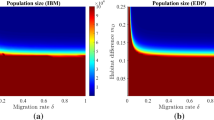
Abstract
We propose a model to describe the adaptation of a phenotypically structured population in a H-patch environment connected by migration, with each patch associated with a different phenotypic optimum, and we perform a rigorous mathematical analysis of this model. We show that the large-time behaviour of the solution (persistence or extinction) depends on the sign of a principal eigenvalue, \(\lambda _H\), and we study the dependency of \(\lambda _H\) with respect to H. This analysis sheds new light on the effect of increasing the number of patches on the persistence of a population, which has implications in agroecology and for understanding zoonoses; in such cases we consider a pathogenic population and the patches correspond to different host species. The occurrence of a springboard effect, where the addition of a patch contributes to persistence, or on the contrary the emergence of a detrimental effect by increasing the number of patches on the persistence, depends in a rather complex way on the respective positions in the phenotypic space of the optimal phenotypes associated with each patch. From a mathematical point of view, an important part of the difficulty in dealing with \(H\ge 3\), compared to \(H=1\) or \(H=2\), comes from the lack of symmetry. Our results, which are based on a fixed point theorem, comparison principles, integral estimates, variational arguments, rearrangement techniques, and numerical simulations, provide a better understanding of these dependencies. In particular, we propose a precise characterisation of the situations where the addition of a third patch increases or decreases the chances of persistence, compared to a situation with only two patches.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
All Matlab source code used to generate the analyses performed here is available at https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/QAV2M.
Notes
In the sequel, we say that \(\varPsi \in L^2(\mathbb {R}^n)^H\) is normalised whenever \(\int _{\mathbb {R}^{n}}\Vert \varPsi (\textbf{x})\Vert ^2\,\textrm{d}\textbf{x}=1.\)
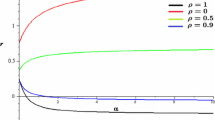
Notice that the inequalities \(0\le \lambda _H'(0)<1\) are coherent with Corollary 1.
The authors are grateful to L. Dupaigne, F. Murat and an anonymous referee for helpful bibliographical comments on this point.
References
Agmon S (1982) Lectures on exponential decay of solutions of second-order elliptic equations: bounds on eigenfunctions of \(N\)-body Schrödinger operators. Mathematical Notes, vol 29. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Alfaro M, Veruete M (2019) Evolutionary branching via replicator-mutator equations. J Dyn Differ Equ 31:2029–2052
Berestycki H, Lachand-Robert T (2004) Some properties of monotone rearrangement with applications to elliptic equations in cylinders. Math Nachr 266:3–19
Berestycki H, Hamel F, Roques L (2005) Analysis of the periodically fragmented environment model: I-species persistence. J Math Biol 51:75–113
Besala P (1979) Fundamental solution and Cauchy problem for a parabolic system with unbounded coefficients. J Differ Equ 33:26–38
Cantrell RS, Cosner C (1989) Diffusive logistic equations with indefinite weights: population models in disrupted environments. Proc R Soc Edinb A 112:293–318
Caquet T, Gascuel C, Tixier-Boichard M (2020) Agroécologie : des recherches pour la transition des filières et des territoires. Quae
Cardoulis L (2009) Systems of Schrödinger equations in the whole space. Rostock Math Kolloq 65:29–49
Cardoulis L (2015) Principal eigenvalues for systems of Schrödinger equations defined in the whole space with indefinite weights. Math Slovaca 65:1079
Damascelli L, Pacella F (2013) Symmetry results for cooperative elliptic systems via linearization. SIAM J Math Anal 45:1003–1026
Débarre F, Ronce O, Gandon S (2013) Quantifying the effects of migration and mutation on adaptation and demography in spatially heterogeneous environments. J Evol Biol 26:1185–1202
