Abstract
Purpose
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) resistance is the main type of drug resistance in lung cancer patients with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations, but its underlying mechanism remains unclear. The purpose of this work was to investigate the mechanism by which PARP1 regulates EGFR-TKI resistance to identify potential targets for combating drug resistance.
Methods
The GEO databases, TCGA databases, western blot and qPCR studies were used to investigate the expression of PARP1 in lung cancer cells and tissues and its correlation with the prognosis of lung cancer. The expression of PARP1 in lung cancer TKI resistant cell PC9-ER and TKI sensitive cell PC9 was analyzed by qPCR and western blot. After knocking down of PARP1, CCK-8 assays, colony formation, flow cytometry were used to investigate its impact on erlotinib sensitivity, cell survival, cell cycle, and apoptosis. RNA-seq was used to investigate the mechanism by which PARP1 participates in EGFR-TKI resistance, and the results were validated in vitro and in vivo studies.
Results
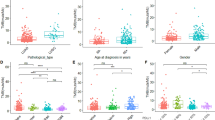
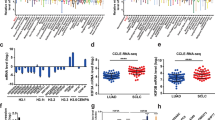
PARP1 was highly expressed in both lung cancer tissues and cells. Subsequently, increased PARP1 expression was observed in PC9-ER compared with its parental cell line. Knockdown of PARP1 increased erlotinib sensitivity, promoted cell apoptosis, and suppressed cell growth. RNA-seq and previous studies have shown that the PI3K/AKT/mTOR/P70S6K pathway is involved in PARP1-mediated TKI resistance, and these results were confirmed by Western blot in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusion
PARP1 may serve as a potential therapeutic target for reversing EGFR-TKI resistance in NSCLC via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR/P70S6K pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of Incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: Cancer J 71(3):209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Blandin Knight S, Crosbie PA, Balata H, Chudziak J, Hussell T, Dive C (2017) Progress and prospects of early detection in lung cancer. Open Biol 7(9):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsob.170070
Bracht JWP, Karachaliou N, Berenguer J, Pedraz-Valdunciel C, Filipska M, Codony-Servat C, Codony-Servat J, Rosell R (2019) Osimertinib and pterostilbene in EGFR-mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Int J Biol Sci 15(12):2607–2614. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.32889
Oxnard GR, Hu Y, Mileham KF, Husain H, Costa DB, Tracy P, Feeney N, Sholl LM, Dahlberg SE, Redig AJ, Kwiatkowski DJ, Rabin MS, Paweletz CP, Thress KS, Jänne PA (2018) Assessment of resistance mechanisms and clinical implications in patients with EGFR T790M-positive lung cancer and acquired resistance to osimertinib. JAMA Oncol 4(11):1527–1534. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.2969
Oser MG, Niederst MJ, Sequist LV, Engelman JA (2015) Transformation from non-small-cell lung cancer to small-cell lung cancer: molecular drivers and cells of origin. Lancet Oncol 16(4):e165-172. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(14)71180-5
Lee S, Rauch J, Kolch W (2020) Targeting MAPK signaling in cancer: mechanisms of drug resistance and sensitivity. Int J Mol Sci 21(3):1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031102
Wang L, Dong X, Ren Y, Luo J, Liu P, Su D, Yang X (2018) Targeting EHMT2 reverses EGFR-TKI resistance in NSCLC by epigenetically regulating the PTEN/AKT signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis 9(2):129. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-017-0120-6
Chen B, Lai J, Dai D, Chen R, Liao N, Gao G, Tang H (2020) PARPBP is a prognostic marker and confers anthracycline resistance to breast cancer. Ther Adv Med Oncol 12:1758835920974212. https://doi.org/10.1177/1758835920974212
Ding L, Chen X, Xu X, Qian Y, Liang G, Yao F, Yao Z, Wu H, Zhang J, He Q, Yang B (2019) PARP1 suppresses the transcription of PD-L1 by poly(ADP-ribosyl)ating STAT3. Cancer Immunol Res 7(1):136–149. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.Cir-18-0071
