Abstract
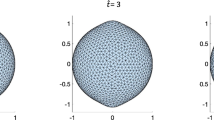
Diffuse interface (phase field) models are developed for multi-component vesicle membranes with different lipid compositions and membranes with free boundary. These models are used to simulate the deformation of membranes under the elastic bending energy and the line tension energy with prescribed volume and surface area constraints. By comparing our numerical simulations with recent biological experiments, it is demonstrated that the diffuse interface models can effectively capture the rich phenomena associated with the multi-component vesicle transformation and thus offering great functionality in their simulation and modelling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson D., McFadden G., Wheeler A. (1998). Diffuse-interface methods in fluid mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 30: 139–165
Baumgart T., Das S., Webb W., Jenkins J. (2005). Membrane elasticity in giant vesicles with fluid phase coexistence. Biophys. J. 89: 1067–1080
Baumgart T., Hess S., Webb W. (2003). Imaging coexisting fluid domains in biomembrane models coupling curvature and line tension. Nature 425: 821–824
Benvegnu D., McConnell M. (1992). Line tension between liquid domains in lipid monolayers. J. Phys. Chem. 96: 6820–6824
Biben T., Kassner K., Misbah C. (2005). Phase-field approach to 3D vesicle dynamics. Phys. Rev. E 72: 041921
Boettinger W., Warren J., Beckermann C., Karma A. (2002). Phase-field simulation of solidification. Ann. Rev. Mater. Res. 32: 163–194
Burchard P., Cheng L.-T., Merriman B., Osher S. (2001). Motion of curves in three spatial dimensions using a level set approach. J. Comput. Phys. 170: 720–741
Caginalp, G., Chen, X.F.: Phase field equations in the singular limit of sharp interface problems. In: On the Evolution of Phase Boundaries (Minneapolis, MN, 1990–1991), pp. 1–27. Springer, New York (1992)
Capovilla R., Guven J., Santiago J. (2002). Lipid membranes with an edge. Phys. Rev. E 66: 021607
Carmo M. (2006). Differential Geometry of Curves and Surfaces. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Chen L.-Q. (2002). Phase-field models for microstructure evolution. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 32: 113–140
Ciarlet P.G. (1998). Introduction to Linear Shell Theory. Gauthier-Villars and Elsevier, Paris
Ciarlet, P.G.: Mathematical elasticity, III: Theory of shells. In: Studies in Mathematics and its Applications. North-Holland, Amsterdam (2000)
Döbereiner, H., Käs, J., Noppl, D., Sprenger, I., Sackmann, E.: Budding and fission of vesicles. Biophys. J. 65, 1396C1403 (1993)
Du Q., Li M., Liu C. (2007). Analysis of a phase field Navier–Stokes vesicle-fluid interaction model. Disc. Cont. Dyn. Sys. B. 8(3): 539–556
Du Q., Liu C., Ryham R., Wang X. (2005). A phase field formulation of the Willmore problem. Nonlinearity 18: 1249–1267
Du Q., Liu C., Ryham R., Wang X. (2006). Modeling the spontaneous curvature effects in static cell membrane deformations by a phase field formulation. Commun. Pure Appl. Anal. 4: 537–548
Du, Q., Liu, C., Ryham, R., Wang, X.: Modeling vesicle deformations in flow fields via energetic variational approaches (2006, preprint)
Du Q., Liu C., Ryham R., Wang X. (2007). Diffuse interface energies capturing the euler number: relaxation and renormalization. Commun. Math. Sci. 5: 233–242
Du Q., Liu C., Wang X. (2004). A phase field approach in the numerical study of the elastic bending energy for vesicle membranes. J. Comput. Phys. 198: 450–468
Du Q., Liu C., Wang X. (2005). Retrieving topological information for phase field models. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 65: 1913–1932
Du Q., Liu C., Wang X. (2006). Simulating the deformation of vesicle membranes under elastic bending energy in three dimensions. J. Comput. Phys. 212: 757–777
Du Q., Wang X. (2007). Convergence of numerical approximations to a phase field bending elasticity model of membrane deformations. Inter. J. Numer. Anal Model. 4: 441–459
Du, Q., Zhang, J.: Adaptive finite element method for a phase field bending elasticity model of vesicle membrane deformations (2007, preprint)
Gozdz W., Gompper G. (1999). Shapes and shape transformations of two-component membranes of complex topology. Phys. Rev. E 59: 4305–4316
Jiang Y., Lookman T., Saxena A. (2000). Phase separation and shape deformation of two-phase membranes. Phys. Rev. E 6: R57–R60
Juelicher F., Lipowsky R. (1996). Shape transformations of vesicles with intramembrane domains. Phys. Rev. E 53: 2670–2683
Kumar P., Gompper G., Lipowsky R. (2001). Budding dynamics of multicomponent membranes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86: 3911–3914
Lipowsky R. (1992). Budding of membranes induced by intramembrane domains. Journal de Physique II, France 2: 1825–1840
Lipowsky R. (1995). The morphology of lipid membranes. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 5: 531–540
Lipowsky R. (2002). Domains and rafts in membranes hidden dimensions of self-organization. J. Biol. Phys. 28: 195–210
McWhirter J., Ayton G., Voth G. (2004). Coupling field theory with mesoscopic dynamical simulations of multicomponent lipid bilayers. Biophys. J. 87: 3242–3263
Mukherjee S., Maxfield F. (2004). Membrane domains. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 20: 839–866
Ou-Yang Z., Liu J., Xie Y. (1999). Geometric Methods in the Elastic Theory of Membranes in Liquid Crystal Phases. World Scientific, Singapore
Osher S., Fedkiw R. (2002). The Level Set Method and Dynamic Implicit Surfaces. Springer, Heidelberg
Saitoh A., Takiguchi K., Tanaka Y., Hotani H. (1998). Opening-up of liposomal membranes by talin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. Biophys. 956: 1026–1031
Seifert U. (1993). Curvature-induced lateral phase separation in two-component vesicles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70: 1335–1338
Sethian J.A. (1999). Level Set Methods and Fast Marching Methods: Evolving Interfaces in Computational Geometry, Fluid Mechanics, Computer Vision and Materials Science. Cambridge University Press, New York
Simons K., Vaz W. (2004). Model systems, lipid rafts and cell membranes. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 33: 269–295
Tu, Z., Ou-Yang, Z.: Lipid membranes with free edges. Phys. Rev. E 68, 061915 (1–7) (2003)
Tu Z., Ou-Yang Z. (2004). A geometric theory on the elasticity of bio-membranes. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 37: 11407–11429
Umeda, T., Suezaki, Y., Takiguchi, K., Hotani, H.: Theoretical analysis of opening-up vesicles with single and two holes. Phys. Rev. E 71, 011913 (1–8) (2005)
Wang, X.: Phase Field Models and Simulations of Vesicle Bio-membranes. Ph.D thesis, Department of Mathematics, Penn State University (2005)
Yin Y., Yin J., Ni D. (2005). General mathematical frame for open or closed biomembranes I: Equilibrium theory and geometrically constraint equation. J. Math. Biol. 51: 403–413
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research is supported in part by NSF-DMS 0409297 and NSF-ITR 0205232. Part of the work was performed while the first author was supported by the Institute for Mathematics and its Applications at the University of Minnesota.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Du, Q. Modelling and simulations of multi-component lipid membranes and open membranes via diffuse interface approaches. J. Math. Biol. 56, 347–371 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-007-0118-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-007-0118-2
Keywords
- Vesicle membrane
- Lipid bilayer
- Multi-component membrane
- Open membrane
- Phase field model
- Diffuse interface model
- Numerical simulation