Abstract
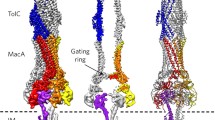
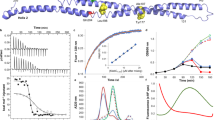
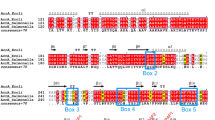
TolC and its homologous family of proteins are outer membrane factors that are essential for exporting small molecules and toxins across the outer membrane in Gram-negative bacteria. Two open reading frames in the Vibrio vulnificus genome that encode proteins homologous to Escherichia coli TolC, designated TolCV1 and TolCV2, have 51.3% and 29.6% amino acid identity to TolC, respectively. In this study, we show that TolCV1 and TolCV2 functionally and physically interacted with the membrane fusion protein, MacA, a component of the macrolide-specific MacAB-TolC pump of E. coli. We further show that the conserved residues located at the aperture tip region of the α-hairpin of TolCV1 and TolCV2 played an essential role in the formation of the functional MacAB-TolC pump using site-directed mutational analyses. Our findings suggest that these outer membrane factors have conserved tip-to-tip interaction with the MacA membrane fusion protein for action of the drug efflux pump in Gramnegative bacteria.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akama, H., Matsuura, T., Kashiwagi, S., Yoneyama, H., Narita, S., Tsukihara, T., Nakagawa, A., and Nakae, T. 2004. Crystal structure of the membrane fusion protein, MexA, of the multidrug transporter in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Biol. Chem.279, 25939–25942.
Bavro, V.N., Pietras, Z., Furnham, N., Perez-Cano, L., Fernandez-Recio, J., Pei, X.Y., Misra, R., and Luisi, B. 2008. Assembly and channel opening in a bacterial drug efflux machine. Mol. Cell30, 114–121.
Bina, J.E., Alm, R.A., Uria-Nickelsen, M., Thomas, S.R., Trust, T.J., and Hancock, R.E. 2000. Helicobacter pylori uptake and efflux: Basis for intrinsic susceptibility to antibiotics in vitro. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.44, 248–254.
Federici, L., Du, D., Walas, F., Matsumura, H., Fernandez-Recio, J., McKeegan, K.S., Borges-Walmsley, M.I., Luisi, B.F., and Walmsley, A.R. 2005. The crystal structure of the outer membrane protein VceC from the bacterial pathogen Vibrio cholerae at 1.8 J. Biol. Chem.280, 15307–15314.
Gerken, H. and Misra, R. 2004. Genetic evidence for functional interactions between TolC and AcrA proteins of a major antibiotic efflux pump of Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol.54, 620–631.
Higgins, M.K., Bokma, E., Koronakis, E., Hughes, C., and Koronakis, V. 2004. Structure of the periplasmic component of a bacterial drug efflux pump. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA101, 9994–9999.
Kim, H.M., Xu, Y., Lee, M., Piao, S., Sim, S.H., Ha, N.C., and Lee, K. 2010. Functional relationships between the AcrA hairpin tip region and the TolC aperture tip region for the formation of the bacterial tripartite efflux pump AcrAB-TolC. J. Bacteriol.192, 4498–4503.
Kobayashi, N., Nishino, K., Hirata, T., and Yamaguchi, A. 2003. Membrane topology of ABC-type macrolide antibiotic exporter MacB in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett.546, 241–246.
Kobayashi, N., Nishino, K., and Yamaguchi, A. 2001. Novel macrolide-specific ABC-type efflux transporter in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol.183, 5639–5644.
Kohler, T., Michea-Hamzehpour, M., Henze, U., Gotoh, N., Curty, L.K., and Pechere, J.C. 1997. Characterization of MexE-MexF-OprN, a positively regulated multidrug efflux system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Microbiol.23, 345–354.
Koronakis, V., Eswaran, J., and Hughes, C. 2004. Structure and function of TolC: The bacterial exit duct for proteins and drugs. Annu. Rev. Biochem.73, 467–489.
Koronakis, V., Sharff, A., Koronakis, E., Luisi, B., and Hughes, C. 2000. Crystal structure of the bacterial membrane protein TolC central to multidrug efflux and protein export. Nature405, 914–919.
Lee, M., Jun, S.Y., Yoon, B.Y., Song, S., Lee, K., and Ha, N.C. 2012. Membrane fusion proteins of type I secretion system and tripartite efflux pumps share a binding motif for TolC in Gramnegative bacteria. PLoS ONE7, e40460.
Lewis, K. 2000. Translocases: A bacterial tunnel for drugs and proteins. Curr. Biol.10, R678–681.
Li, X.Z., Nikaido, H., and Poole, K. 1995. Role of mexA-mexB-oprM in antibiotic efflux in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.39, 1948–1953.
Lin, H.T., Bavro, V.N., Barrera, N.P., Frankish, H.M., Velamakanni, S., van Veen, H.W., Robinson, C.V., Borges-Walmsley, M.I., and Walmsley, A.R. 2009. MacB ABC transporter is a dimer whose ATPase activity and macrolide-binding capacity are regulated by the membrane fusion protein MacA. J. Biol. Chem.284, 1145–1154.
Lobedanz, S., Bokma, E., Symmons, M.F., Koronakis, E., Hughes, C., and Koronakis, V. 2007. A periplasmic coiled-coil interface underlying TolC recruitment and the assembly of bacterial drug efflux pumps. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA104, 4612–4617.