Dellomo AJ, Abbotts R, Eberly CL, Karbowski M, Baer MR, Kingsbury TJ, Rassool FV (2022) PARP1 PARylates and stabilizes STAT5 in FLT3-ITD acute myeloid leukemia and other STAT5-activated cancers. Transl Oncol 15(1):101283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranon.2021.101283
Fang Z, Gong C, Ye Z, Wang W, Zhu M, Hu Y, Liu Z, Zhou W, Li H (2022) TOPBP1 regulates resistance of gastric cancer to oxaliplatin by promoting transcription of PARP1. DNA Repair 111:103278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dnarep.2022.103278
de Souza França PD, Guru N, Kostolansky AR, Mauguen A, Pirovano G, Kossatz S, Roberts S, Abrahão M, Patel SG, Park KJ, Reiner T, Jewell E (2021) PARP1: a potential molecular marker to identify cancer during colposcopy procedures. J Nucl Med 62(7):941–948. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.120.253575
Montaldi AP, Lima SCG, Godoy P, Xavier DJ, Sakamoto-Hojo ET (2020) PARP-1 inhibition sensitizes temozolomide-treated glioblastoma cell lines and decreases drug resistance independent of MGMT activity and PTEN proficiency. Oncol Rep 44(5):2275–2287. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2020.7756
Wang Q, Xiong J, Qiu D, Zhao X, Yan D, Xu W, Wang Z, Chen Q, Panday S, Li A, Wang S, Zhou J (2017) Inhibition of PARP1 activity enhances chemotherapeutic efficiency in cisplatin-resistant gastric cancer cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 92:164–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2017.08.001
Zhang Z, Lian X, Xie W, Quan J, Liao M, Wu Y, Yang ZZ, Wang G (2020) Role of PARP1-mediated autophagy in EGFR-TKI resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Rep 10(1):20924. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-77908-z
Erguven M, Bilir A, Yazihan N, Ermis E, Sabanci A, Aktas E, Aras Y, Alpman V (2011) Decreased therapeutic effects of noscapine combined with imatinib mesylate on human glioblastoma in vitro and the effect of midkine. Cancer Cell Int 11(1):18. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2867-11-18
Tong Y, Wang R, Liu X, Tian M, Wang Y, Cui Y, Zou W, Zhao Y (2021) Zuojin pill ameliorates chronic atrophic gastritis induced by MNNG through TGF-β1/PI3K/Akt axis. J Ethnopharmacol 271:113893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2021.113893
Jeong KY, Park MH (2021) The significance of targeting poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 in pancreatic cancer for providing a new therapeutic paradigm. Int J Mol Sci 22(7):3509. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073509
Engbrecht M, Mangerich A (2020) The nucleolus and PARP1 in cancer biology. Cancers (Basel) 12(7):1813. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12071813
Yamashita S, Tanaka M, Ida C, Kouyama K, Nakae S, Matsuki T, Tsuda M, Shirai T, Kamemura K, Nishi Y, Moss J, Miwa M (2022) Physiological levels of poly(ADP-ribose) during the cell cycle regulate HeLa cell proliferation. Exp Cell Res 417(1):113163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2022.113163
Choi EB, Yang AY, Kim SC, Lee J, Choi JK, Choi C, Kim MY (2016) PARP1 enhances lung adenocarcinoma metastasis by novel mechanisms independent of DNA repair. Oncogene 35(35):4569–4579. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.3
Marcar L, Bardhan K, Gheorghiu L, Dinkelborg P, Pfäffle H, Liu Q, Wang M, Piotrowska Z, Sequist LV, Borgmann K, Settleman JE, Engelman JA, Hata AN, Willers H (2019) Acquired resistance of EGFR-mutated lung cancer to tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment promotes PARP inhibitor sensitivity. Cell Rep 27(12):3422-3432.e3424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.05.058
Zhang H, Wang Y, Wu H, Zhou S, Li S, Meng X, Tao R, Yu J (2022) Olaparib combined with dacomitinib in osimertinib-resistant brain and leptomeningeal metastases from non-small cell lung cancer: a case report and systematic review. Front Oncol 12:877279. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.877279
Yang J, Nie J, Ma X, Wei Y, Peng Y, Wei X (2019) Targeting PI3K in cancer: mechanisms and advances in clinical trials. Mol Cancer 18(1):26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-0954-x
