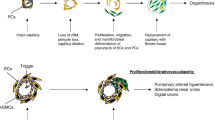
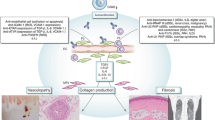
Abstract
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a devastating chronic autoimmune connective tissue disease characterized by vasculopathy, autoimmunity with inflammation, and progressive fibrogenesis. The current paradigm of the pathogenesis of SSc is that of an unknown initial trigger, leading to a complex interaction of immune cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts, producing cytokines, growth and angiogenic factors, and resulting in uncontrolled and persistent tissue fibrogenesis by an altered mesenchymal cell compartment. Animal models are of utmost importance to investigate the different steps in the pathogenesis. This review will elaborate on recent findings in established and more recently developed animal models, presenting data on compounds that are in or ready to be translated into clinical trials, or provide interesting new findings in the understanding of the pathophysiology of SSc. We focus on recent findings concerning the vessel—extracellular matrix interaction, the initial triggering aggressor, the concept of autoimmunity and inflammatory changes, the effector cells and their origins, and the complex interaction of the different signaling pathways in fibrogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gabrielli A, Avvedimento EV, Krieg T (2009) Scleroderma. N Engl J Med 360:1989–2003
Wynn TA (2008) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of fibrosis. J Pathol 214:199–210
Ishikawa O, Ishikawa H (1992) Macrophage infiltration in the skin of patients with systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol 19:1202–1206
Kraling BM, Maul GG, Jimenez SA (1995) Mononuclear cellular infiltrates in clinically involved skin from patients with systemic sclerosis of recent onset predominantly consist of monocytes/macrophages. Pathobiology 63:48–56
Liakouli V, Cipriani P, Marrelli A, Alvaro S, Ruscitti P, Giacomelli R (2011) Angiogenic cytokines and growth factors in systemic sclerosis. Autoimmun Rev 10:590–594
Eferl R, Hasselblatt P, Rath M, Popper H, Zenz R, Komnenovic V, Idarraga MH, Kenner L, Wagner EF (2008) Development of pulmonary fibrosis through a pathway involving the transcription factor Fra-2/AP-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:10525–10530
Maurer B, Busch N, Jungel A, Pileckyte M, Gay RE, Michel BA, Schett G, Gay S, Distler J, Distler O (2009) Transcription factor fos-related antigen-2 induces progressive peripheral vasculopathy in mice closely resembling human systemic sclerosis. Circulation 120:2367–2376
Maurer B, Reich N, Juengel A, Kriegsmann J, Gay RE, Schett G, Michel BA, Gay S, Distler JH, Distler O (2012) Fra-2 transgenic mice as a novel model of pulmonary hypertension associated with systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 71(8):1382–7
Venalis P, Kumanovics G, Schulze-Koops H, Distler A, Dees C, Zerr P, Palumbo-Zerr K, Czirjak L, Mackevic Z, Lundberg IE, Distler O, Schett G, Distler JH (2015) Cardiomyopathy in murine models of systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 67:508–516
Kramer M, Dees C, Huang J, Schlottmann I, Palumbo-Zerr K, Zerr P, Gelse K, Beyer C, Distler A, Marquez VE, Distler O, Schett G, Distler JH (2013) Inhibition of H3K27 histone trimethylation activates fibroblasts and induces fibrosis. Ann Rheum Dis 72:614–620
Manetti M, Allanore Y, Revillod L, Fatini C, Guiducci S, Cuomo G, Bonino C, Riccieri V, Bazzichi L, Liakouli V, Cipriani P, Giacomelli R, Abbate R, Bombardieri S, Valesini G, Montecucco C, Valentini G, Ibba-Manneschi L, Matucci-Cerinic M (2011) A genetic variation located in the promoter region of the UPAR (CD87) gene is associated with the vascular complications of systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 63:247–256