Ma, D., Cook, D.N., Alberti, M., Pon, N.G., Nikaido, H., and Hearst, J.E. 1995. Genes acrA and acrB encode a stress-induced efflux system of Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol.16, 45–55.
Mikolosko, J., Bobyk, K., Zgurskaya, H.I., and Ghosh, P. 2006. Conformational flexibility in the multidrug efflux system protein AcrA. Structure14, 577–587.
Misra, R. and Bavro, V.N. 2009. Assembly and transport mechanism of tripartite drug efflux systems. Biochim. Biophys. Acta.1794, 817–825.
Nishino, K. and Yamaguchi, A. 2001. Analysis of a complete library of putative drug transporter genes in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol.183, 5803–5812.
Park, J.H., Cho, Y.J., Chun, J., Seok, Y.J., Lee, J.K., Kim, K.S., Lee, K.H., Park, S.J., and Choi, S.H. 2011. Complete genome sequence of Vibrio vulnificus MO6-24/O. J. Bacteriol.193, 2062–2063.
Paulsen, I.T., Park, J.H., Choi, P.S., and Saier, M.H., Jr. 1997. A family of Gram-negative bacterial outer membrane factors that function in the export of proteins, carbohydrates, drugs and heavy metals from Gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Lett.156, 1–8.
Piao, S., Xu, Y., and Ha, N.C. 2008. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of MacA from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Acta. Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun.64, 391–393.
Poole, K., Gotoh, N., Tsujimoto, H., Zhao, Q., Wada, A., Yamasaki, T., Neshat, S., Yamagishi, J., Li, X.Z., and Nishino, T. 1996. Overexpression of the mexC-mexD-oprJ efflux operon in nfxBtype multidrug-resistant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Microbiol.21, 713–724.
Poole, K., Heinrichs, D.E., and Neshat, S. 1993. Cloning and sequence analysis of an EnvCD homologue in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Regulation by iron and possible involvement in the secretion of the siderophore pyoverdine. Mol. Microbiol.10, 529–544.
Symmons, M.F., Bokma, E., Koronakis, E., Hughes, C., and Koronakis, V. 2009. The assembled structure of a complete tripartite bacterial multidrug efflux pump. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA106, 7173–7178.
Thanabalu, T., Koronakis, E., Hughes, C., and Koronakis, V. 1998. Substrate-induced assembly of a contiguous channel for protein export from E. coli: Reversible bridging of an inner-membrane translocase to an outer membrane exit pore. Embo. J.17, 6487–6496.
Tikhonova, E.B., Devroy, V.K., Lau, S.Y., and Zgurskaya, H.I. 2007. Reconstitution of the Escherichia coli macrolide transporter: the periplasmic membrane fusion protein MacA stimulates the ATPase activity of MacB. Mol. Microbiol.63, 895–910.
Xu, Y., Lee, M., Moeller, A., Song, S., Yoon, B.Y., Kim, H.M., Jun, S.Y., Lee, K., and Ha, N.C. 2011a. Funnel-like hexameric assembly of the periplasmic adapter protein in the tripartite multidrug efflux pump in Gram-negative bacteria. J. Biol. Chem.286, 17910–17920.
Xu, Y., Moeller, A., Jun, S.Y., Lee, M., Yoon, B.Y., Kim, J.S., Lee, K., and Ha, N.C. 2012. Assembly and channel opening of outer membrane protein in tripartite drug efflux pumps of Gram-negative bacteria. J. Biol. Chem.287, 11740–11750.
Xu, Y., Sim, S.H., Song, S., Piao, S., Kim, H.M., Jin, X.L., Lee, K., and Ha, N.C. 2010. The tip region of the MacA alpha-hairpin is important for the binding to TolC to the Escherichia coli MacAB-TolC pump. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.394, 962–965.
Xu, Y., Song, S., Moeller, A., Kim, N., Piao, S., Sim, S.H., Kang, M., Yu, W., Cho, H.S., Chang, I., andet al. 2011b. Functional implications of an intermeshing cogwheel-like interaction between TolC and MacA in the action of macrolide-specific efflux pump MacAB-TolC. J. Biol. Chem.286, 13541–13549.
Yum, S., Xu, Y., Piao, S., Sim, S.H., Kim, H.M., Jo, W.S., Kim, K.J., Kweon, H.S., Jeong, M.H., Jeon, H., andet al. 2009. Crystal structure of the periplasmic component of a tripartite macrolide-specific efflux pump. J. Mol. Biol.387, 1286–1297.
Zgurskaya, H.I., Krishnamoorthy, G., Ntreh, A., and Lu, S. 2011. Mechanism and function of the outer membrane channel TolC in multidrug resistance and physiology of Enterobacteria. Front Microbiol.2, 189.
Zgurskaya, H.I. and Nikaido, H. 1999. Bypassing the periplasm: reconstitution of the AcrAB multidrug efflux pump of Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA96, 7190–7195.
Zgurskaya, H.I., Yamada, Y., Tikhonova, E.B., Ge, Q., and Krishnamoorthy, G. 2009. Structural and functional diversity of bacterial membrane fusion proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta.1794, 794–807.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://www.springer.com/content/120956.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, M., Kim, HL., Song, S. et al. The α-barrel tip region of Escherichia coli TolC homologs of Vibrio vulnificus interacts with the MacA protein to form the functional macrolide-specific efflux pump MacAB-TolC. J Microbiol. 51, 154–159 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-013-2699-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-013-2699-3