared by hot-pressing technique improved the tensile strength and tensile modulus at 0.4 vol% MWCNT loading as confirmed by morphological analysis. The DMA properties of MWCNT/epoxy composites prepared by both post-processing techniques showed no significant change in storage modulus and T g values. The increment of MWCNT loading slightly increased the electrical and thermal properties of MWCNT/epoxy composites via the hot-pressing technique. These findings indicate that different post-processing techniques and filler loading govern the properties of MWCNT/epoxy composites.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mittal G, Dhand V, Rhee KY, Park SJ, Lee WR (2015) A review on carbon nanotubes and graphene as fillers in reinforced polymer nanocomposites. J Ind Eng Chem 21:11–25
Njuguna J, Pielichowski K, Alcock JR (2007) Epoxy-based fibre reinforced nanocomposites. Adv Eng Mater 9(10):835–847
Allaoui A, Bai S, Cheng HM, Bai JB (2002) Mechanical and electrical properties of a MWNT/epoxy composite. Compos Sci Technol 62(15):1993–1998
Gojny FH, Wichmann MHG, Köpke U, Fiedler B, Schulte K (2004) Carbon nanotube-reinforced epoxy-composites: enhanced stiffness and fracture toughness at low nanotube content. Compos Sci Technol 64:2363–2371
Bai JB, Allaoui A (2003) Effect of the length and the aggregate size of MWNTs on the improvement efficiency of the mechanical and electrical properties of nanocomposites-experimental investigation. Compos Part A-Appl S 34(8):689–694
Cooper CA, Ravich D, Lips D, Mayer J, Wagner HD (2002) Distribution and alignment of carbon nanotubes and nanofibrils in a polymer matrix. Compos Sci Technol 62(7):1105–1112
Guo P, Chen X, Gao X, Song H, Shen H (2007) Fabrication and mechanical properties of well-dispersed multiwalled carbon nanotubes/epoxy composites. Compos Sci Technol 67(15–16):3331–3337
Ma PC, Siddiqui NA, Marom G, Kim JK (2010) Dispersion and functionalization of carbon nanotubes for polymer-based nanocomposites: a Review. Compos Part A-Appl S 41(10):1345–1367
Martone A, Formicola C, Giordano M, Zarrelli M (2010) Reinforcement efficiency of multi-walled carbon nanotube/epoxy nano composites. Compos Sci Technol 70(7):1154–1160
Saw LN, Mariatti M, Azura AR, Azizan A, Kim JK (2012) Transparent, electrically conductive and flexible films made from multiwalled carbon nanotube/epoxy composites. Compos Part B-Eng 43:2973–2979
Ghaleb ZA, Mariatti M, Ariff ZM (2014) Properties of graphene nanopowder and multi-walled carbon nanotube-filled epoxy thin-film nanocomposites for electronic applications: the effect of sonication time and filler loading. Compos Part A-Appl S 58:77–83
Du C, Heldebrant D, Pan N (2002) Preparation of carbon nanotubes composite sheet using electrophoretic deposition process. J Mater Sci Lett 21:565–568
Nayak RK, Mahato KK, Ray BC (2016) Water absorption behavior, mechanical and thermal properties of nano TiO2 enhanced glass fiber reinforced polymer composites. Compos Part A-Appl S 90:736–747
Guermazi N, Haddar N, Elleuch K, Ayedi HF (2014) Investigations on the fabrication and the characterization of glass/epoxy, carbon/epoxy and hybrid composites used in the reinforcement and the repair of aeronautic structures. Mater Design 56:714–724
Song YS, Youn JR (2005) Influence of dispersion states of carbon nanotubes on physical properties of epoxy nanocomposites. Carbon 43(7):1378–1385
Hollertz R, Chatterjee S, Gutmann H, Geiger T, Nüesch FA, Chu BTT (2011) Improvement of toughness and electrical properties of epoxy composites with carbon nanotubes prepared by industrially relevant processes. Nanotechnology 22(12):125702
Martin CA, Sandler JKW, Shaffer MSP, Schwarz MK, Bauhofer W, Schulte K, Windle AH (2004) Formation of percolating networks in multi-wall carbon-nanotube–epoxy composites. Compos Sci Technol 64(15):2309–2316
Ma PC, Mo SY, Tang BZ, Kim JK (2010) Dispersion, interfacial interaction and re-agglomeration of functionalized carbon nanotubes in epoxy composites. Carbon 48(6):1824–1834