Dewerchin M, Nuffelen AV, Wallays G, Bouche A, Moons L, Carmeliet P, Mulligan RC, Collen D (1996) Generation and characterization of urokinase receptor-deficient mice. J Clin Invest 97:870–878
Manetti M, Rosa I, Milia AF, Guiducci S, Carmeliet P, Ibba-Manneschi L, Matucci-Cerinic M (2014) Inactivation of urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) gene induces dermal and pulmonary fibrosis and peripheral microvasculopathy in mice: a new model of experimental scleroderma? Ann Rheum Dis 73:1700–1709
Ben-David Y, Giddens EB, Bernstein A (1990) Identification and mapping of a common proviral integration site Fli-1 in erythroleukemia cells induced by Friend murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 87:1332–1336
Czuwara-Ladykowska J, Shirasaki F, Jackers P, Watson DK, Trojanowska M (2001) Fli-1 inhibits collagen type I production in dermal fibroblasts via an Sp1-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem 276:20839–20848
Kubo M, Czuwara-Ladykowska J, Moussa O, Markiewicz M, Smith E, Silver RM, Jablonska S, Blaszczyk M, Watson DK, Trojanowska M (2003) Persistent down-regulation of Fli1, a suppressor of collagen transcription, in fibrotic scleroderma skin. Am J Pathol 163:571–581
Wang Y, Fan PS, Kahaleh B (2006) Association between enhanced type I collagen expression and epigenetic repression of the FLI1 gene in scleroderma fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum 54:2271–2279
Asano Y, Czuwara J, Trojanowska M (2007) Transforming growth factor-beta regulates DNA binding activity of transcription factor Fli1 by p300/CREB-binding protein-associated factor-dependent acetylation. J Biol Chem 282:34672–34683
Spyropoulos DD, Pharr PN, Lavenburg KR, Jackers P, Papas TS, Ogawa M, Watson DK (2000) Hemorrhage, impaired hematopoiesis, and lethality in mouse embryos carrying a targeted disruption of the Fli1 transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol 20:5643–5652
Rao VN, Ohno T, Prasad DD, Bhattacharya G, Reddy ES (1993) Analysis of the DNA-binding and transcriptional activation functions of human Fli-1 protein. Oncogene 8:2167–2173
Asano Y, Markiewicz M, Kubo M, Szalai G, Watson DK, Trojanowska M (2009) Transcription factor Fli1 regulates collagen fibrillogenesis in mouse skin. Mol Cell Biol 29:425–434
Nakerakanti SS, Kapanadze B, Yamasaki M, Markiewicz M, Trojanowska M (2006) Fli1 and Ets1 have distinct roles in connective tissue growth factor/CCN2 gene regulation and induction of the profibrotic gene program. J Biol Chem 281:25259–25269
Asano Y, Stawski L, Hant F, Highland K, Silver R, Szalai G, Watson DK, Trojanowska M (2010) Endothelial Fli1 deficiency impairs vascular homeostasis: a role in scleroderma vasculopathy. Am J Pathol 176:1983–1998
Allanore Y, Borderie D, Lemarechal H, Ekindjian OG, Kahan A (2004) Nifedipine decreases sVCAM-1 concentrations and oxidative stress in systemic sclerosis but does not affect the concentrations of vascular endothelial growth factor or its soluble receptor 1. Arthritis Res Ther 6:R309–R314
Distler O, Distler JH, Scheid A, Acker T, Hirth A, Rethage J, Michel BA, Gay RE, Muller-Ladner U, Matucci-Cerinic M, Plate KH, Gassmann M, Gay S (2004) Uncontrolled expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors leads to insufficient skin angiogenesis in patients with systemic sclerosis. Circ Res 95:109–116
Maurer B, Distler A, Suliman YA, Gay RE, Michel BA, Gay S, Distler JH, Distler O (2014) Vascular endothelial growth factor aggravates fibrosis and vasculopathy in experimental models of systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 73:1880–1887
Sambo P, Jannino L, Candela M, Salvi A, Donini M, Dusi S, Luchetti MM, Gabrielli A (1999) Monocytes of patients with systemic sclerosis (scleroderma spontaneously release in vitro increased amounts of superoxide anion. J Invest Dermatol 112:78–84
