Abstract
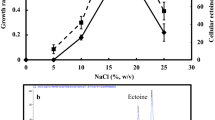
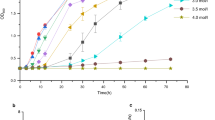
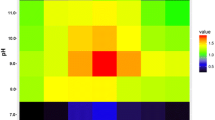
Acidiphilium cryptum is an acidophilic, heterotrophic α-Proteobacterium which thrives in acidic, metal-rich environments (e.g. acid mine drainage). Recently, an ectABCDask gene cluster for biosynthesis of the compatible solutes ectoine and hydroxyectoine was detected in the genome sequence of A. cryptum JF-5. We were able to demonstrate that the type strain A. cryptum DSM 2389T is capable of synthesizing the compatible solute hydroxyectoine in response to moderate osmotic stress caused by sodium chloride and aluminium sulphate, respectively. Furthermore, we used the A. cryptum JF-5 sequence to amplify the ectABCDask gene cluster from strain DSM 2389T and achieved heterologous expression of the gene cluster in Escherichia coli. Hence, we could for the first time prove metabolic functionality of the genes responsible for hydroxyectoine biosynthesis in the acidophile A. cryptum. In addition, we present information on specific enzyme activity of A. cryptum DSM 2389T ectoine synthase (EctC) in vitro. In contrast to EctCs from halophilic microorganisms, the A. cryptum enzyme exhibits a higher isoelectric point, thus a lower acidity, and has maximum specific activity in the absence of sodium chloride.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker J, Schäfer R, Kohlstedt M, Harder BJ, Borchert NS, Stöveken N, Bremer E, Wittmann C (2013) Systems metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for production of the chemical chaperone ectoine. Microb Cell Fact 12:110. doi:10.1186/1475-2859-12-110
Bertani G (1951) Studies on lysogenesis. I.: The mode of phage liberation by lysogenic Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 62:293–300
Bestvater T, Louis P, Galinski EA (2008) Heterologous ectoine production in Escherichia coli: by-passing the metabolic bottle-neck. Saline Syst 4:12. doi:10.1186/1746-1448-4-12
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:911–917. doi:10.1139/o59-099
Borges N, Ramos A, Raven ND, Sharp RJ, Santos H (2002) Comparative study of the thermostabilizing properties of mannosylglycerate and other compatible solutes on model enzymes. Extremophiles 6:209–216. doi:10.1007/s007920100236
Brown AD (1976) Microbial water stress. Bacteriol Rev 40:803–846
Bursy J, Pierik AJ, Pica N, Bremer E (2007) Osmotically induced synthesis of the compatible solute hydroxyectoine is mediated by an evolutionarily conserved ectoine hydroxylase. J Biol Chem 282:31147–31155. doi:10.1074/jbc.M704023200
Cummings DE, Fendorf S, Singh N, Sani RK, Peyton BM, Magnuson TS (2007) Reduction of Cr(VI) under acidic conditions by the facultative Fe(lll)-reducing bacterium Acidiphilium cryptum. Environ Sci Technol 41:146–152. doi:10.1021/es061333k
Dinnbier U, Limpinsel E, Schmid R, Bakker EP (1988) Transient accumulation of potassium glutamate and its replacement by trehalose during adaptation of growing cells of Escherichia coli K-12 to elevated sodium chloride concentrations. Arch Microbiol 150:348–357. doi:10.1007/BF00408306
Dötsch A, Severin J, Alt W, Galinski EA, Kreft JU (2008) A mathematical model for growth and osmoregulation in halophilic bacteria. Microbiology 154:2956–2969. doi:10.1099/mic.0.2007/012237-0
Eilert E, Kranz A, Hollenberg CP, Piontek M, Suckow M (2013) Synthesis and release of the bacterial compatible solute 5-hydroxyectoine in Hansenula polymorpha. J Biotechnol 167:85–93. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2013.02.005
Elevi Bardavid R, Oren A (2012) The amino acid composition of proteins from anaerobic halophilic bacteria of the order Halanaerobiales. Extremophiles 16:567–572. doi:10.1007/s00792-012-0455-y
Fischer J, Quentmeier A, Gansel S, Sabados V, Friedrich CG (2002) Inducible aluminum resistance of Acidiphilium cryptum and aluminum tolerance of other acidophilic bacteria. Arch Microbiol 178:554–558. doi:10.1007/s00203-002-0482-7
