Abstract
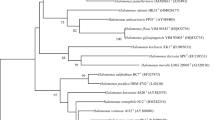
A novel aerobic bacterium designated DX6T was isolated from a Gobi soil sample collected in Bachu County, China. Cells are Gram-stain-negative and rod-shaped and colonies are creamy, circular and smooth. The growth range of NaCl concentration was 1–15% (optimum 2–10%, w/v). Growth occurs at 10–45 °C (optimum 37 °C) and pH 5.0–10.0 (optimum pH 7.0–9.0). Phylogenetic analysis of the 16S rRNA gene sequences indicated that strain DX6T formed a distinct lineage in the clade of genus Halomonas and is related to Halomonas desiderata DSM 9502T (98.3%), Halomonas kenyensis AIR-2T (97.7%), Halomonas daqingensis DQD2-30T (97.6%), Halomonas saliphila LCB169T (97.4%) and Halomonas endophytica MC28T (96.2%). Analysis of the housekeeping genes gryB and rpoD and calculation of the average nucleotide identities and the digital DNA-DNA hybridization values between strain DX6T and the related type Halomonas strains further revealed that strain DX6T represented a distinct species. The main respiratory quinones of strain DX6T were ubiquinone 9 (Q-9) and ubiquinone 8 (Q-8). The predominant cellular fatty acids were summed feature 8 (C18:1ω7c and/or C18:1ω6c), summed feature 3 (C16:1ω7c and/or C16:1ω6c) and C16:0. The major polar lipids consisted of diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylethanolamine, two unidentified phospholipids, an unidentified phosphatidylglycolipid, and four unidentified lipids. Based on the phenotypic, phylogenetic, chemotaxonomic and genomic features, strain DX6T represents a novel species of the genus Halomonas. The name Halomonas bachuensis sp. nov. is proposed with strain DX6T (= CCTCC AB 2020094T = KCTC 82196T) designated as the type strain.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim KK, Lee JS, Stevens DA (2013) Microbiology and epidemiology of Halomonas species. Future Microbiol 8:1559–1573
Zhao B, Yan Y, Chen S (2014) How could haloalkaliphilic microorganisms contribute to biotechnology? Can J Microbiol 60:717–727
Chen C, Anwar N, Wu C, Fu G, Wang R, Zhang C, Wu Y, Sun C, Wu M (2018) Halomonas endophytica sp. nov., isolated from liquid in the stems of Populus euphratica. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68:1633–1638
Jensen MP, Ardö Y, Vogensen FK (2009) Isolation of cultivable thermophilic lactic acid bacteria from cheeses made with mesophilic starter and molecular comparison with dairy-related Lactobacillus helveticus strains. Lett Appl Microbiol 49:396–402
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, Park SC, Jeon YS, Lee JH, Yi H, Won S, Chun J (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Micr 62:716–721
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35:1547–1549
Goris J, Konstantinidis KT, Klappenbach JA, Coenye T, Vandamme P, Tiedje JM (2007) DNA-DNA hybridization values and their relationship to whole-genome sequence similarities. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:81–91
De Ley J, Cattoir H, Reynaerts A (1970) The quantitative measurement of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Eur J Biochem 12:133–142
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk H-P, Göker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform 14:60
Claus D (1992) A standardized gram staining procedure. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 8:451–452
Bauer AW, Kirby WM, Sherris JC, Turck M (1966) Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol 45(4):493–496
Liu Y, Zhai L, Yao S, Cao Y, Cao Y, Zhang X, Su J, Ge Y, Zhao R, Cheng C (2015) Brachybacterium hainanense sp. nov., isolated from noni (Morinda citrifolia L.) branch. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:4196–4201
Komagata K, Suzuki K (1987) Lipid and cell-wall analysis in bacterial systematics. Methods Microbiol 19:161–207
Richter M, Rosselló-Móra R (2009) Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:19126–19131
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Wu G, Wu XQ, Wang YN, Chi CQ, Tang YQ, Kida K, Wu XL, Luan ZK (2008) Halomonas daqingensis sp. nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium isolated from an oilfield soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2859–2865
Gan L, Long X, Zhang H, Hou Y, Tian J, Zhang Y, Tian Y (2018) Halomonas saliphila sp. nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium isolated from a saline soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68:1153–1159
Boltyanskaya YV, Kevbrin VV, Lysenko AM, Kolganova TV, Tourova TP, Osipov GA, Zhilina TN (2007) Halomonas mongoliensis sp. nov. and Halomonas kenyensis sp. nov., new haloalkaliphilic denitrifiers capable of N2O reduction, isolated from soda lakes. Microbiology 76:739–747
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31771946).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: ZX. Performed the experiments: JS ZW FD. Analyzed the data: ZX JZ. Contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools: ZX JZ. Wrote the paper: ZX.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, Z., Shen, J., Wang, Z. et al. Halomonas bachuensis sp. nov., Isolated from Gobi Soil. Curr Microbiol 78, 397–402 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-02268-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-02268-w