Herrick AL, Matucci CM (2001) The emerging problem of oxidative stress and the role of antioxidants in systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 19:4–8
Servettaz A, Goulvestre C, Kavian N, Nicco C, Guilpain P, Chereau C, Vuiblet V, Guillevin L, Mouthon L, Weill B, Batteux F (2009) Selective oxidation of DNA topoisomerase 1 induces systemic sclerosis in the mouse. J Immunol 182:5855–5864
Bagnato G, Bitto A, Pizzino G, Irrera N, Sangari D, Cinquegrani M, Roberts WN, Matucci Cerinic M, Squadrito F, Altavilla D, Bagnato G, Saitta A (2013) Simvastatin attenuates the development of pulmonary and cutaneous fibrosis in a murine model of systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 52:1377–1386
Marut WK, Kavian N, Servettaz A, Nicco C, Ba LA, Doering M, Chereau C, Jacob C, Weill B, Batteux F (2012) The organotelluride catalyst (PHTE)(2)NQ prevents HOCl-induced systemic sclerosis in mouse. J Invest Dermatol 132:1125–1132
Kavian N, Marut W, Servettaz A, Nicco C, Chereau C, Lemarechal H, Borderie D, Dupin N, Weill B, Batteux F (2012) Reactive oxygen species-mediated killing of activated fibroblasts by arsenic trioxide ameliorates fibrosis in a murine model of systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 64:3430–3440
van Bon L, Cossu M, Radstake TR (2011) An update on an immune system that goes awry in systemic sclerosis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 23:505–510
Horikawa M, Hasegawa M, Komura K, Hayakawa I, Yanaba K, Matsushita T, Takehara K, Sato S (2005) Abnormal natural killer cell function in systemic sclerosis: altered cytokine production and defective killing activity. J Invest Dermatol 125:731–737
Sakkas LI, Xu B, Artlett CM, Lu S, Jimenez SA, Platsoucas CD (2002) Oligoclonal T cell expansion in the skin of patients with systemic sclerosis. J Immunol 168:3649–3659
van Bon L, Popa C, Huijbens R, Vonk M, York M, Simms R, Hesselstrand R, Wuttge DM, Lafyatis R, Radstake TR (2010) Distinct evolution of TLR-mediated dendritic cell cytokine secretion in patients with limited and diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 69:1539–1547
Bhattacharyya S, Kelley K, Melichian DS, Tamaki Z, Fang F, Su Y, Feng G, Pope RM, Budinger GR, Mutlu GM, Lafyatis R, Radstake T, Feghali-Bostwick C, Varga J (2013) Toll-like receptor 4 signaling augments transforming growth factor-beta responses: a novel mechanism for maintaining and amplifying fibrosis in scleroderma. Am J Pathol 182:192–205
Takahashi T, Asano Y, Ichimura Y, Toyama T, Taniguchi T, Noda S, Akamata K, Tada Y, Sugaya M, Kadono T, Sato S (2015) Amelioration of tissue fibrosis by toll-like receptor 4 knockout in murine models of systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 67:254–265
Daoussis D, Liossis SN, Yiannopoulos G, Andonopoulos AP (2011) B-cell depletion therapy in systemic sclerosis: experimental rationale and update on clinical evidence. Int J Rheum 2011:214013
Whitfield ML, Finlay DR, Murray JI, Troyanskaya OG, Chi JT, Pergamenschikov A, McCalmont TH, Brown PO, Botstein D, Connolly MK (2003) Systemic and cell type-specific gene expression patterns in scleroderma skin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:12319–12324
Francois A, Gombault A, Villeret B, Alsaleh G, Fanny M, Gasse P, Adam SM, Crestani B, Sibilia J, Schneider P, Bahram S, Quesniaux V, Ryffel B, Wachsmann D, Gottenberg JE, Couillin I (2015) B cell activating factor is central to bleomycin- and IL-17-mediated experimental pulmonary fibrosis. J Autoimmun 56:1–11
Mavalia C, Scaletti C, Romagnani P, Carossino AM, Pignone A, Emmi L, Pupilli C, Pizzolo G, Maggi E, Romagnani S (1997) Type 2 helper T-cell predominance and high CD30 expression in systemic sclerosis. Am J Pathol 151:1751–1758