Follmann M, Becker M, Ochrombel I, Ott V, Krämer R, Marin K (2009) Potassium transport in Corynebacterium glutamicum is facilitated by the putative channel protein CglK, which is essential for pH homeostasis and growth at acidic pH. J Bacteriol 191:2944–2952. doi:10.1128/JB.00074-09
Fukuchi S, Yoshimune K, Wakayama M, Moriguchi M, Nishikawa K (2003) Unique amino acid composition of proteins in halophilic bacteria. J Mol Biol 327:347–357. doi:10.1016/S0022-2836(03)00150-5
Galinski EA, Oren A (1991) Isolation and structure determination of a novel compatible solute from the moderately halophilic purple sulfur bacterium Ectothiorhodospira marismortui. Eur J Biochem 198:593–598. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16055.x
Galinski EA, Pfeiffer HP, Trüper HG (1985) 1,4,5,6-Tetrahydro-2-methyl-4-pyrimidinecarboxylic acid. A novel cyclic amino acid from halophilic phototrophic bacteria of the genus Ectothiorhodospira. Eur J Biochem 149:135–139. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08903.x
Gandbhir M, Rasched I, Marlière P, Mutzel R (1995) Convergent evolution of amino acid usage in archaebacterial and eubacterial lineages adapted to high salt. Res Microbiol 146:113–120. doi:10.1016/0923-2508(96)80889-8
Göller K, Galinski EA (1999) Protection of a model enzyme (lactate dehydrogenase) against heat, urea and freeze-thaw treatment by compatible solute additives. J Mol Catal B Enzym 7:37–45. doi:10.1016/S1381-1177(99)00043-0
Goltsman DS, Denef VJ, Singer SW, VerBerkmoes NC, Lefsrud M, Mueller RS, Dick GJ, Sun CL, Wheeler KE, Zemla A, Baker BJ, Hauser L, Land M, Shah MB, Thelen MP, Hettich RL, Banfield JF (2009) Community genomic and proteomic analyses of chemoautotrophic iron-oxidizing “Leptospirillum rubarum” (Group II) and “Leptospirillum ferrodiazotrophum” (Group III) bacteria in acid mine drainage biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:4599–4615. doi:10.1128/AEM.02943-08
Guida L, Saidi Z, Hughes MN, Poole RK (1991) Aluminium toxicity and binding to Escherichia coli. Arch Microbiol 156:507–512. doi:10.1007/BF00245400
Hanahan D (1983) Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol 166:557–580. doi:10.1016/S0022-2836(83)80284-8
Harrison AP (1981) Acidiphilium cryptum gen. nov., sp. nov., heterotrophic bacterium from acidic mineral environments. Int J Syst Bacteriol 31:327–332. doi:10.1099/00207713-31-3-327
Harrison AP, Jarvis BW, Johnson JL (1980) Heterotrophic bacteria from cultures of autotrophic Thiobacillus ferrooxidans: relationships as studied by means of deoxyribonucleic acid homology. J Bacteriol 143:448–454
Imhoff JF, Trüper HG (1977) Ectothiorhodospira halochloris sp. nov., a new extremely halophilic phototropic bacterium containing bacteriochlorophyll b. Arch Microbiol 114:115–121. doi:10.1007/BF00410772
Inbar L, Lapidot A (1988) The structure and biosynthesis of new tetrahydropyrimidine derivatives in actinomycin D producer Streptomyces parvulus. Use of 13C- and 15N-labeled L-glutamate and 13C and 15N NMR spectroscopy. J Biol Chem 263:16014–16022
Johnson DB, McGinness S (1991) Ferric iron reduction by acidophilic heterotrophic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:207–211
Kishimoto N, Tano T (1987) Acidophilic heterotrophic bacteria isolated from acidic mine drainage, sewage, and soils. J Gen Appl Microbiol 33:11–25. doi:10.2323/jgam.33.11
Koichi M, Mitsuhiko M, Tatsuo N, Yoshio S; Takeda Chem Ind Ltd (Take), assignee (1991) Production of tetrahydropyrimidine derivatives. Jp Patent JP3031265
Kraegeloh A, Kunte HJ (2002) Novel insights into the role of potassium for osmoregulation in Halomonas elongata. Extremophiles 6:453–462. doi:10.1007/s00792-002-0277-4
Krämer R, Lambert C, Hoischen C, Ebbighausen H (1990) Uptake of glutamate in Corynebacterium glutamicum. 1. Kinetic properties and regulation by internal pH and potassium. Eur J Biochem 194:929–935. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19488.x
