Abstract
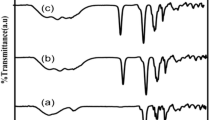
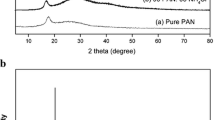
Proton-conducting polymer blend electrolytes based on PVA–PVP–NH4NO3 were prepared for different compositions by solution cast technique. The prepared films are investigated by different techniques. The XRD study reveals the amorphous nature of the polymer electrolyte. The FTIR and laser Raman studies confirm the complex formation between the polymer and salt. DSC measurements show decrease in T g with increasing salt concentration. The ionic conductivity of the prepared polymer electrolyte was found by ac impedance spectroscopy analysis. The maximum ionic conductivity was found to be 1.41 × 10−3 S cm−1 at ambient temperature for the composition of 50PVA:50PVP:30 wt% NH4NO3 with low-activation energy 0.29 eV. The conductivity temperature plots are found to follow an Arrhenius nature. The dielectric behavior was analyzed using dielectric permittivity (ε*) and the relaxation frequency (τ) was calculated from the loss tangent spectra (tan δ). Using this maximum ionic conducting polymer blend electrolyte, the primary proton battery with configuration Zn + ZnSO4·7H2O/50PVA:50PVP:30 wt% NH4NO3/PbO2 + V2O5 was fabricated and their discharge characteristics studied.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maccullum JR, Vincent CA (eds) (1987) Polymer electrolyte reviews. Elsevier, London
Bruce PG, Campbell SA, Lightfoot P, Mehta MA (1995) Polymer electrolytes: structure and electrode processes. Solid State Ion 78:191–198
Blonsky PM, Clancy S, Hardy LC, Harris CS, Spindler R, Tonge JS, Shriver DF (1989) Polymeric Electrolytes. Chem Tech 758
Subba Reddy ChV, Sharmanad AK, NarasimhaRao VVR (2004) Characterization of a solid state battery based on polyblend of (PVP + PVA + KBr O3) electrolyte. Ionics 10:142–147
Varnell DF, Cole man MM (1981) FT I.R. Studies of polymer blends: V. Further observations on polyester-poly(vinyl chloride) blends. Polymer 22:1324–1328
Coleman MM, Zarin JJ (1797) Fourier-transform infrared studies of polymer blends. II. Poly(ϵ-caprolactone)–poly(vinyl chloride) system. Polym Sci Polymer Phys Edn 17:837–850
Garton A, Aubin M, Prudhomme RE (1983) FTIR of polycaprolactone/poly(vinylidene chloride-co-acrylonitrile) miscible blends. J Poly Sci Polym Lett Edn 21:45–47
Varnell DF, Runt JP, Coleman MM (1983) FT I.R. and thermal analysis studies of blends of poly(ε-caprolactone) with homo- and copolymers of poly(vinylidene chloride). Polymer 24:37–42
Woo EM, Barlow JW, Paul DR (1986) Phase behavior of blends of aliphatic polyesters with a vinylidene chloride/vinyl chloride copolymer. J Appl Polym Sci 32:3889–3897
Nishi T, Wang TT, Kwel TK (1975) Thermally induced phase separation behavior of compatible polymer mixtures. Macro Mol 8:227–234
Chandra S, Hashmi SA, Prasad G (1990) Studies on ammonium perchlorate doped polyethylene oxide polymer electrolyte. Solid State Ionics 40:651–654
Kumar M, Sekhon SS (2002) Ionic conductance behaviour of plasticized polymer electrolytes containing different plasticizers. Ionics 8:223–233
Selvasekarapandian S, Hirankumar G, Kawamura J, Kuwata N, Hattori T (2005) 1H solid state NMR studies on the proton conducting polymer electrolytes. Mater Lett 59:2741–2745
Selvasekarapandian S, Hema M, Kawamura J, Kamishima O, Baskaran R (2010) Characterization of PVA–NH4NO3 polymer electrolyte and its application in rechargeable proton battery. J Phys Soc Jpn Suppl A 79:163–168
Jonscher AK (1977) The universal dielectric response. Nature 267:673–679
Vijaya N, Selvasekarapandian S, Hirankumar G, Karthikeyan S, Nithya H, Ramya CS (2012) Structural, vibrational, thermal, and conductivity studies on proton-conducting polymer electrolyte based on poly (N-vinylpyrrolidone). Ionics 18:91–99
Ramya CS, Selvasekarapandian S, Savitha T, Hirankumar G (2007) Vibrational and impedance spectroscopic study on PVP–NH4SCN based polymer electrolytes. Physics B 393:11–17
Mauritz KA (1989) Dielectric relaxation studies of ion motions in electrolyte-containing perfluorosulfonate ionomers. 4. Long-range ion transport. Macromolecules 22:4483–4488
Kyritsis A, Pissis P, Grammatikakis J (1995) Dielectric relaxation spectroscopy in poly(hydroxyethyl acrylates)/water hydrogels. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 33:1737–1750
Armstrong RD, Dickinson T, Wills PM (1974) The A.C. impedance of powdered and sintered solid ionic conductors. J Electroanal Chem 53:389–405
Schmidt-Rohr K, Kulik AS, Beckham HW, Ohlemacher A, Pawelzik U, Boffel C, Spiess HW (1994) Molecular nature of the beta relaxation in poly(methyl methacrylate) investigated by multidimensional NMR. Macromolecules 27:4733–4745
Dieterich W, Maass P (2002) Non-Debye relaxations in disordered ionic solids. Chem Phys 284:439–467
Agrawal RC, Hashmi SA, Pandey GP (2007) Electrochemical cell performance studies on all-solid-state battery using nano-composite polymer electrolyte membrane. Ionics 13:295–298
Subba Reddy ChV, Sharma AK, Narasimha Rao VVR (2003) Conductivity and discharge characteristics of polyblend (PVP + PVA + KIO3) electrolyte. J Power Sources 114:338–345
Acknowledgement
One of the authors (N. Rajeswari) wishes to thank Prof S. R. S. Prabaharan, VIT University, Chennai and Director, Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials IMRAM, Tohoku University, Japan for providing facilities and permission to carry out work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajeswari, N., Selvasekarapandian, S., Sanjeeviraja, C. et al. A study on polymer blend electrolyte based on PVA/PVP with proton salt. Polym. Bull. 71, 1061–1080 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-014-1111-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-014-1111-8