Avouac J, Elhai M, Tomcik M, Ruiz B, Friese M, Piedavent M, Colonna M, Bernhardt G, Kahan A, Chiocchia G, Distler JH, Allanore Y (2013) Critical role of the adhesion receptor DNAX accessory molecule-1 (DNAM-1) in the development of inflammation-driven dermal fibrosis in a mouse model of systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 72:1089–1098
Perez-Frias A, Gonzalez-Tajuelo R, Nunez-Andrade N, Tejedor R, Garcia-Blanco MJ, Vicente-Rabaneda E, Castaneda S, Gamallo C, Silvan J, Esteban-Villafruela A, Cubero-Rueda L, Garcia-Garcia C, Munoz-Calleja C, Garcia-Diez A, Urzainqui A (2014) Development of an autoimmune syndrome affecting the skin and internal organs in P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 leukocyte receptor-deficient mice. Arthritis Rheum 66:3178–3189
Kalluri R, Neilson EG (2003) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its implications for fibrosis. J Clin Invest 112:1776–1784
Bogatkevich GS (2015) Editorial: fate of fat tissue adipocytes: do they transform into myofibroblasts in scleroderma? Arthritis Rheum 67:860–861
Dees C, Tomcik M, Zerr P, Akhmetshina A, Horn A, Palumbo K, Beyer C, Zwerina J, Distler O, Schett G, Distler JH (2011) Notch signalling regulates fibroblast activation and collagen release in systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 70:1304–1310
Dees C, Zerr P, Tomcik M, Beyer C, Horn A, Akhmetshina A, Palumbo K, Reich N, Zwerina J, Sticherling M, Mattson MP, Distler O, Schett G, Distler JH (2011) Inhibition of Notch signaling prevents experimental fibrosis and induces regression of established fibrosis. Arthritis Rheum 63:1396–1404
Piera-Velazquez S, Li Z, Jimenez SA (2011) Role of endothelial-mesenchymal transition (EndoMT) in the pathogenesis of fibrotic disorders. Am J Pathol 179:1074–1080
Rajkumar VS, Howell K, Csiszar K, Denton CP, Black CM, Abraham DJ (2005) Shared expression of phenotypic markers in systemic sclerosis indicates a convergence of pericytes and fibroblasts to a myofibroblast lineage in fibrosis. Arthritis Res Ther 7:R1113–R1123
Bucala R, Spiegel LA, Chesney J, Hogan M, Cerami A (1994) Circulating fibrocytes define a new leukocyte subpopulation that mediates tissue repair. Mol Med 1:71–81
Liu S, Herault Y, Pavlovic G, Leask A (2014) Skin progenitor cells contribute to bleomycin-induced skin fibrosis. Arthritis Rheum 66:707–713
Marangoni RG, Korman BD, Wei J, Wood TA, Graham LV, Whitfield ML, Scherer PE, Tourtellotte WG, Varga J (2015) Myofibroblasts in murine cutaneous fibrosis originate from adiponectin-positive intradermal progenitors. Arthritis Rheum 67:1062–1073
Akhmetshina A, Palumbo K, Dees C, Bergmann C, Venalis P, Zerr P, Horn A, Kireva T, Beyer C, Zwerina J, Schneider H, Sadowski A, Riener MO, MacDougald OA, Distler O, Schett G, Distler JH (2012) Activation of canonical Wnt signalling is required for TGF-beta-mediated fibrosis. Nat Commun 3:735
Horn A, Kireva T, Palumbo-Zerr K, Dees C, Tomcik M, Cordazzo C, Zerr P, Akhmetshina A, Ruat M, Distler O, Beyer C, Schett G, Distler JH (2012) Inhibition of hedgehog signalling prevents experimental fibrosis and induces regression of established fibrosis. Ann Rheum Dis 71(5):785–789
Clevers H, Nusse R (2012) Wnt/beta-Catenin signaling and disease. Cell 149:1192–1205
Beyer C, Schramm A, Akhmetshina A, Dees C, Kireva T, Gelse K, Sonnylal S, de Crombrugghe B, Taketo MM, Distler O, Schett G, Distler JH (2012) Beta-catenin is a central mediator of pro-fibrotic Wnt signaling in systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 71:761–767
Lam AP, Flozak AS, Russell S, Wei J, Jain M, Mutlu GM, Budinger GR, Feghali-Bostwick CA, Varga J, Gottardi CJ (2011) Nuclear beta-catenin is increased in systemic sclerosis pulmonary fibrosis and promotes lung fibroblast migration and proliferation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 45:915–922