Wang L, Zhou Y, Jiang L, Lu L, Dai T, Li A, Chen Y, Zhang L (2021) CircWAC induces chemotherapeutic resistance in triple-negative breast cancer by targeting miR-142, upregulating WWP1 and activating the PI3K/AKT pathway. Mol Cancer 20(1):43. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-021-01332-8
Wang Z, Jia L, Sun Y, Li C, Zhang L, Wang X, Chen H (2021) CORO1C is associated with poor prognosis and promotes metastasis through PI3K/AKT pathway in colorectal cancer. Front Mol Biosci 8:682594. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2021.682594
Wu MD, Zhang YY, Yi SY, Sun BB, Lan J, Jiang HM, Hao GP (2022) Acetylshikonin induces autophagy-dependent apoptosis through the key LKB1-AMPK and PI3K/Akt-regulated mTOR signalling pathways in HL-60 cells. J Cell Mol Med 26(5):1606–1620. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.17202
Verret B, Cortes J, Bachelot T, Andre F, Arnedos M (2019) Efficacy of PI3K inhibitors in advanced breast cancer. Ann Oncol 30(Suppl_10):x12–x20. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdz381
Dong C, Wu J, Chen Y, Nie J, Chen C (2021) Activation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway causes drug resistance in breast cancer. Front Pharmacol 12:628690. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.628690
Wang W, Xia X, Chen K, Chen M, Meng Y, Lv D, Yang H (2021) Reduced PHLPP expression leads to EGFR-TKI resistance in lung cancer by activating PI3K-AKT and MAPK-ERK dual signaling. Front Oncol 11:665045. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.665045
Zhou H, Zhao H, Liu H, Xu X, Dong X, Zhao E (2018) Influence of carboplatin on the proliferation and apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells through mTOR/p70s6k signaling pathway. J BUON 23(6):1732–1738
Li Z, Li Y, Jia Y, Ding B, Yu J (2020) Rab1A knockdown represses proliferation and promotes apoptosis in gastric cancer cells by inhibition of mTOR/p70S6K pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys 685:108352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2020.108352
Jin J, Qiu S, Wang P, Liang X, Huang F, Wu H, Zhang B, Zhang W, Tian X, Xu R, Shi H, Wu X (2019) Cardamonin inhibits breast cancer growth by repressing HIF-1α-dependent metabolic reprogramming. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38(1):377. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1351-4
Liu Y, Wang D, Lei M, Gao J, Cui Y, Jin X, Yu Q, Jiang Y, Guo Y, Liu Y, Cai L, Chen X (2021) GABARAP suppresses EMT and breast cancer progression via the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Aging (Albany N Y) 13(4):5858–5874. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.202510
Zhao S, Jiang Y, Zhao J, Li H, Yin X, Wang Y, Xie Y, Chen X, Lu J, Dong Z, Liu K (2018) Quercetin-3-methyl ether inhibits esophageal carcinogenesis by targeting the AKT/mTOR/p70S6K and MAPK pathways. Mol Carcinog 57(11):1540–1552. https://doi.org/10.1002/mc.22876
Zhang S, Xu Q, Sun W, Zhou J, Zhou J (2023) Immunomodulatory effects of CDK4/6 inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1878(4):188912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2023.188912
Cai Z, Wang J, Li Y, Shi Q, Jin L, Li S, Zhu M, Wang Q, Wong LL, Yang W, Lai H, Gong C, Yao Y, Liu Y, Zhang J, Yao H, Liu Q (2023) Overexpressed Cyclin D1 and CDK4 proteins are responsible for the resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitor in breast cancer that can be reversed by PI3K/mTOR inhibitors. Sci China Life Sci 66(1):94–109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-021-2140-8
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from Chongqing Yuzhong District Science and Technology Committee (grant number 20190118).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LZB: Contributed to the conception of the study; XXP: performed the experiment and wrote this manuscript; WW: contributed significantly to analysis and manuscript preparation; YL, GQ and ML: performed collecting clinical data and analyzing it; ZLQ : helped perform the analysis with constructive discussions. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Liu, Y., Gong, Q. et al. PARP1 promotes EGFR-TKI drug-resistance via PI3K/AKT pathway in non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-024-04668-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-024-04668-2