Abstract
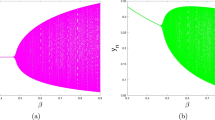
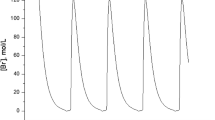
Predator–prey models with Michaelis–Menten–Holling type ratio- dependent functional response exhibit very rich and complex dynamical behavior, such as the existence of degenerate equilibria, appearance of limit cycles and heteroclinic loops, and the coexistence of two attractive equilibria. In this paper, we study heteroclinic bifurcations of such a predator–prey model. We first calculate the higher order Melnikov functions by transforming the model into a Hamiltonian system and then provide an algorithm for computing higher order approximations of the heteroclinic bifurcation curves.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arditi R. and Ginzburg L.R. (1989). Coupling in predator–prey dynamics: ratio-dependence. J. Theor. Biol. 139: 311–326
Berezovskaya F., Karev G. and Arditi R. (2001). Parametric analysis of the ratio-dependent predator–prey model. J. Math. Biol. 43: 221–246
Burden R.L. and Faires J.D. (2001). Numerical Analysis, 7th edn. Thomson Learning Inc., Boston
Davis P.J. and Rabinowitz P. (1975). Methods of Numerical Integtation. Academic Press, New York
Du Z. and Zhang W. (2005). Melnikov method for homoclinic bifurcation in nonlinear impact oscillators. Comput. Math. Appl. 50: 445–458
Ermentrout, B.: Simulating, Analyzing, and Animating Dynamical Systems: A Guide to XPPAUT for Researchers and Students. SIAM, Pheladelphia (2002)
Guckenheimer J. and Holmes P. (1983). Nonlinear Oscillations, Dynamical Systems and Bifurcations of Vector Fields. Springer, New York
Hsu S.-B., Hwang T.-W. and Kuang Y. (2001). Global analysis of the Michaelis–Menten-type ratio-dependent predator–prey system. J. Math. Biol. 42: 489–506
Kuang Y. and Beretta E. (1998). Global qualitative analysis of a ratio-dependent predator–prey system. J. Math. Biol. 36: 389–406
Li B. and Kuang Y. (2007). Heteroclinic bifurcation in the Michaelis–Menten type ratio-dependent predator–prey system. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 67: 1453–1464
Li B.-Y. and Zhang Z.-F. (1995). A note on a result of G. S. Petrov about the weakened 16th Hilbert problem.. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 190: 489–516
Poggiale, J.C.: Applications des variétés invariantes á la modélisation de l’hétérogénéité en dynamique des populations. Thése, Université de Bourgogne, France (1992)
Sanders J.A. (1982). Melnikov’s method and averaging. Celest. Mech. 28: 171–181
Tang Y. and Zhang W. (2005). Heteroclinic bifurcation in a ratio-dependent predator–prey system. J. Math. Biol. 50: 699–712
Hermerik L., Boer M.P., Kooi B.W. and Voorn G.A.K. van (2007). Heteroclitic orbits indicate overexploitation in predator–prey systems with a strong Allee effect. Math. Biosci. 209: 451–469
Xiao D. and Ruan S. (2001). Global dynamics of a ratio-dependent predator–prey system. J. Math. Biol. 43: 268–290
Zhang Z.-F. and Li B.-Y. (1992). High order Melnikov functions and the problem of uniformity in global bifurcation. Ann. Mat. Pura Appl. CLXI: 181–212
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
S. Ruan research was supported by NSF grant DMS-0715772.
W. Zhang research was supported by NSFC(China), TRAPOYT, CPSF and China MOE Research Grants.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruan, S., Tang, Y. & Zhang, W. Computing the heteroclinic bifurcation curves in predator–prey systems with ratio-dependent functional response. J. Math. Biol. 57, 223–241 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-007-0153-z
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-007-0153-z
Keywords
- Approximation
- Melnikov functions
- Heteroclinic loop
- Hamiltonian system
- Beta functions
- Predator–prey system