Abstract
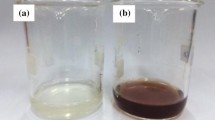
In the present investigation, synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) has been successfully carried out in a very simple and cost-effective manner by reducing Ag+ ions in sodium alginate solution and further stabilizing the colloidal mixture with gelatin solution. The ultraviolet–visible (UV–vis) spectra were in excellent agreement with the nanostructure morphology obtained from dynamic light scattering transmission electron microscopy and their size distributions. Increase in precursor concentration was found to promote agglomeration of AgNPs. Antibacterial assays revealed that the nanoformulations were more active against Gram-negative bacteria. Swelling studies of the hydrogel films demonstrated a rapid increase in water uptake. However, an increase in swelling % was observed with decreasing AgNP content. The use of biocompatible materials such as sodium alginate and gelatin not only provides green and economic attributes to this piece of research work but, at the same time, also opens up possibilities of using the nanoformulations in wound dressings, active packaging and several other biomedical applications.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blanco-Andujar C, Tung LD, Thanh NTK (2010) Synthesis of nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Annu Rep Sect A Inorg Chem 106:553. doi:10.1039/b920666n
Zhang G-R, Xu B-Q (2010) Surprisingly strong effect of stabilizer on the properties of Au nanoparticles and Pt^Au nanostructures in electrocatalysis. Nanoscale 2:2798. doi:10.1039/c0nr00295j
Tsuji T, Thang D-H, Okazaki Y et al (2008) Preparation of silver nanoparticles by laser ablation in polyvinylpyrrolidone solutions. Appl Surf Sci 254:5224–5230. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.02.048
Lu Q, Rosen J, Zhou Y et al (2014) A selective and efficient electrocatalyst for carbon dioxide reduction. Nat Commun 5:3242. doi:10.1038/ncomms4242
Fleming LAH, Tang G, Zolotovskaya SA, Abdolvand A (2014) Controlled modification of optical and structural properties of glass with embedded silver nanoparticles by nanosecond pulsed laser irradiation. Opt Mater Express 4:969. doi:10.1364/OME.4.000969
De A, Bose R, Kumar A, Mozumdar S (2014) Management of insect pests using nanotechnology: as modern approaches. In: Targeted delivery of pesticides using biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles, 1st edn. Springer, India, pp 29–33. doi:10.1007/978-81-322-1689-6_8
Swain P, Sasmal A, Nayak SK et al (2014) Evaluation of selected metal nanoparticles on hatching and survival of larvae and fry of Indian major carp, rohu (Labeo rohita). Aquac Res. doi:10.1111/are.12510
Huang K-J, Wang L, Wang H-B et al (2013) Electrochemical biosensor based on silver nanoparticles–polydopamine–graphene nanocomposite for sensitive determination of adenine and guanine. Talanta 114:43–48. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2013.04.017
Arunachalam KD, Annamalai SK, Arunachalam AM, Kennedy S (2013) Green synthesis of crystalline silver nanoparticles using Indigofera aspalathoides-medicinal plant extract for wound healing applications. Asian J Chem 25:311–314
Kwan KHL, Liu X, To MKT et al (2011) Modulation of collagen alignment by silver nanoparticles results in better mechanical properties in wound healing. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med 7:497–504. doi:10.1016/j.nano.2011.01.003
Rigo C, Ferroni L, Tocco I et al (2013) Active silver nanoparticles for wound healing. Int J Mol Sci 14:4817–4840. doi:10.3390/ijms14034817
Mohan S, Oluwafemi OS, George SC et al (2014) Completely green synthesis of dextrose reduced silver nanoparticles, its antimicrobial and sensing properties. Carbohydr Polym 106:469–474. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.01.008
Swain P, Nayak SK, Sasmal A et al (2014) Antimicrobial activity of metal based nanoparticles against microbes associated with diseases in aquaculture. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30:2491–2502. doi:10.1007/s11274-014-1674-4
Guo D, Zhu L, Huang Z et al (2013) Anti-leukemia activity of PVP-coated silver nanoparticles via generation of reactive oxygen species and release of silver ions. Biomaterials 34:7884–7894. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.07.015
Bae CH, Nam SH, Park SM (2002) Formation of silver nanoparticles by laser ablation of a silver target in NaCl solution. Appl Surf Sci 197–198:628–634. doi:10.1016/S0169-4332(02)00430-0
Lee KJ, Jun BH, Choi J et al (2007) Environmentally friendly synthesis of organic-soluble silver nanoparticles for printed electronics. Nanotechnology 18:335601. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/18/33/335601
Mukherjee P, Roy M, Mandal BP et al (2008) Green synthesis of highly stabilized nanocrystalline silver particles by a non-pathogenic and agriculturally important fungus T. asperellum. Nanotechnology 19:075103. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/19/7/075103
