Abstract
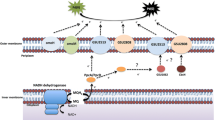
Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans can obtain energy from the oxidation of various reduced inorganic sulfur compounds (RISCs, e.g., sulfur) and ferrous iron in bioleaching so has multiple branched respiratory pathways with a diverse range of electron transporters, especially cytochrome c proteins. A cytochrome c family gene, afe1130, which has never been reported before, was found by screening the whole genome of A. ferrooxidans. Here we report the differential gene transcription, bioinformatics analysis, and molecular modeling of the protein encoded by the afe1130 gene (AFE1130). The differential transcription of the target afe1130 gene versus the reference rrs gene in the A. ferrooxidans, respectively, on the culture conditions of sulfur and ferrous energy sources was performed through quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) with a SYBR green-based assay according to the standard curves method. The qRT-PCR results showed that the afe1130 gene in sulfur culture condition was obviously more transcribed than that in ferrous culture condition. Bioinformatics analysis indicated that the AFE1130 was affiliated to the subclass ID of class I of cytochrome c and located in cytoplasm. Molecular modeling results exhibited that the AFE1130 protein consisted of 5 alpha-helices harboring one heme c group covalently bonded by Cys13 and Cys16 and ligated by His17 and Met62 and owned a big raised hydrophobic surface responsible for attaching to inner cytomembrane. So the AFE1130 in A. ferrooxidans plays a role in the RISCs oxidation in bioleaching in cytoplasm bound to inner membrane.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambler RP (1991) Sequence variability in bacterial cytochromes c. Biochim Biophys Acta 1058(1):42–47
Bobadilla Fazzini RA, Cortés MP, Padilla L, Maturana D, Budinich M, Maass A, Parada P (2013) Stoichiometric modeling of oxidation of reduced inorganic sulfur compounds (Riscs) in Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans. Biotechnol Bioeng 110(8):2242–2251. doi:10.1002/bit.24875
Bruscella P, Appia-Ayme C, Levican G, Ratouchniak J, Jedlicki E, Holmes DS, Bonnefoy V (2007) Differential expression of two bc1 complexes in the strict acidophilic chemolithoautotrophic bacterium Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans suggests a model for their respective roles in iron or sulfur oxidation. Microbiology 153:102–110
Chung YC, Huang C, Tseng CP, Pan JR (2000) Biotreatment of H2S- and NH3-containing waste gases by co-immobilized cells biofilter. Chemosphere 41(3):329–336
Colmer AR, Hinkle ME (1947) The role of microorganisms in acid mine drainage: a preliminary report. Science 106(2751):253–256
Cai M, Bradford EG, Timkovich R (1992) Investigation of the solution conformation of cytochrome c-551 from Pseudomonas stutzeri. Biochemistry 31(36):8603–8612
Deng TLLM, Wang MH, Chen Y-W, Belzile N (2000) Investigations of accelerating parameters for the biooxidation of low-grade refractory gold ore. Miner Eng 13:11
Detlefsen DJ, Thanabal V, Pecoraro VL, Wagner G (1991) Solution structure of Fe(II) cytochrome c551 from Pseudomonas aeruginosa as determined by two-dimensional 1H NMR. Biochemistry 30(37):9040–9046
Larionov A, Krause A, Miller W (2005) A standard curve based method for relative real time PCR data processing. BMC Bioinformatics 6:62
Liu Y, Ji J, Yu R, Qiu G (2012) Expression, purification and molecular modeling of another HdrC from Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans which binds only one [4fe-4s] cluster. Curr Microbiol 65(4):416–423. doi:12.1007/s00284-012-0173-9
Liu Y, Guo S, Yu R, Ji J, Qiu G (2013) HdrC2 from Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans owns two iron-sulfur binding motifs but binds only one variable cluster between [4Fe-4S] and [3Fe-4S]. Curr Microbiol 66(1):88–95. doi:10.1007/s00284-012-0244-y