Herrera-Ramírez LC, Castell P, Fernández-Blázquez JP, Fernández A, Guzmán de Villoria R (2015) How do graphite nanoplates affect the fracture toughness of polypropylene composites? Compos Sci Technol 111:9–16
Costa ML, Rezende MC, de Almeida SFM (2006) Effect of void content on the moisture absorption in polymeric composites. Polym-Plast Technol Eng 45(6):691–698
Im H, Kim J (2012) Thermal conductivity of a graphene oxide–carbon nanotube hybrid epoxy composite. Carbon 50(15):5429–5440
Hosur M, Barua R, Zainuddin S, Kumar A, Trovillion J, Jeelani S (2013) Effect of processing techniques on the performance of Epoxy MWCNT nanocomposites. J Appl Polym Sci 127:4211–4224
Zhang AY, Li DH, Zhang DX, Lu HB, Xiao HY, Jia J (2011) Qualitative separation of the effect of voids on the static mechanical properties of hygrothermally conditioned carbon/epoxy composites. Express Polym Lett 5(8):708–716
Gkikas G, Barkoula NM, Paipetis AS (2012) Effect of dispersion conditions on the thermo-mechanical and toughness properties of multi walled carbon nanotubes-reinforced epoxy. Compos Part B-Eng 43:2697–2705
Yang Z, McElrath K, Bahr J, D’Souza NA (2012) Effect of matrix glass transition on reinforcement efficiency of epoxy-matrix composites with single walled carbon nanotubes, multi-walled carbon nanotubes, carbon nanofibers and graphite. Compos Part B-Eng 43(4):2079–2086
Du JH, Bai J, Cheng HM (2007) The present status and key problems of carbon nanotube based polymer composites. Express Polym Lett 1(5):253–273
Tang LC, Wan YJ, Peng K, Pei YB, Wu LB, Chen LM, Shu LJ, Jiang JX, Lai GQ (2013) Fracture toughness and electrical conductivity of epoxy composites filled with carbon nanotubes and spherical particles. Compos Part A-Appl S 45:95–101
Prolongo SG, Moriche R, Jiménez-Suárez A, Sánchez M, Ureña A (2014) Advantages and disadvantages of the addition of graphene nanoplatelets to epoxy resins. Eur Polym J 61:206–214
Starkova O, Chandrasekaran S, Prado LASA, Folke Tölle, Mülhaupt R, Schulte K (2013) Hydrothermally resistant thermally reduced graphene oxide and multi-wall carbon nanotube based epoxy nanocomposites. Polym Degrad Stabil 98(2):519–526
Araby S, Saber N, Ma X, Kawashima N, Kang H, Shen H, Zhang L, Xu J, Majewski P, Ma J (2015) Implication of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on polymer/graphene composites. Mater Design 65:690–699
Min C, Shen X, Shi Z, Chen L, Xu Z (2010) The electrical properties and conducting mechanisms of carbon nanotube/polymer nanocomposites: a review. Polym-Plast Technol Eng 49(12):1172–1181
Marinho B, Ghislandi M, Tkalya E, Koning CE, de With G (2012) Electrical conductivity of compacts of graphene, multi-wall carbon nanotubes, carbon black, and graphite powder. Powder Technol 221:351–358
Hu N, Masuda Z, Yamamoto G, Fukunaga H, Hashida T, Qiu J (2008) Effect of fabrication process on electrical properties of polymer/multi-wall carbon nanotube nanocomposites. Compos Part A-Appl S 39(5):893–903
Evseeva LE, Tanaeva SA (2008) Thermal conductivity of micro and nanostructural epoxy composites at low temperatures. Mech Compos Mater 44(1):87–92
Gardea F, Lagoudas DC (2014) Characterization of electrical and thermal properties of carbon nanotube/epoxy composites. Compos Part B-Eng 56:611–620
Han Z, Fina A (2011) Thermal conductivity of carbon nanotubes and their polymer nanocomposites: a review. Prog Polym Sci 36:914–944
Phillpot SR, McGaughey AJH (2005) Introduction to thermal transport. Mater Today 8(6):18–20
Wang S, Liang R, Wang B, Zhang C (2009) Dispersion and thermal conductivity of carbon nanotube composites. Carbon 47(1):53–57
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of the University Sains Malaysia, for Research University Grant used for this project (Project No. 1001/PBAHAN/814153).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ervina, J., Mariatti, M. & Hamdan, S. Mechanical, electrical and thermal properties of multi-walled carbon nanotubes/epoxy composites: effect of post-processing techniques and filler loading. Polym. Bull. 74, 2513–2533 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-016-1853-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-016-1853-6