Abstract
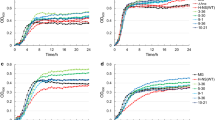
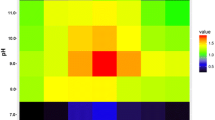
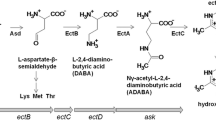
The histidine decarboxylase gene cluster of Morganella morganii DSM30146T was sequenced, and four open reading frames, named hdcT1, hdc, hdcT2, and hisRS were identified. Two putative histidine/histamine antiporters (hdcT1 and hdcT2) were located upstream and downstream the hdc gene, codifying a pyridoxal-P dependent histidine decarboxylase, and followed by hisRS gene encoding a histidyl-tRNA synthetase. This organization was comparable with the gene cluster of other known Gram negative bacteria, particularly with that of Klebsiella oxytoca. Recombinant Escherichia coli strains harboring plasmids carrying the M. morganii hdc gene were shown to overproduce histidine decarboxylase, after IPTG induction at 37 °C for 4 h. Quantitative RT-PCR experiments revealed the hdc and hisRS genes were highly induced under acidic and histidine-rich conditions. This work represents the first description and identification of the hdc-related genes in M. morganii. Results support the hypothesis that the histidine decarboxylation reaction in this prolific histamine producing species may play a role in acid survival. The knowledge of the role and the regulation of genes involved in histidine decarboxylation should improve the design of rational strategies to avoid toxic histamine production in foods.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albuquerque P, Mendes MV, Santos CL, Moradas-Ferreira P, Tavares F (2009) DNA signature-based approaches for bacterial detection and identification. Sci Total Environ 407:3641–3651
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Arnez JG, Harris DC, Mitschler A, Rees B, Francklyn CS, Moras D (1995) Crystal structure of histidyl-tRNA synthetase from Escherichia coli complexed with histidyl-adenylate. EMBO J 14:4143–4155
Bjornsdottir K, Bolton GE, McClellan-Green PD, Jaykus LA, Green DP (2009) Detection of Gram-negative histamine-producing bacteria in fish: a comparative study. J Food Prot 72:1987–1991
Curiel JA, de las Rivas B, Mancheño JM, Muñoz R (2011) The pURI family of expression vectors: a versatile set of ligation independent cloning plasmids for producing recombinant His-fusion proteins. Prot Expr Purif 76:44–53
Davies H (2010) A role for “omics” technologies in food safety assessment. Food Control 21:1601–1610
de las Rivas B, Curiel JA, Mancheño JM, Muñoz R (2007) Expression vectors for enzyme restriction- and ligation-independent cloning for producing recombinant his-fusion proteins. Biotechnol Prog 23:680–686
Eitenmiller RR, De Souza SC (1984) Enzymic mechanisms for amine formation in fish. In: Ragelis P (ed) Seafood toxins. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, pp 431–442
Ferrario C, Pegollo C, Ricci G, Borgo F, Fortina MG (2012) PCR detection and identification of histamine-forming bacteria in filleted tuna fish samples. J Food Sci 77:115–120
Ferrario C, Ricci G, Borgo F, Fortina MG (2012) Species-specific DNA probe and development of a quantitative PCR assay for the detection of Morganella morganii. Lett Appl Microbiol 54:292–298
Francklyn C, Adams J, Augustine J (1998) Catalytic defects in mutants of class II histidyl-tRNA synthetase from Salmonella typhimurium previously linked to decreased control of histidine biosynthesis regulation. J Mol Biol 280:847–858
Garcìa-Moruno E, Carrascosa A, Muñoz R (2005) A rapid and inexpensive method for the determination of biogenic amines from bacterial cultures by thin-layer chromatography. J Food Prot 68:625–629
Giulietti A, Overbergh L, Valckx D, Decallonne B, Bouillon R, Mathieu C (2001) An overview of real-time quantitative PCR: applications to quantify cytokine gene expression. Methods 25:386–401
Gökoğlu N (2003) Changes in biogenic amines during maturation of sardine (Sardina pilchardus) marinade. Fisheries Sci 69:823–829
Guth EC, Francklyn CS (2007) Kinetic discrimination of tRNA identity by the conserved motif 2 loop of a class II aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. Mol Cell 25:531–542
Kamath AV, Vaaler GL, Snell EE (1991) Pyridoxal phosphate-dependent histidine decarboxylases. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of genes from Klebsiella planticola and Enterobacter aerogenes and properties of the overexpressed enzymes. J Biol Chem 266:9432–9437
Kanki M, Yoda T, Tsukamoto T, Baba E (2007) Histidine decarboxylases and their role in accumulation of histamine in tuna and dried saucy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:1467–1473
Kimura B, Takahashi H, Hokimoto S, Tanaka Y, Fujii T (2009) Induction of the histidine decarboxylase genes of Photobacterium damselae subsp. damselae (formally P. histaminum) at low pH. J Appl Microbiol 107:485–497
Koral S, Tufan B, Ščavničar A, Kočar D, Pompe M, Köse S (2013) Investigation of the contents of biogenic amines and some food safety parameters of various commercially salted fish products. Food Control 32:597–606
Köse S (2010) Evaluation of seafood safety health hazards for traditional fish products: preventive measures and monitoring issues. Turkish J Fish Aquat Sci 10:139–160
Lehane L, Olley J (2000) Histamine fish poisoning revisited. Int J Food Microbiol 58:1–37
Lindkvist KB, Gallart-Jornet L, Stabel MC (2008) The restructuring of the Spanish salted fish market. Canadian Geographer/Le Géographie Canadien 52:105–120
Morii H, Kasama K, Herrera-Espinoza R (2006) Cloning and sequencing of the histidine decarboxylase gene from Photobacterium phosphoreum and its functional expression in Escherichia coli. J Food Prot 69:1768–1776
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:2002–2007
Prester L (2011) Biogenic amines in fish, fish products and shellfish: a review. Food Add Contaminants 28:1547–1560
Rasmussen R (2001) Quantification on the LightCycler. In: Meuer S, Wittwer C, Nakagawara K (eds) Rapid cycle real-time PCR, methods and applications. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 21–34
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Takahashi H, Kimura B, Yoshikawa M, Fujii T (2003) Cloning and sequencing of the histidine decarboxylase genes of gram-negative, histamine-producing bacteria and their application in detection and identification of these organisms in fish. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:2568–2579
Taylor SL, Stratton JE, Nordlee JA (1989) Histamine poisoning (scombroid fish poisoning): an allergy-like intoxication. Clin Toxicol 62:225–240
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) Clustal W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, positions-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Vaaler GL, Snell EE (1989) Pyridoxal 5′-phosphate dependent histidine decarboxylase: overproduction, purification, biosynthesis of soluble site-directed mutant proteins, and replacement of conserved residues. Biochemistry 28:7306–7313
Vaaler GL, Brasch MA, Snell EE (1986) Pyridoxal 5′-phosphate-dependent histidine decarboxylase. Nucleotide sequence of the hdc gene and the corresponding amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem 261:11010–11014
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants AGL2008-01052, AGL2011-22745, and Consolider INGENIO 2010 CSD2007-00063 FUN-C-FOOD (CICYT), S2009/AGR-1469 (ALIBIRD) (CAM), and RM.2012-00004 (INIA). We are grateful to J. Barcenilla and M. V. Santamaria.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferrario, C., Borgo, F., de las Rivas, B. et al. Sequencing, Characterization, and Gene Expression Analysis of the Histidine Decarboxylase Gene Cluster of Morganella morganii . Curr Microbiol 68, 404–411 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-013-0490-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-013-0490-7