Abstract
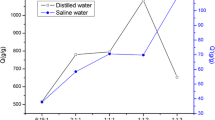
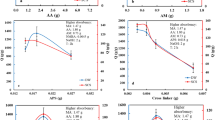
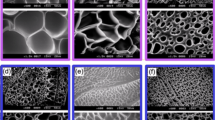
A series of novel copolymer superabsorbents based on acrylamide (AM), acrylic acid(AA) were prepared by inverse microemulsion copolymerization using ammonium persulfate (APS) as the initiator and N,N-methylenebisacrylamide (MBA) as the crosslinking agent and OP-10 and SDS as complex surfactants. The synthetic variables (amount of crosslinking agent and initiator, water/oil ratio, monomer/surfactant ratio and AA/ Am ratio) and their effects on the absorbencies of the synthesized superabsorbents were investigated. The experimental results of superabsorbent polymers (SAPs) showed the maximum saline solution absorbency of 130 g/g within 75 min, and the saline solution absorbency of 111 g/g within 30 min. FTIR indicated the structure of the acrylic acid and acrylamide copolymer. SEM indicated that the particles prepared with higher crosslinker content (0.03%) showed smaller pore sizes and less porous structures compared with those with less crosslinker content (0.01%) and the number of the micropores largely decreased with the water/oil ratio increasing from 8% to 14%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pourjavadi A, Barzegar S, Zeidabadi F (2007) Reactive and Functional Polymers 67:644
Zhang JP, Wang Q, Wang AQ (2007) Carbohydrate Polymers 68:367
Zhang J, Yuan K, Wang YP, Gu SJ, Zhang ST (2007) Materials Letters 61:316
Sevil SY, Dilek K, Muammer E, Mustafa Ö, Riza A (2007) European Polymer Journal 43:1923
Wan T, Wang XQ, Yuan Y, He WQ (2006) Polymer International 55:1413
Wan T, Wang XQ, Yuan Y, He WQ (2006) Journal of Applied Polymer Science 102:2875
Raju KM, Raju MP (2001) Advances in Polymer Technology 20:146
Li A, Wang AQ (2005) European Polymer Journal 41:1630
Chen ZB, Liu MZ, Ma SM (2005) Reactive & Functional Polymers 62:85
Lee WF, Chen YC (2005) European Polymer Journal 41:1605
Omidian H, Hashemi SA, Sammes PG, Meldrum I (1999) Polymer 40:1753
Lim DW, Song KG, Yoon KJ, Ko SW (2002) European Polymer Journal 38:579
Flory PJ (1953) Principles of Polymer Chemistry. Cornell University Press, Ithaca, NY
Chen JW, Zhao YM (2000) J Appl Polym Sci 75:808
Chen JW, Zhao YM (1999) J Appl Polym Sci 74:119
Zhang YQ, Tanaka T, Shibayama M (1992) Nature 360:142
Liu ZS, Remple GL (1997) J Appl Polym Sci 64:1345
Li A, Wang AQ, Chen JM (2004) J Appl Polym Sci 92:1596
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, T., Wang, L., Yao, J. et al. Saline solution absorbency and structure study of poly (AA-AM) water superabsorbent by inverse microemulsion polymerization . Polym. Bull. 60, 431–440 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-007-0875-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-007-0875-5