Beyer C, Reichert H, Akan H, Mallano T, Schramm A, Dees C, Palumbo-Zerr K, Lin NY, Distler A, Gelse K, Varga J, Distler O, Schett G, Distler JH (2013) Blockade of canonical Wnt signalling ameliorates experimental dermal fibrosis. Ann Rheum Dis 72:1255–1258
Bergmann C, Akhmetshina A, Dees C, Palumbo K, Zerr P, Beyer C, Zwerina J, Distler O, Schett G, Distler JH (2011) Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta induces dermal fibrosis by activation of the canonical Wnt pathway. Ann Rheum Dis 70:2191–2198
Henderson WR Jr, Chi EY, Ye X, Nguyen C, Tien YT, Zhou B, Borok Z, Knight DA, Kahn M (2010) Inhibition of Wnt/beta-catenin/CREB binding protein (CBP) signaling reverses pulmonary fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:14309–14314
Beyer C, Dees C, Distler JH (2013) Morphogen pathways as molecular targets for the treatment of fibrosis in systemic sclerosis. Arch Dermatol Res 305:1–8
De Langhe E, Aznar-Lopez C, De Vooght V, Vanoirbeek JA, Luyten FP, Lories RJ (2014) Secreted frizzled related proteins inhibit fibrosis in vitro but appear redundant in vivo. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 7:14
Wei J, Melichian D, Komura K, Hinchcliff M, Lam AP, Lafyatis R, Gottardi CJ, MacDougald OA, Varga J (2011) Canonical Wnt signaling induces skin fibrosis and subcutaneous lipoatrophy: a novel mouse model for scleroderma? Arthritis Rheum 63:1707–1717
Distler A, Deloch L, Huang J, Dees C, Lin NY, Palumbo-Zerr K, Beyer C, Weidemann A, Distler O, Schett G, Distler JH (2013) Inactivation of tankyrases reduces experimental fibrosis by inhibiting canonical Wnt signalling. Ann Rheum Dis 72:1575–1580
Dees C, Schlottmann I, Funke R, Distler A, Palumbo-Zerr K, Zerr P, Lin NY, Beyer C, Distler O, Schett G, Distler JH (2014) The Wnt antagonists DKK1 and SFRP1 are downregulated by promoter hypermethylation in systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 73:1232–1239
Distler A, Ziemer C, Beyer C, Lin NY, Chen CW, Palumbo-Zerr K, Dees C, Weidemann A, Distler O, Schett G, Distler JH (2014) Inactivation of evenness interrupted (EVI) reduces experimental fibrosis by combined inhibition of canonical and non-canonical Wnt signalling. Ann Rheum Dis 73:624–627
Vorstenbosch J, Al-Ajmi H, Winocour S, Trzeciak A, Lessard L, Philip A (2013) CD109 overexpression ameliorates skin fibrosis in a mouse model of bleomycin-induced scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum 65:1378–1383
Rubin LJ, Galie N, Grimminger F, Grunig E, Humbert M, Jing ZC, Keogh A, Langleben D, Fritsch A, Menezes F, Davie N, Ghofrani HA (2015) Riociguat for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension: a long-term extension study (PATENT-2). Eur Respir J 45:1303–1313
Ghofrani HA, Galie N, Grimminger F, Grunig E, Humbert M, Jing ZC, Keogh AM, Langleben D, Kilama MO, Fritsch A, Neuser D, Rubin LJ, Group P-S (2013) Riociguat for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med 369:330–340
Beyer C, Zenzmaier C, Palumbo-Zerr K, Mancuso R, Distler A, Dees C, Zerr P, Huang J, Maier C, Pachowsky ML, Friebe A, Sandner P, Distler O, Schett G, Berger P, Distler JH (2014) Stimulation of the soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) inhibits fibrosis by blocking non-canonical TGFbeta signalling. Ann Rheum Dis. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204508
Dees C, Beyer C, Distler A, Soare A, Zhang Y, Palumbo-Zerr K, Distler O, Schett G, Sandner P, Distler JH (2015) Stimulators of soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) inhibit experimental skin fibrosis of different aetiologies. Ann Rheum Dis. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206809