Parikh RY, Singh S, Prasad BLV et al (2008) Extracellular synthesis of crystalline silver nanoparticles and molecular evidence of silver resistance from Morganella sp.: towards understanding biochemical synthesis mechanism. ChemBioChem 9:1415–1422. doi:10.1002/cbic.200700592
Raffi M, Rumaiz AK, Hasan MM, Shah SI (2007) Studies of the growth parameters for silver nanoparticle synthesis by inert gas condensation. J Mater Res 22:3378–3384. doi:10.1557/JMR.2007.0420
Ingale AG, Chaudhari AN (2013) Biogenic synthesis of nanoparticles and potential applications: an eco-friendly approach. J Nanomed Nanotechnol 04:165. doi:10.4172/2157-7439.1000165
Mason C, Vivekanandhan S, Misra M, Mohanty AK (2012) Switchgrass (Panicum virgatum) extract mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles. World J Nano Sci Eng 2:47–52. doi:10.4236/wjnse.2012.22008
Ghorbani HR, Safekordi AA, Attar H, Sorkhabadi SMR (2011) Biological and non-biological methods for silver nanoparticles synthesis. Chem Biochem Eng Q J 25:317–326
Sathishkumar M, Sneha K, Kwak IS et al (2009) Phyto-crystallization of palladium through reduction process using Cinnamom zeylanicum bark extract. J Hazard Mater 171:400–404. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.06.014
Božanić DK, Dimitrijević-Branković S, Bibić N et al (2011) Silver nanoparticles encapsulated in glycogen biopolymer: morphology, optical and antimicrobial properties. Carbohydr Polym 83:883–890. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.08.070
Raveendran P, Fu J, Wallen SL (2003) Completely “green” synthesis and stabilization of metal nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 125:13940–13941. doi:10.1021/ja029267j
Kalaycı ÖA, Cömert FB, Hazer B, Atalay T, Cavicchi KA, Cakmak M (2010) Synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activity of metal nanoparticles embedded into amphiphilic comb-type graft copolymers. Polym Bull 65(3):215–226. doi:10.1007/s00289-009-0196-y
Jayaramudu T, Raghavendra GM, Varaprasad K et al (2013) Development of novel biodegradable Au nanocomposite hydrogels based on wheat: for inactivation of bacteria. Carbohydr Polym 92:2193–2200. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.12.006
Keleş E, Hazer B, Cömert FB (2013) Synthesis of antibacterial amphiphilic elastomer based on polystyrene-block-polyisoprene-block-polystyrene via thiol-ene addition. Mater Sci Eng C 33(3):1061–1066. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2012.11.029
Monteiro DR, Gorup LF, Takamiya AS et al (2009) The growing importance of materials that prevent microbial adhesion: antimicrobial effect of medical devices containing silver. Int J Antimicrob Agents 34:103–110. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2009.01.017
Hasirci N (2007) Micro and nano systems in biomedicine and drug delivery. In: Mozaferi MR (ed) Nanomaterials and nanosystems for biomedical applications. Springer, Netherlands, pp 1–26. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-6289-6_1
Carneiro-da-Cunha MG, Cerqueira MA, Souza BWS et al (2010) Physical and thermal properties of a chitosan/alginate nanolayered PET film. Carbohydr Polym 82:153–159. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.04.043
Yang J-S, Xie Y-J, He W (2011) Research progress on chemical modification of alginate: a review. Carbohydr Polym 84:33–39. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.11.048
Raveendran P, Fu J, Wallen SL (2006) A simple and “green” method for the synthesis of Au, Ag, and Au–Ag alloy nanoparticles. Green Chem 8:34–38. doi:10.1039/B512540E
Kawanishi N, Christenson HK, Ninham BW (1990) Measurement of the interaction between adsorbed polyelectrolytes: gelatin on mica surfaces. J Phys Chem 94:4611–4617. doi:10.1021/j100374a045
Likos CN, Vaynberg KA, Löwen H, Wagner NJ (2000) Colloidal stabilization by adsorbed gelatin. Langmuir 16:4100–4108. doi:10.1021/la991142d
Akbulut M, Reddy NK, Bechtloff B et al (2008) Flow-induced conformational changes in gelatin structure and colloidal stabilization. Langmuir 24:9636–9641. doi:10.1021/la800487b
Djagny VB, Wang Z, Xu S (2001) Gelatin: a valuable protein for food and pharmaceutical industries: review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 41:481–492. doi:10.1080/20014091091904
Tabata Y, Ikada Y (1998) Protein release from gelatin matrices. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 31:287–301. doi:10.1016/S0169-409X(97)00125-7
De Wael K, Verstraete A (2011) The electrochemistry of a gelatin modified gold electrode. Int J Electrochem Sci 6:1810–1819
Yang J, Pan J (2012) Hydrothermal synthesis of silver nanoparticles by sodium alginate and their applications in surface-enhanced Raman scattering and catalysis. Acta Mater 60:4753–4758. doi:10.1016/j.actamat.2012.05.037