Kunte HJ, Galinski EA, Trüper HG (1993) A modified FMOC-method for the detection of amino acid-type osmolytes and tetrahydropyrimidines (ectoines). J Microbiol Methods 17:129–136. doi:10.1016/0167-7012(93)90006-4
Kunte HJ, Lentzen G, Galinski EA (2014) Industrial production of the cell protectant ectoine: protection mechanisms, processes, and products. Curr Biotechnol 3:10–25. doi:10.2174/22115501113026660037
Küsel K, Dorsch T, Acker G, Stackebrandt E (1999) Microbial reduction of Fe(III) in acidic sediments: isolation of Acidiphilium cryptum JF-5 capable of coupling the reduction of Fe(III) to the oxidation of glucose. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:3633–3640
Lang YJ, Bai L, Ren YN, Zhang LH, Nagata S (2011) Production of ectoine through a combined process that uses both growing and resting cells of Halomonas salina DSM 5928T. Extremophiles 15:303–310. doi:10.1007/s00792-011-0360-9
Larsen PI, Sydnes LK, Landfald B, Strom AR (1987) Osmoregulation in Escherichia coli by accumulation of organic osmolytes: betaines, glutamic acid, and trehalose. Arch Microbiol 147:1–7. doi:10.1007/BF00492896
Lentzen G, Schwarz T (2006) Extremolytes: natural compounds from extremophiles for versatile applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:623–634. doi:10.1007/s00253-006-0553-9
Lippert K, Galinski EA (1992) Enzyme stabilization by ectoine-type compatible solutes: protection against heating, freezing and drying. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 37:61–65. doi:10.1007/BF00174204
Lo CC, Bonner CA, Xie G, D’Souza M, Jensen RA (2009) Cohesion group approach for evolutionary analysis of aspartokinase, an enzyme that feeds a branched network of many biochemical pathways. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 73:594–651. doi:10.1128/mmbr.00024-09
Louis P, Trüper HG, Galinski EA (1994) Survival of Escherichia coli during drying and storage in the presence of compatible solutes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 41:684–688. doi:10.1007/BF00167285
Magnuson TS, Swenson MW, Paszczynski AJ, Deobald LA, Kerk D, Cummings DE (2010) Proteogenomic and functional analysis of chromate reduction in Acidiphilium cryptum JF-5, an Fe(III)-respiring acidophile. Biometals 23:1129–1138. doi:10.1007/s10534-010-9360-y
Manzanera M, Vilchez S, Tunnacliffe A (2004) High survival and stability rates of Escherichia coli dried in hydroxyectoine. FEMS Microbiol Lett 233:347–352. doi:10.1016/j.femsle.2004.03.005
Mosier AC, Justice NB, Bowen BP, Baran R, Thomas BC, Northen TR, Banfield JF (2013) Metabolites associated with adaptation of microorganisms to an acidophilic, metal-rich environment identified by stable-isotope-enabled metabolomics. M Bio 4:e00484-12. doi:10.1128/mBio.00484-12
Mustakhimov II, Reshetnikov AS, Khmelenina VN, Trotsenko YA (2009) EctR—a novel transcriptional regulator of ectoine biosynthesis genes in the haloalcaliphilic methylotrophic bacterium Methylophaga alcalica. Dokl Biochem Biophys 429:305–308. doi:10.1134/S1607672909060052
Mustakhimov II, Reshetnikov AS, Glukhov AS, Khmelenina VN, Kalyuzhnaya MG, Trotsenko YA (2010) Identification and characterization of EctR1, a new transcriptional regulator of the ectoine biosynthesis genes in the halotolerant methanotroph Methylomicrobium alcaliphilum 20Z. J Bacteriol 192:410–417. doi:10.1128/jb.00553-09
Ono H, Sawada K, Khunajakr N, Tao T, Yamamoto M, Hiramoto M, Shinmyo A, Takano M, Murooka Y (1999) Characterization of biosynthetic enzymes for ectoine as a compatible solute in a moderately halophilic eubacterium, Halomonas elongata. J Bacteriol 181:91–99
Oren A, Larimer F, Richardson P, Lapidus A, Csonka LN (2005) How to be moderately halophilic with broad salt tolerance: clues from the genome of Chromohalobacter salexigens. Extremophiles 9:275–279. doi:10.1007/s00792-005-0442-7
Peters P, Galinski EA, Trüper HG (1990) The biosynthesis of ectoine. FEMS Microbiol Lett 71:157–162. doi:10.1016/0378-1097(90)90049-V