Djidjou-Demasse R, Ducrot A, Fabre F (2017) Steady state concentration for a phenotypic structured problem modeling the evolutionary epidemiology of spore producing pathogens. Math Models Methods Appl Sci 27:385–426
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (2018) The 10 Elements of Agroecology. Guiding the Transition to Sustainable Food and Agricultural Systems, FAO
García-Ramos G, Kirkpatrick M (1997) Genetic models of adaptation and gene flow in peripheral populations. Evolution 51:21–28
Hamel F, Lavigne F, Roques L (2021) Adaptation in a heterogeneous environment. I: persistence versus extinction. J Math Biol 83:1–42
Klausmeier CA, Osmond MM, Kremer CT, Litchman E (2020) Ecological limits to evolutionary rescue. Phil Trans R Soc B 373:20190453
Latinne A, Hu B, Olival KJ, Zhu G, Zhang L, Li H, Chmura AA, Field HE, Zambrana-Torrelio C, Epstein JH, Li B, Zhang W, Wang L-F, Shi Z-L, Daszak P (2020) Origin and cross-species transmission of bat coronaviruses in China. Nature Commun 11:1–15
Lau SKP, Woo PCY, Li KSM, Huang Y, Tsoi H-W, Wong BHL, Wong SSY, Leung S-Y, Chan K-H, Yuen K-Y (2005) Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-like virus in Chinese horseshoe bats. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102:14040–14045
Lavigne F, Martin G, Anciaux Y, Papaïx J, Roques L (2020) When sinks become sources: adaptive colonization in asexuals. Evolution 74:29–42
Lieberman GM (1996) Second order parabolic differential equations. World Scientific Publishing Co. Inc., River Edge
Littman W, Stampacchia G, Weinberger HF (1963) Regular points for elliptic equations with discontinuous coefficients. Ann Scuola Norm Sup Pisa 3(17):43–77
Martin G (2014) Fisher’s geometrical model emerges as a property of complex integrated phenotypic networks. Genetics 197:237–255
Martin G, Lenormand T (2015) The fitness effect of mutations across environments: Fisher’s geometrical model with multiple optima. Evolution 69:1433–1447
Meszéna G, Czibula I, Geritz S (1997) Adaptive dynamics in a 2-patch environment: a toy model for allopatric and parapatric speciation. J Biol Syst 5:265–284
Mirrahimi S (2017) A Hamilton–Jacobi approach to characterize the evolutionary equilibria in heterogeneous environments. Math Models Methods Appl Sci 27:2425–2460
Mirrahimi S, Gandon S (2020) Evolution of specialization in heterogeneous environments: equilibrium between selection, mutation and migration. Genetics 214:479–491
Papaïx J, David O, Lannou C, Monod H (2013) Dynamics of adaptation in spatially heterogeneous metapopulations. PLoS ONE 8:e54697
Parrish CR, Murcia PR, Holmes EC (2015) Influenza virus reservoirs and intermediate hosts: dogs, horses, and new possibilities for influenza virus exposure of humans. J Virol 89:2990–2994
Ponce AC (2016) Elliptic PDEs, measures and capacities, from the Poisson equation to nonlinear Thomas-Fermi problems, vol 23 of Tracts in Mathematics. European Math. Society
Roughgarden J (1971) Density-dependent natural selection. Ecology 52:453–468
Tenaillon O (2014) The utility of Fisher’s geometric model in evolutionary genetics. Ann Rev Ecol Evol Syst 45:179–201
Waxman D, Peck JR (1998) Pleiotropy and the preservation of perfection. Science 279:1210–1213
Webby RJ, Webster RG (2001) Emergence of influenza A viruses. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 356:1817–1828
Funding
This work has received funding from the French ANR RESISTE (ANR-18-CE45-0019) and DEEV (ANR-20-CE40-0011-01) projects, from Excellence Initiative of Aix-Marseille Université - A*MIDEX, a French “Investissements d’Avenir” program, and from the région Normandie BIOMA-NORMAN (21E04343) project. The authors acknowledge support of the Institut Henri Poincaré (UAR 839 CNRS-Sorbonne Université) and LabEx CARMIN (ANR-10-LABX-59-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alfaro, M., Hamel, F., Patout, F. et al. Adaptation in a heterogeneous environment II: to be three or not to be. J. Math. Biol. 87, 68 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-023-01996-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-023-01996-4