Kanmani P, Rhim J-W (2014) Physicochemical properties of gelatin/silver nanoparticle antimicrobial composite films. Food Chem 148:162–169. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.10.047
Rosellini E, Cristallini C, Barbani N et al (2009) Preparation and characterization of alginate/gelatin blend films for cardiac tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res Part A 91:447–453. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.32216
Kirby W, Bauer A, Sherris J, Turk M (1966) Antibiotic susceptibility testing by standard single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol 45:493–496
Goia DV (2004) Preparation and formation mechanisms of uniform metallic particles in homogeneous solutions. J Mater Chem 14:451. doi:10.1039/b311076a
Zamiri R, Azmi BZ, Ahangar HA et al (2012) Preparation and characterization of silver nanoparticles in natural polymers using laser ablation. Bull Mater Sci 35:727–731. doi:10.1007/s12034-012-0360-0
Heath JR (1989) Size dependent surface-plasmon resonances of bare silver particles. Phys Rev B 40:9982–9985. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.40.9982
Huang RYM, Pal R, Moon G (1999) Characteristics of sodium alginate membranes for the pervaporation dehydration of ethanol–water and isopropanol–water mixtures. J Memb Sci 160:101–113. doi:10.1016/S0376-7388(99)00071-X
Xiao C, Liu H, Lu Y, Zhang L (2001) Blend films from sodium alginate and gelatin solutions. J Macromol Sci Part A 38:317–328. doi:10.1081/MA-100103352
Jia-hui Y, Yu-min D, Hua Z (1999) Blend films of chitosan-gelatin. Wuhan Univ J Nat Sci 4:476. doi:10.1007/BF02832288
Nayak RR, Pradhan N, Behera D et al (2011) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticle by Penicillium purpurogenum NPMF: the process and optimization. J Nanoparticle Res 13:3129–3137. doi:10.1007/s11051-010-0208-8
LaMer V, Dinegar R (1950) Theory, production and mechanism of formation of monodispersed hydrosols. J Am Chem Soc 72:4847–4854. doi:10.1021/ja01167a001
Boyd RD, Pichaimuthu SK, Cuenat A (2011) New approach to inter-technique comparisons for nanoparticle size measurements; using atomic force microscopy, nanoparticle tracking analysis and dynamic light scattering. Coll Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 387:35–42. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2011.07.020
Sibiya PN, Moloto MJ (2014) Effect of precursor concentration and pH on the shape and size of starch capped silver selenide (Ag2Se) nanoparticles. Chalcogenide Lett 11:577–588
Zielińska A, Skwarek E, Zaleska A et al (2009) Preparation of silver nanoparticles with controlled particle size. Procedia Chem 1:1560–1566. doi:10.1016/j.proche.2009.11.004
Ajitha B, Divya A, Harish G, Sreedhara RP (2013) The influence of silver precursor concentration on size of silver nanoparticles grown by soft chemical route. Res J Phys Sci 1:11–14
Bar H, Bhui DK, Sahoo GP et al (2009) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using latex of Jatropha curcas. Coll Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 339:134–139. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2009.02.008
Murray RGE, Steed P, Elson HE (1965) The location of the mucopeptide in sections of the cell wall of Escherichia coli and other gram-negative bacteria. Can J Microbiol 11:547–560. doi:10.1139/m65-072
Shockman GD, Barren JF (1983) Structure, function, and assembly of cell walls of gram-positive bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 37:501–527. doi:10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.002441
Kawahara K, Tsuruda K, Morishita M, Uchida M (2000) Antibacterial effect of silver zeolite on oral bacteria under anaerobic conditions. Dent Mater 16:452–455. doi:10.1016/S0109-5641(00)00050-6
Davis PJ, Austin AJ, Insense limited (2010) Wound dressings comprising hydrated hydrogels and enzymes. US patent 7,731,954
Martínez-Ruvalcaba A, González-Álvarez A, Becerra-Bracamontes F, Sánchez-Díaz JC (2009) Polyacrylamide-gelatin polymeric networks: effect of pH and gelatin concentration on the swelling kinetics and mechanical properties. Polym Bull 62:539–548. doi:10.1007/s00289-008-0037-4
Acknowledgments
PKB and AS are thankful to Department of Biotechnology, New Delhi for financing the project under the DBT-MSUB Programme (BT/PR4800/INF/22/152/2012 dated 22/03/2012). CA and CRP are thankful to Director, Institute of Minerals and Materials Technology (CSIR-IMMT), Bhubaneswar, Odisha for providing necessary facilities to carry out the present work. The authors are also thankful to Dr. S. Vivekanandhan, VHNSN College, Tamil Nadu, India for his valuable suggestions during preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Acharya, C., Panda, C.R., Bhaskara, P.K. et al. Physicochemical and antimicrobial properties of sodium alginate/gelatin-based silver nanoformulations. Polym. Bull. 74, 689–706 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-016-1738-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-016-1738-8