Reed CJ, Lewis H, Trejo E, Winston V, Evilia C (2013) Protein adaptations in archaeal extremophiles. Archaea 2013:373275. doi:10.1155/2013/373275
Rodríguez-Moya J, Argandoña M, Iglesias-Guerra F, Nieto JJ, Vargas C (2013) Temperature- and salinity-decoupled overproduction of hydroxyectoine by Chromohalobacter salexigens. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:1018–1023. doi:10.1128/AEM.02774-12
Salis HM (2011) The ribosome binding site calculator. Meth Enzymol 498:19–42. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-385120-8.00002-4
Salis HM, Mirsky EA, Voigt CA (2009) Automated design of synthetic ribosome binding sites to control protein expression. Nat Biotechnol 27:946–950. doi:10.1038/nbt.1568
Sauer T (1995) Untersuchungen zur Nutzung von Halomonas elongata für die Gewinnung kompatibler Solute. Dissertation, Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn
Sauer T, Galinski EA (1998) Bacterial milking: a novel bioprocess for production of compatible solutes. Biotechnol Bioeng 57:306–313. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0290(19980205)57:3<306::AID-BIT7>3.0.CO;2-L
Schubert T, Maskow T, Benndorf D, Harms H, Breuer U (2007) Continuous synthesis and excretion of the compatible solute ectoine by a transgenic, nonhalophilic bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:3343–3347. doi:10.1128/AEM.02482-06
Seip B, Galinski EA, Kurz M (2011) Natural and engineered hydroxyectoine production based on the Pseudomonas stutzeri ectABCD-ask gene cluster. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:1368–1374. doi:10.1128/AEM.02124-10
Studier FW, Moffatt BA (1986) Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol 189:113–130. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2
Tanne C, Golovina EA, Hoekstra FA, Meffert A, Galinski EA (2014) Glass-forming property of hydroxyectoine is the cause of its superior function as a desiccation protectant. Front Microbiol 5:150. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2014.00150
Voß P (2002) Synthese von kompatiblen Soluten mit ectoinanaloger Struktur und Charakterisierung des protektiven Effektes auf biochemische Modellsysteme und Escherichia coli. Dissertation, Westfälische Wilhelms-Universität Münster, http://d-nb.info/967452503/34
Widderich N, Höppner A, Pittelkow M, Heider J, Smits SHJ, Bremer E (2014) Biochemical properties of ectoine hydroxylases from extremophiles and their wider taxonomic distribution among microorganisms. PLoS ONE 9:e93809. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0093809
Wilkinson SP, Grove A (2006) Ligand-responsive transcriptional regulation by members of the MarR family of winged helix proteins. Curr Issues Mol Biol 8:51–62
Witt E (2011) Nebenreaktionen der Ectoin-Synthase aus Halomonas elongata DSM 2581T und Entwicklung eines salzinduzierten Expressionssystems. Dissertation, Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn. http://hss.ulb.uni-bonn.de/2012/2822/2822.pdf
Witt EMHJ, Davies NW, Galinski EA (2011) Unexpected property of ectoine synthase and its application for synthesis of the engineered compatible solute ADPC. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91:113–122. doi:10.1007/s00253-011-3211-9
Yanisch-Perron C, Vieira J, Messing J (1985) Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene 33:103–119. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Marlene Hecker for skilful technical assistance with the osmotic pressure measurements.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
The authors declare that the experiments comply with the current laws of the country in which they were performed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by L. Huang.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moritz, K.D., Amendt, B., Witt, E.M.H.J. et al. The hydroxyectoine gene cluster of the non-halophilic acidophile Acidiphilium cryptum . Extremophiles 19, 87–99 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-014-0687-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-014-0687-0