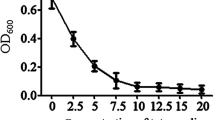
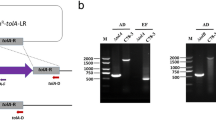
Abstract
Gram-negative bacteria use tripartite pumps to transport antibacterial drugs and other toxic compounds across the inner and outer membranes, which are separated by the periplasmic space. The TolC protein is an outer membrane factor that participates in the formation of tripartite efflux pumps. The genome of Vibrio vulnificus encodes two E. coli TolC homologs, TolCV1 and TolCV2. Here, we show that both TolCV1 and TolCV2 are involved in the efflux of antimicrobial agents. Deletion of tolCV1 resulted in increased susceptibility of V. vulnificus to chemical detergents, DNA intercalating agents, and antibiotics including erythromycin, novobiocin, and tetracycline, whereas deletion of tolCV2 rendered V. vulnificus more susceptible to the above mentioned antibiotics only. We also observed that tolCV1 deletion resulted in reduced motility of V. vulnificus. Our results indicate active roles for TolCV1 and TolCV2 in the physiology of V. vulnificus.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cameron DE, Urbach JM, Mekalanos JJ (2008) A defined transposon mutant library and its use in identifying motility genes in Vibrio cholerae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:8736–8741
Djordjevic D, Wiedmann M, McLandsborough LA (2002) Microtiter plate assay for assessment of Listeria monocytogenes biofilm formation. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:2950–2958
Federici L, Du D, Walas F, Matsumura H, Fernandez-Recio J, McKeegan KS, Borges-Walmsley MI, Luisi BF, Walmsley AR (2005) The crystal structure of the outer membrane protein VceC from the bacterial pathogen Vibrio cholerae at 1.8 Å resolution. J Biol Chem 280:15307–15314
Ge Q, Yamada Y, Zgurskaya H (2009) The C-terminal domain of AcrA is essential for the assembly and function of the multidrug efflux pump AcrAB-TolC. J Bacteriol 191:4365–4371
Kim HM, Xu Y, Lee M, Piao S, Sim SH, Ha NC, Lee K (2010) Functional relationships between the AcrA hairpin tip region and the TolC aperture tip region for the formation of the bacterial tripartite efflux pump AcrAB-TolC. J Bacteriol 192:4498–4503
Koronakis V, Eswaran J, Hughes C (2004) Structure and function of TolC: the bacterial exit duct for proteins and drugs. Annu Rev Biochem 73:467–489
Le Roux F, Binesse J, Saulnier D, Mazel D (2007) Construction of a Vibrio splendidus mutant lacking the metalloprotease gene vsm by use of a novel counterselectable suicide vector. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:777–784
Lee M, Jun SY, Yoon BY, Song S, Lee K, Ha NC (2012) Membrane fusion proteins of type I secretion system and tripartite efflux pumps share a binding motif for TolC in gram-negative bacteria. PLoS One 7(7):e40460
Lee M, Kim HL, Song S, Joo M, Lee S, Kim D, Hahn Y, Ha NC, Lee K (2013) The α-barrel tip region of Escherichia coli TolC homologs of Vibrio vulnificus interacts with the MacA protein to form the functional macrolide-specific efflux pump MacAB-TolC. J Microbiol 51(2):154–159
Lee S, Song S, Lee M, Kim JS, Hwang S, Ha NC, Lee K (2014) Interaction between the α-barrel tip region of Vibrio vulnificusTolC homologs and AcrA implies the adapter bridging model. J Microbiol 52(2):148–153
Milton DL, O’Toole R, Horstedt P, Wolf-Watz H (1996) Flagellin A is essential for the virulence of Vibrio anguillarum. J Bacteriol 178:1310–1319
Nikaido H, Pages JM (2012) Broad-specificity efflux pumps and their role in multidrug resistance of Gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 36:340–363
Paulsen IT, Park JH, Choi PS, Saier MH Jr (1997) A family of gram-negative bacterial outer membrane factors that function in the export of proteins, carbohydrates, drugs and heavy metals from gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 156:1–8
Simon R, Priefer U, Pühler A (1983) A broad host range mobilization system for in vivo genetic engineering: transposon mutagenesis in gram negative bacteria. Nat Biotechnol 1:784–791
Val ME, Kennedy SP, El Karoui M, Bonne L, Chevalier F, Barre FX (2008) FtsK-dependent dimer resolution on multiple chromosomes in the pathogen Vibrio cholerae. PLoS Genet 4(9):e1000201
Webber MA, Bailey AM, Blair JMA, Morgan E, Stevens MP, Hinton JCD, Ivens A, Wain J, Piddock LJ (2009) The global consequence of disruption of the AcrAB-TolC efflux pump in Salmonella enterica includes reduced expression of SPI-1 and other attributes required to infect the host. J Bacteriol 191(13):4276–4285
Wright AC, Morris JG Jr, Maneval DR Jr, Richardson K, Kaper JB (1985) Cloning of the cytotoxin-hemolysin gene of Vibrio vulnificus. Infect Immun 50:922–924
Xu Y, Lee M, Moeller A, Song S, Yoon BY, Kim HM, Jun SY, Lee K, Ha NC (2011) Funnel-like hexameric assembly of the periplasmic adapter protein in the tripartite multidrug efflux pump in gram-negative bacteria. J Biol Chem 286:17910–17920
Xu Y, Song S, Moeller A, Kim N, Piao S, Sim SH, Kang M, Yu W, Cho HS, Chang I, Lee K, Ha NC (2011) Functional implications of an intermeshing cogwheel-like interaction between TolC and MacA in the action of macrolide-specific efflux pump MacAB-TolC. J Biol Chem 286:13541–13549
Zgurskaya HI, Nikaido H (1999) Bypassing the periplasm: reconstitution of the AcrAB multidrug efflux pump of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:7190–7195
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Next-Generation BioGreen 21 Program (SSAC, PJ009025), Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea, and an NRF grant (2011-0028553) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, Republic of Korea. It is also partially supported by Chung-Ang University Excellent Student Scholarship in 2014. The authors thank Dr. Minho Lee for his helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S., Song, S. & Lee, K. Functional Analysis of TolC Homologs in Vibrio vulnificus . Curr Microbiol 68, 729–734 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-014-0537-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-014-0537-4