Huang J, Beyer C, Palumbo-Zerr K, Zhang Y, Ramming A, Distler A, Gelse K, Distler O, Schett G, Wollin L, Distler JH (2015) Nintedanib inhibits fibroblast activation and ameliorates fibrosis in preclinical models of systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-207109
Tomcik M, Palumbo-Zerr K, Zerr P, Sumova B, Avouac J, Dees C, Distler A, Becvar R, Distler O, Schett G, Senolt L, Distler JH (2015) Tribbles homologue 3 stimulates canonical TGF-beta signalling to regulate fibroblast activation and tissue fibrosis. Ann Rheum Dis. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206234
Tomcik M, Zerr P, Pitkowski J, Palumbo-Zerr K, Avouac J, Distler O, Becvar R, Senolt L, Schett G, Distler JH (2014) Heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) inhibition targets canonical TGF-beta signalling to prevent fibrosis. Ann Rheum Dis 73:1215–1222
Dees C, Akhmetshina A, Zerr P, Reich N, Palumbo K, Horn A, Jungel A, Beyer C, Kronke G, Zwerina J, Reiter R, Alenina N, Maroteaux L, Gay S, Schett G, Distler O, Distler JH (2011) Platelet-derived serotonin links vascular disease and tissue fibrosis. J Exp Med 208:961–972
Marquart S, Zerr P, Akhmetshina A, Palumbo K, Reich N, Tomcik M, Horn A, Dees C, Engel M, Zwerina J, Distler O, Schett G, Distler JH (2010) Inactivation of the cannabinoid receptor CB1 prevents leukocyte infiltration and experimental fibrosis. Arthritis Rheum 62:3467–3476
Daniels CE, Wilkes MC, Edens M, Kottom TJ, Murphy SJ, Limper AH, Leof EB (2004) Imatinib mesylate inhibits the profibrogenic activity of TGF-beta and prevents bleomycin-mediated lung fibrosis. J Clin Invest 114:1308–1316
Dees C, Tomcik M, Palumbo-Zerr K, Distler A, Beyer C, Lang V, Horn A, Zerr P, Zwerina J, Gelse K, Distler O, Schett G, Distler JH (2012) JAK-2 as a novel mediator of the profibrotic effects of transforming growth factor beta in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 64:3006–3015
Reich N, Tomcik M, Zerr P, Lang V, Dees C, Avouac J, Palumbo K, Horn A, Akhmetshina A, Beyer C, Xie W, Bennett BL, Distler O, Schett G, Distler JH (2012) Jun N-terminal kinase as a potential molecular target for prevention and treatment of dermal fibrosis. Ann Rheum Dis 71:737–745
Seibold JR, Denton CP, Furst DE, Guillevin L, Rubin LJ, Wells A, Matucci Cerinic M, Riemekasten G, Emery P, Chadha-Boreham H, Charef P, Roux S, Black CM (2010) Randomized, prospective, placebo-controlled trial of bosentan in interstitial lung disease secondary to systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 62:2101–2108
Daniels CE, Lasky JA, Limper AH, Mieras K, Gabor E, Schroeder DR (2010) Imatinib treatment for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: randomized placebo-controlled trial results. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 181:604–610
Maurer B, Distler A, Dees C, Khan K, Denton CP, Abraham D, Gay RE, Michel BA, Gay S, Hw Distler J, Distler O (2013) Levels of target activation predict antifibrotic responses to tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Ann Rheum Dis 72:2039–2046
Distler A, Lang V, Del Vecchio T, Huang J, Zhang Y, Beyer C, Lin NY, Palumbo-Zerr K, Distler O, Schett G, Distler JH (2014) Combined inhibition of morphogen pathways demonstrates additive antifibrotic effects and improved tolerability. Ann Rheum Dis 73:1264–1268
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is a contribution to the Special Issue on Immunopathology of Systemic Sclerosis - Guest Editors: Jacob M. van Laar and John Varga
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Langhe, E., Lories, R. Fibrogenesis, novel lessons from animal models. Semin Immunopathol 37, 565–574 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-015-0510-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-015-0510-8