Liu Y, Qiu G, Wang H, Jiang Y, Zhang C, Xia L (2008) Full structure building and docking studies of NifS from extremophile Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Trans Nonferr Met Soc 18(4):995–1002
Mangold S, Valdés J, Holmes DS, Dopson M (2011) Sulfur metabolism in the extreme acidophile Acidithiobacillus caldus. Front Microbiol 2:17. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2011.00017
Moffat AS (1994) Microbial mining boosts the environment, bottom line. Science 264(5160):778–779. doi:10.1126/science.264.5160.778
Ossaa DMH, Oliveira RR, Murakami MT, Vicentini R, Costa-Filho AJ, Alexandrino F, Ottoboni LMM, Garcia O Jr (2011) Expression, purification and spectroscopic analysis of an HdrC: an iron–sulfur cluster-containing protein from Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Process Biochem 46:1335–1341
Quatrini R, Appia-Ayme C, Denis Y, Jedlicki E, Holmes DS, Bonnefoy V (2009) Extending the models for iron and sulfur oxidation in the extreme acidophile Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. BMC Genomics 10:394
Quatrini R, Appia-Ayme C, Denis Y, Ratouchniak J, Veloso F, Valdes J, Lefimil C, Silver S, Roberto F, Orellana O, Denizot F, Jedlicki E, Holmes DS, Bonnefoy V (2006) Insights into the iron and sulfur energetic metabolism of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans by microarray transcriptome profiling. Hydrometallurgy 83:263–272
Salemme FR (1977) Structure and function of cytochromes c. Annu Rev Biochem 46:299–329
Travaglini-Allocatelli C, Gianni S, Dubey VK, Borgia A, Di Matteo A, Bonivento D, Cutruzzolà F, Bren KL, Brunori M (2005) An obligatory intermediate in the folding pathway of cytochrome c552 from Hydrogenobacter thermophilus. J Biol Chem 280(27):25729–25734
Valdes J, Pedroso I, Quatrini R, Dodson RJ, Tettelin H, Blake R 2nd, Eisen JA, Holmes DS (2008) Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans metabolism: from genome sequence to industrial applications. BMC Genomics 9:597
Wakai S, Kikumoto M, Kanao T, Kamimura K (2004) Involvement of sulfide:quinone oxidoreductase in sulfur oxidation of an acidophilic iron-oxidizing bacterium, Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans NASF-1. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 68(12):2519–2528
Yarzábal A, Appia-Ayme C, Ratouchniak J, Bonnefoy V (2004) Regulation of the expression of the Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans rus operon encoding two cytochromes c, a cytochrome oxidase and rusticyanin. Microbiology 150(Pt 7):2113–2123
Yarzábal A, Duquesne K, Bonnefoy V (2003) Rusticyanin gene expression of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans ATCC 33020 in sulfur- and in ferrous iron media. Hydrometallurgy 71(1–2):107–114
Zheng C, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Wu A, Xia L, Zeng J, Liu J, Qiu G (2009) Characterization and reconstitute of a [Fe4S4] adenosine 5′-phosphosulfate reductase from Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Curr Microbiol 58(6):586–592. doi:10.1007/s00284-009-9375-1
Zheng C, Li Y, Nie L, Qian L, Cai L, Liu J (2012) Transcriptional and functional studies of a Cd(II)/Pb(II)-responsive transcriptional regulator(CmtR) from Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans ATCC 23270. Curr Microbiol 65(2):117–121. doi:10.1007/s00284-012-0117-4
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of P. R. China (51274268 and 50904080), the National Basic Research Program of P. R. China (2010CB630900), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2013M540643).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Guo, S., Yu, R. et al. A New Cytoplasmic Monoheme Cytochrome c from Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans Involved in Sulfur Oxidation. Curr Microbiol 68, 285–292 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-013-0473-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-013-0473-8